Bis-benzylidine Piperidone RA190 treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma via binding RPN13 and inhibiting NF-κB signaling
- PMID: 32375699
- PMCID: PMC7201939
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-020-06896-0
Bis-benzylidine Piperidone RA190 treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma via binding RPN13 and inhibiting NF-κB signaling
Abstract
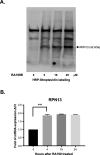
Background: According to GLOBOSCAN, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) claimed 782,000 lives in 2018. The tyrosine kinase inhibitor sofafenib is used to treat HCC, but new anticancer agents targeting different pathways are urgently needed to improve outcomes for patients with advanced disease. The aberrant metabolism and aggressive growth of cancer cells can render them particularly susceptible to proteasome inhibition, as demonstrated by bortezomib treatment of multiple myeloma. However, resistance does emerge, and this 20S proteasome inhibitor has not proven active against HCC. The bis-benzylidine piperidone RA190 represents a novel class of proteasome inhibitor that covalently binds to cysteine 88 of RPN13, an ubiquitin receptor subunit of the proteasome's 19S regulatory particle. RA190 treatment inhibits proteasome function, causing rapid accumulation of polyubiquitinated proteins. Considerable evidence suggests that nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) signaling, which is dependent upon the proteasome, is a major driver of inflammation-associated cancers, including HCC.
Methods: Human HCC cell lines were treated with titrations of RA190. The time course of endoplasmic reticulum stress and NF-κB-related mechanisms by which RA190 may trigger apoptosis were assessed. The therapeutic activity of RA190 was also determined in an orthotopic HCC xenograft mouse model.
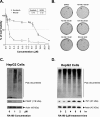
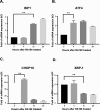
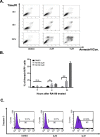
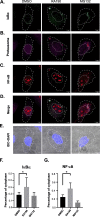
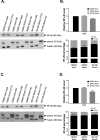
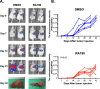
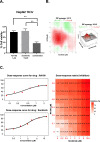
Results: RA190 is toxic to HCC cells and synergizes with sofafenib. RA190 triggers rapid accumulation of polyubiquitinated proteins, unresolved endoplasmic reticulum stress, and cell death via apoptosis. RA190 blocks proteasomal degradation of IκBα and consequent release of NF-κB into the nuclei of HCC cells. Treatment of mice bearing an orthotopic HCC model with RA190 significantly reduced tumor growth.
Conclusions: RA190 has therapeutic activity in a xenograft model, and with sorafenib exhibited synergetic killing of HCC cells in vitro, suggesting further exploration of such a combination treatment of HCC is warranted.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Hepatocellular carcinoma; NF-κB; Proteasome inhibitor; RA190.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare the following competing financial interest(s): Under a licensing agreement between Pontifax/PI Therapeutics and Johns Hopkins University, Drs. Anchoori and Roden are entitled to royalties on an invention (US patent application 20190175572) described in this article. This arrangement has been reviewed and approved by Johns Hopkins University in accordance with its conflict of interest policies. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structure-function analyses of candidate small molecule RPN13 inhibitors with antitumor properties.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 15;15(1):e0227727. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227727. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31940398 Free PMC article.
-
A bis-benzylidine piperidone targeting proteasome ubiquitin receptor RPN13/ADRM1 as a therapy for cancer.Cancer Cell. 2013 Dec 9;24(6):791-805. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2013.11.001. Cancer Cell. 2013. PMID: 24332045 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-mediated sorafenib resistance can be overcome by EF24 through Von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor-dependent HIF-1α inhibition in hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepatology. 2013 May;57(5):1847-57. doi: 10.1002/hep.26224. Epub 2013 Mar 14. Hepatology. 2013. PMID: 23299930
-
Role of Ubiquitin-specific Proteases in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Pathogenesis.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(3):179-191. doi: 10.2174/0115680266279228231219101233. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38173207 Review.
-
Pharmacologically inducing anoikis offers novel therapeutic opportunities in hepatocellular carcinoma.Biomed Pharmacother. 2024 Jul;176:116878. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2024.116878. Epub 2024 Jun 5. Biomed Pharmacother. 2024. PMID: 38843588 Review.
Cited by
-
Pharmacological Modulation of Ubiquitin-Proteasome Pathways in Oncogenic Signaling.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 4;22(21):11971. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111971. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34769401 Free PMC article. Review.
-
19S Proteasome Subunits as Oncogenes and Prognostic Biomarkers in FLT3-Mutated Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML).Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Nov 23;23(23):14586. doi: 10.3390/ijms232314586. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36498916 Free PMC article.
-
The prognostic value of 19S ATPase proteasome subunits in acute myeloid leukemia and other forms of cancer.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Jul 12;10:1209425. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1209425. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37502358 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical studies of RA475, a guanidine-substituted spirocyclic candidate RPN13/ADRM1 inhibitor for treatment of ovarian cancer.PLoS One. 2024 Jul 11;19(7):e0305710. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0305710. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38990850 Free PMC article.
-
RPNs Levels Are Prognostic and Diagnostic Markers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Oncol. 2022 Aug 29;2022:7270541. doi: 10.1155/2022/7270541. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36072976 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;68(6):394–424. - PubMed
-
- Liver EAFTSOT EASL–EORTC clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2012;56(4):908–943. - PubMed
-
- Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, Wilkie D, McNabola A, Rong H, Chen C, Zhang X, et al. BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2004;64(19):7099–7109. - PubMed
-
- Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(4):378–390. - PubMed
-
- Bruix J, Qin S, Merle P, Granito A, Huang YH, Bodoky G, Pracht M, Yokosuka O, et al. Regorafenib for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma who progressed on sorafenib treatment (RESORCE): a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet. 2017;389(10064):56–66. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

