Tocilizumab for Treatment of Severe COVID-19 Patients: Preliminary Results from SMAtteo COvid19 REgistry (SMACORE)
- PMID: 32397399
- PMCID: PMC7285503
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms8050695
Tocilizumab for Treatment of Severe COVID-19 Patients: Preliminary Results from SMAtteo COvid19 REgistry (SMACORE)
Abstract
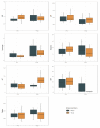
Objective: This study aimed to assess the role of Tocilizumab therapy (TCZ) in terms of ICU admission and mortality rate of critically ill patients with severe COVID-19 pneumonia. Design: Patients with COVID-19 pneumonia were prospectively enrolled in SMAtteo COvid19 REgistry (SMACORE). A retrospective analysis of patients treated with TCZ matched using propensity score to patients treated with Standard Of Care (SOC) was conducted. Setting: The study was conducted at IRCCS Policlinico San Matteo Hospital, Pavia, Italy, from March 14, 2020 to March 27, 2020. Participants: Patients with a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 hospitalized in our institution at the time of TCZ availability. Interventions: TCZ was administered to 21 patients. The first administration was 8 mg/kg (up to a maximum 800 mg per dose) of Tocilizumab intravenously, repeated after 12 h if no side effects were reported after the first dose. Main Outcomes and Measures: ICU admission and 7-day mortality rate. Secondary outcomes included clinical and laboratory data. Results: There were 112 patients evaluated (82 were male and 30 were female, with a median age of 63.55 years). Using propensity scores, the 21 patients who received TCZ were matched to 21 patients who received SOC (a combination of hydroxychloroquine, azithromycin and prophylactic dose of low weight heparin). No adverse event was detected following TCZ administration. This study found that treatment with TCZ did not significantly affect ICU admission (OR 0.11; 95% CI between 0.00 and 3.38; p = 0.22) or 7-day mortality rate (OR 0.78; 95% CI between 0.06 and 9.34; p = 0.84) when compared with SOC. Analysis of laboratory measures showed significant interactions between time and treatment regarding C-Reactive Protein (CRP), alanine aminotransferase (ALT), platelets and international normalized ratio (INR) levels. Variation in lymphocytes count was observed over time, irrespective of treatment. Conclusions: TCZ administration did not reduce ICU admission or mortality rate in a cohort of 21 patients. Additional data are needed to understand the effect(s) of TCZ in treating patients diagnosed with COVID-19.
Keywords: COVID-19 pneumonia; ICU; mortality rate; off label therapy; propensity score matching; tocilizumab.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of Early Tocilizumab Effect on Multiorgan Dysfunction in Critically Ill Patients With COVID-19: A Propensity Score-Matched Study.J Intensive Care Med. 2023 Jun;38(6):534-543. doi: 10.1177/08850666221150886. Epub 2023 Jan 22. J Intensive Care Med. 2023. PMID: 36683420 Free PMC article.
-
Low-dose subcutaneous tocilizumab to prevent disease progression in patients with moderate COVID-19 pneumonia and hyperinflammation.Int J Infect Dis. 2020 Nov;100:421-424. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2020.07.078. Epub 2020 Aug 6. Int J Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32768701 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial and harmful outcomes of tocilizumab in severe COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Pharmacotherapy. 2021 Nov;41(11):884-906. doi: 10.1002/phar.2627. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Pharmacotherapy. 2021. PMID: 34558742 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of the early treatment with tocilizumab-hydroxychloroquine and tocilizumab-remdesivir in severe COVID-19 Patients.J Infect Public Health. 2022 Jan;15(1):116-122. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2021.10.024. Epub 2021 Nov 2. J Infect Public Health. 2022. PMID: 34764044 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Tocilizumab for the treatment of severe COVID-19 pneumonia with hyperinflammatory syndrome and acute respiratory failure: A single center study of 100 patients in Brescia, Italy.Autoimmun Rev. 2020 Jul;19(7):102568. doi: 10.1016/j.autrev.2020.102568. Epub 2020 May 3. Autoimmun Rev. 2020. PMID: 32376398 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Development and utility of a SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus assay for compound screening and antibody neutralization assays.Heliyon. 2024 May 19;10(10):e31392. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e31392. eCollection 2024 May 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38826759 Free PMC article.
-
Cytokine storm and translating IL-6 biology into effective treatments for COVID-19.Front Med. 2023 Dec;17(6):1080-1095. doi: 10.1007/s11684-023-1044-4. Epub 2023 Dec 29. Front Med. 2023. PMID: 38157195 Review.
-
Potential treatments of COVID-19: Drug repurposing and therapeutic interventions.J Pharmacol Sci. 2023 May;152(1):1-21. doi: 10.1016/j.jphs.2023.02.004. Epub 2023 Feb 15. J Pharmacol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37059487 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An overview on the treatments and prevention against COVID-19.Virol J. 2023 Feb 8;20(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12985-023-01973-9. Virol J. 2023. PMID: 36755327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Cu(dipicolinoylamide)(NO3)(H2O)] as anti-COVID-19 and antibacterial drug candidate: Design, synthesis, crystal structure, DFT and molecular docking.J Mol Struct. 2022 Jan 5;1247:131348. doi: 10.1016/j.molstruc.2021.131348. Epub 2021 Aug 22. J Mol Struct. 2022. PMID: 36406284 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zhou F., Yu T., Du R., Fan G., Liu Y., Liu Z., Xiang J., Wang Y., Song B., Gu X., et al. Clinical course and risk factors for mortality of adult inpatients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China: A retrospective cohort study. Lancet. 2020;395:1054–1062. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30566-3. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus (COVID-19) Events as They Happen. [(accessed on 20 April 2020)];2020 Available online: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/events-a....
-
- Ghebreyesus T.A. WHO Director-General’s Opening REMARKS at the media Briefing on COVID-19–11 March 2020. [(accessed on 20 April 2020)]; Available online: https://www.whoint/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-rem....
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

