COVID-19 pneumonia: CT findings of 122 patients and differentiation from influenza pneumonia
- PMID: 32399710
- PMCID: PMC7216854
- DOI: 10.1007/s00330-020-06928-0
COVID-19 pneumonia: CT findings of 122 patients and differentiation from influenza pneumonia
Abstract
Objectives: To investigate the clinical and chest CT characteristics of COVID-19 pneumonia and explore the radiological differences between COVID-19 and influenza.
Materials and methods: A total of 122 patients (61 men and 61 women, 48 ± 15 years) confirmed with COVID-19 and 48 patients (23 men and 25 women, 47 ± 19 years) confirmed with influenza were enrolled in the study. Thin-section CT was performed. The clinical data and the chest CT findings were recorded.
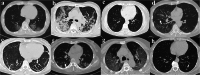
Results: The most common symptoms of COVID-19 were fever (74%) and cough (63%), and 102 patients (83%) had Wuhan contact. Pneumonia in 50 patients with COVID-19 (45%) distributed in the peripheral regions of the lung, while it showed mixed distribution in 26 patients (74%) with influenza (p = 0.022). The most common CT features of the COVID-19 group were pure ground-glass opacities (GGO, 36%), GGO with consolidation (51%), rounded opacities (35%), linear opacities (64%), bronchiolar wall thickening (49%), and interlobular septal thickening (66%). Compared with the influenza group, the COVID-19 group was more likely to have rounded opacities (35% vs. 17%, p = 0.048) and interlobular septal thickening (66% vs. 43%, p = 0.014), but less likely to have nodules (28% vs. 71%, p < 0.001), tree-in-bud sign (9% vs. 40%, p < 0.001), and pleural effusion (6% vs. 31%, p < 0.001).
Conclusions: There are significant differences in the CT manifestations of patients with COVID-19 and influenza. Presence of rounded opacities and interlobular septal thickening, with the absence of nodules and tree-in-bud sign, and with the typical peripheral distribution, may help us differentiate COVID-19 from influenza.
Key points: • Typical CT features of COVID-19 include pure ground-glass opacities (GGO), GGO with consolidation, rounded opacities, bronchiolar wall thickening, interlobular septal thickening, and a peripheral distribution. • Presence of rounded opacities and interlobular septal thickening, with the absence of nodules and tree-in-bud sign, and with the typical peripheral distribution, may help us differentiate COVID-19 from influenza.
Keywords: Coronavirus infections; Human; Influenza; Pneumonia, viral; Tomography, x-ray computed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare no relationships with any companies, whose products or services may be related to the subject matter of the article.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Characteristic CT findings distinguishing 2019 novel coronavirus disease (COVID-19) from influenza pneumonia.Eur Radiol. 2020 Sep;30(9):4910-4917. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-06880-z. Epub 2020 Apr 22. Eur Radiol. 2020. PMID: 32323011 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparison of Clinical and Chest CT Findings in Patients With Influenza A (H1N1) Virus Infection and Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19).AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020 Nov;215(5):1065-1071. doi: 10.2214/AJR.20.23214. Epub 2020 May 26. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2020. PMID: 32452731
-
Imaging and clinical features of patients with 2019 novel coronavirus SARS-CoV-2.Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020 May;47(5):1275-1280. doi: 10.1007/s00259-020-04735-9. Epub 2020 Feb 28. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32107577 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and radiological features of novel coronavirus pneumonia.J Xray Sci Technol. 2020;28(3):391-404. doi: 10.3233/XST-200687. J Xray Sci Technol. 2020. PMID: 32538893 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chest Computed Tomography Findings in COVID-19 and Influenza: A Narrative Review.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jun 5;2020:6928368. doi: 10.1155/2020/6928368. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32596354 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Chest CT in COVID-19 pneumonia: A review of current knowledge.Diagn Interv Imaging. 2020 Jul-Aug;101(7-8):431-437. doi: 10.1016/j.diii.2020.06.001. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2020. PMID: 32571748 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antibodies Can Last for More Than 1 Year After SARS-CoV-2 Infection: A Follow-Up Study From Survivors of COVID-19.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Jul 16;8:684864. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.684864. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34336891 Free PMC article.
-
Chest CT performance and features of COVID-19 in the region of Abu Dhabi, UAE: a single institute study.Chin J Acad Radiol. 2021;4(4):248-256. doi: 10.1007/s42058-021-00075-1. Epub 2021 Jun 17. Chin J Acad Radiol. 2021. PMID: 34179688 Free PMC article.
-
Tomographic findings and mortality in patients with severe and critical pneumonia with COVID-19 diagnosis.Respir Med Case Rep. 2022;40:101752. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2022.101752. Epub 2022 Oct 5. Respir Med Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 36217353 Free PMC article.
-
CT Examinations for COVID-19: A Systematic Review of Protocols, Radiation Dose, and Numbers Needed to Diagnose and Predict.Taehan Yongsang Uihakhoe Chi. 2021 Nov;82(6):1505-1523. doi: 10.3348/jksr.2021.0096. Epub 2021 Nov 4. Taehan Yongsang Uihakhoe Chi. 2021. PMID: 36238884 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) Situation Report – 72. https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2.... Accessed 1 Apr 2020
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

