Symptomatic Infection is Associated with Prolonged Duration of Viral Shedding in Mild Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Study of 110 Children in Wuhan
- PMID: 32379191
- PMCID: PMC7279058
- DOI: 10.1097/INF.0000000000002729
Symptomatic Infection is Associated with Prolonged Duration of Viral Shedding in Mild Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Retrospective Study of 110 Children in Wuhan
Abstract
Background: Information regarding viral shedding in children with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) was limited. This study aims to investigate the clinical and laboratory characteristics associated with viral shedding in children with mild COVID-19.
Methods: The clinical and laboratory information of 110 children with COVID-19 at Wuhan Children's Hospital, Wuhan, China, from January 30 to March 10, 2020, were analyzed retrospectively.
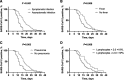
Results: The median age was 6 years old. The median period of viral shedding of COVID-19 was 15 days (interquartile range [IQR], 11-20 days) as measured from illness onset to discharge. This period was shorter in asymptomatic patients (26.4%) compared with symptomatic patients (73.6%) (11 days vs. 17 days). Multivariable regression analysis showed increased odds of symptomatic infection was associated with age <6 years (odds ratio [OR] 8.94, 95% confidence interval [CI]: 2.55-31.35; P = 0.001), hypersensitive C-reactive protein >3.0 mg/L (OR 4.89; 95% CI: 1.10-21.75; P = 0.037) and presenting pneumonia in chest radiologic findings (OR 8.45; 95% CI: 2.69-26.61; P < 0.001). Kaplan-Meier analysis displayed symptomatic infection (P < 0.001), fever (P = 0.006), pneumonia (P = 0.003) and lymphocyte counts <2.0 × 10/L (P = 0.008) in children with COVID-19 were associated with prolonged duration of viral shedding in children with COVID-19.
Conclusion: Prolonged duration of viral shedding in children with COVID-19 was associated with symptomatic infection, fever, pneumonia and lymphocyte count less than 2.0 × 10/L. Monitoring of symptoms could help to know the viral shedding in children with COVID-19.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Factors Associated With Prolonged Viral RNA Shedding in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19).Clin Infect Dis. 2020 Jul 28;71(15):799-806. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciaa351. Clin Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32271376 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Characteristics and Factors Associated With Long-Term Viral Excretion in Patients With Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Infection: a Single-Center 28-Day Study.J Infect Dis. 2020 Aug 17;222(6):910-918. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa388. J Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32614392 Free PMC article.
-
Duration of Respiratory and Gastrointestinal Viral Shedding in Children With SARS-CoV-2: A Systematic Review and Synthesis of Data.Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2020 Sep;39(9):e249-e256. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000002814. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2020. PMID: 32618932
-
Laboratory abnormalities in children with mild and severe coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19): A pooled analysis and review.Clin Biochem. 2020 Jul;81:1-8. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2020.05.012. Epub 2020 May 27. Clin Biochem. 2020. PMID: 32473151 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prolonged viral shedding in feces of children with COVID-19: a systematic review and synthesis of data.Eur J Pediatr. 2022 Dec;181(12):4011-4017. doi: 10.1007/s00431-022-04622-5. Epub 2022 Sep 17. Eur J Pediatr. 2022. PMID: 36114833 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tools and Techniques for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2)/COVID-19 Detection.Clin Microbiol Rev. 2021 May 12;34(3):e00228-20. doi: 10.1128/CMR.00228-20. Print 2021 Jun 16. Clin Microbiol Rev. 2021. PMID: 33980687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transmission of SARS-CoV-2 through breast milk and breastfeeding: a living systematic review.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2021 Jan;1484(1):32-54. doi: 10.1111/nyas.14477. Epub 2020 Aug 28. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2021. PMID: 32860259 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Laboratory Characteristics of Pediatric COVID-19 Population-A Bibliometric Analysis.J Clin Med. 2022 Oct 11;11(20):5987. doi: 10.3390/jcm11205987. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36294306 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Children Without Symptoms of Coronavirus Disease 2019.JAMA Pediatr. 2021 Feb 1;175(2):198-201. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2020.4095. JAMA Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 32840605 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of chest involvement at computed tomography in children with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).Pediatr Radiol. 2021 Feb;51(2):222-230. doi: 10.1007/s00247-020-04826-7. Epub 2020 Oct 21. Pediatr Radiol. 2021. PMID: 33084963 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019) situation reports-51. 2020. Available at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2.... Accessed March 11, 2020.
-
- National Health Commission of People’s Republic of China. National Recommendations for Diagnosis and Treatment of COVID-19 (the 7th edition). 2020. Available at: http://www.nhc.gov.cn/xcs/zhengcwj/202003/46c9294a7dfe4cef80dc7f5912eb19.... Accessed 3 March 2020.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

