DNA Helicase Mph1FANCM Ensures Meiotic Recombination between Parental Chromosomes by Dissociating Precocious Displacement Loops
- PMID: 32386601
- PMCID: PMC7386354
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.04.010
DNA Helicase Mph1FANCM Ensures Meiotic Recombination between Parental Chromosomes by Dissociating Precocious Displacement Loops
Abstract
Meiotic pairing between parental chromosomes (homologs) is required for formation of haploid gametes. Homolog pairing depends on recombination initiation via programmed double-strand breaks (DSBs). Although DSBs appear prior to pairing, the homolog, rather than the sister chromatid, is used as repair partner for crossing over. Here, we show that Mph1, the budding yeast ortholog of Fanconi anemia helicase FANCM, prevents precocious DSB strand exchange between sister chromatids before homologs have completed pairing. By dissociating precocious DNA displacement loops (D-loops) between sister chromatids, Mph1FANCM ensures high levels of crossovers and non-crossovers between homologs. Later-occurring recombination events are protected from Mph1-mediated dissociation by synapsis protein Zip1. Increased intersister repair in absence of Mph1 triggers a shift among remaining interhomolog events from non-crossovers to crossover-specific strand exchange, explaining Mph1's apparent anti-crossover function. Our findings identify temporal coordination between DSB strand exchange and homolog pairing as a critical determinant for recombination outcome.
Keywords: D-loop; DNA helicase; DSB repair; FANCM; Fanconi anemia; Mph1; homologous pairing; meiosis; partner choice; recombination.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

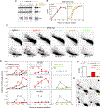
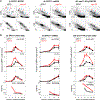
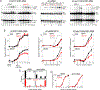
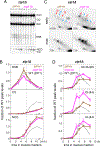

Comment in
-
Don't Forget Your Sister: Directing Double-Strand Break Repair at Meiosis.Dev Cell. 2020 May 18;53(4):374-376. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2020.04.021. Dev Cell. 2020. PMID: 32428453
Similar articles
-
Meiotic crossover control by concerted action of Rad51-Dmc1 in homolog template bias and robust homeostatic regulation.PLoS Genet. 2013;9(12):e1003978. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1003978. Epub 2013 Dec 19. PLoS Genet. 2013. PMID: 24367271 Free PMC article.
-
Yeast Mph1 helicase dissociates Rad51-made D-loops: implications for crossover control in mitotic recombination.Genes Dev. 2009 Jan 1;23(1):67-79. doi: 10.1101/gad.1737809. Genes Dev. 2009. PMID: 19136626 Free PMC article.
-
Rad51-mediated interhomolog recombination during budding yeast meiosis is promoted by the meiotic recombination checkpoint and the conserved Pif1 helicase.PLoS Genet. 2022 Dec 12;18(12):e1010407. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010407. eCollection 2022 Dec. PLoS Genet. 2022. PMID: 36508468 Free PMC article.
-
The meiotic-specific Mek1 kinase in budding yeast regulates interhomolog recombination and coordinates meiotic progression with double-strand break repair.Curr Genet. 2019 Jun;65(3):631-641. doi: 10.1007/s00294-019-00937-3. Epub 2019 Jan 22. Curr Genet. 2019. PMID: 30671596 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A new role for the synaptonemal complex in the regulation of meiotic recombination.Genes Dev. 2020 Dec 1;34(23-24):1562-1564. doi: 10.1101/gad.345488.120. Genes Dev. 2020. PMID: 33262143 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dna2 removes toxic ssDNA-RPA filaments generated from meiotic recombination-associated DNA synthesis.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Aug 25;51(15):7914-7935. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad537. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37351599 Free PMC article.
-
Meiosis in budding yeast.Genetics. 2023 Oct 4;225(2):iyad125. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyad125. Genetics. 2023. PMID: 37616582 Free PMC article.
-
RAD54 is essential for RAD51-mediated repair of meiotic DSB in Arabidopsis.PLoS Genet. 2021 May 18;17(5):e1008919. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008919. eCollection 2021 May. PLoS Genet. 2021. PMID: 34003859 Free PMC article.
-
Meiotic recombination mirrors patterns of germline replication in mice and humans.Cell. 2021 Aug 5;184(16):4251-4267.e20. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2021.06.025. Epub 2021 Jul 13. Cell. 2021. PMID: 34260899 Free PMC article.
-
Let's get physical - mechanisms of crossover interference.J Cell Sci. 2021 May 15;134(10):jcs255745. doi: 10.1242/jcs.255745. Epub 2021 May 26. J Cell Sci. 2021. PMID: 34037217 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ahuja JS, and Börner GV (2011). Analysis of meiotic recombination intermediates by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Methods Mol. Biol. 745, 99–116. - PubMed
-
- Allers T, and Lichten M. (2001). Differential timing and control of noncrossover and crossover recombination during meiosis. Cell 106, 47–57. - PubMed
-
- Bishop DK (1994). RecA homologs Dmc1 and Rad51 interact to form multiple nuclear complexes prior to meiotic chromosome synapsis. Cell 79, 1081–1092. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

