An injectable microparticle formulation for the sustained release of the specific MEK inhibitor PD98059: in vitro evaluation and pharmacokinetics
- PMID: 32378175
- PMCID: PMC7647946
- DOI: 10.1007/s13346-020-00758-9
An injectable microparticle formulation for the sustained release of the specific MEK inhibitor PD98059: in vitro evaluation and pharmacokinetics
Abstract
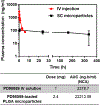
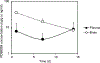
PD98059 is a reversible MEK inhibitor that we are investigating as a potential treatment for neurochemical changes in the brain that drive neurohumoral excitation in heart failure. In a rat model that closely resembles human heart failure, we found that central administration of PD98059 inhibits phosphorylation of ERK1/2 in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus, ultimately reducing sympathetic excitation which is a major contributor to clinical deterioration. Studies revealed that the pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of PD98059 match a two-compartment model, with drug found in brain as well as other body tissues, but with a short elimination half-life in plasma (approximately 73 min) that would severely limit its potential clinical usefulness in heart failure. To increase its availability to tissues, we prepared a sustained release PD98059-loaded PLGA microparticle formulation, using an emulsion solvent evaporation technique. The average particle size, yield percent, and encapsulation percent were found to be 16.73 μm, 76.6%, and 43%, respectively. In vitro drug release occurred over 4 weeks, with no noticeable burst release. Following subcutaneous injection of the microparticles in rats, steady plasma levels of PD98059 were detected by HPLC for up to 2 weeks. Furthermore, plasma and brain levels of PD98059 in rats with heart failure were detectable by LC/MS, despite expected erratic absorption. These findings suggest that PD98059-loaded microparticles hold promise as a novel therapeutic intervention countering sympathetic excitation in heart failure, and perhaps in other disease processes, including cancers, in which activated MAPK signaling is a significant contributing factor. Graphical abstract.
Keywords: Heart failure; LC/MS; MEK1/2 inhibitor; Microparticles; PD98059; Sustained release.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
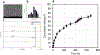
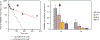
Similar articles
-
An Injectable Microparticle Formulation Provides Long-Term Inhibition of Hypothalamic ERK1/2 Activity and Sympathetic Excitation in Rats with Heart Failure.Mol Pharm. 2020 Sep 8;17(9):3643-3648. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00501. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Mol Pharm. 2020. PMID: 32786958 Free PMC article.
-
Angiotensin II-triggered p44/42 mitogen-activated protein kinase mediates sympathetic excitation in heart failure rats.Hypertension. 2008 Aug;52(2):342-50. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.108.110445. Epub 2008 Jun 23. Hypertension. 2008. PMID: 18574076 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo evaluation of solid lipid microparticles and hybrid polymer-lipid microparticles for sustained delivery of leuprolide.Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2019 Sep;142:315-321. doi: 10.1016/j.ejpb.2019.07.010. Epub 2019 Jul 9. Eur J Pharm Biopharm. 2019. PMID: 31299277
-
Development of andrographolide loaded PLGA microspheres: optimization, characterization and in vitro-in vivo correlation.Int J Pharm. 2014 Nov 20;475(1-2):475-84. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2014.09.016. Epub 2014 Sep 16. Int J Pharm. 2014. PMID: 25219858
-
Subconjunctivally administered celecoxib-PLGA microparticles sustain retinal drug levels and alleviate diabetes-induced oxidative stress in a rat model.Eur J Pharmacol. 2005 Mar 28;511(2-3):191-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.02.019. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005. PMID: 15792788
Cited by
-
Injectable long-acting ivacaftor-loaded poly (lactide-co-glycolide) microparticle formulations for the treatment of cystic fibrosis: In vitro characterization and in vivo pharmacokinetics in mice.Int J Pharm. 2024 Jan 25;650:123693. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2023.123693. Epub 2023 Dec 9. Int J Pharm. 2024. PMID: 38081555 Free PMC article.
-
Paclitaxel anticancer activity is enhanced by the MEK 1/2 inhibitor PD98059 in vitro and by PD98059-loaded nanoparticles in BRAFV600E melanoma-bearing mice.Int J Pharm. 2021 Sep 5;606:120876. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2021.120876. Epub 2021 Jul 10. Int J Pharm. 2021. PMID: 34252520 Free PMC article.
-
An Injectable Microparticle Formulation Provides Long-Term Inhibition of Hypothalamic ERK1/2 Activity and Sympathetic Excitation in Rats with Heart Failure.Mol Pharm. 2020 Sep 8;17(9):3643-3648. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.0c00501. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Mol Pharm. 2020. PMID: 32786958 Free PMC article.
-
Tuning the Emulsion Properties Influences the Size of Poly(Caprolactone) Particles for Drug Delivery Applications.AAPS J. 2023 Oct 27;25(6):100. doi: 10.1208/s12248-023-00869-4. AAPS J. 2023. PMID: 37891411
-
Hyperglycemia aggravates ischemic brain damage via ERK1/2 activated cell autophagy and mitochondrial fission.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Aug 5;13:928591. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.928591. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35992111 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Blaukat A, Barac A, Cross MJ, Offermanns S, Dikic I. G protein-coupled receptor-mediated mitogen-activated protein kinase activation through cooperation of Galpha(q) and Galpha(i) signals. Molecular and cellular biology. 2000;20(18):6837–48. doi:10.1128/mcb.20.18.6837-6848.2000. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

