Generation and reactivity analysis of human recombinant monoclonal antibodies directed against epitopes on HLA-DR
- PMID: 32342632
- PMCID: PMC7754395
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.15950
Generation and reactivity analysis of human recombinant monoclonal antibodies directed against epitopes on HLA-DR
Abstract
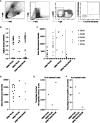
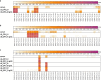
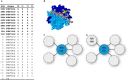
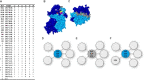
In kidney transplantation, eplet mismatches between donor and recipient have been associated with de novo donor-specific antibody development. Eplets are theoretically defined configurations of polymorphic amino acids and require experimental verification to establish whether they can be bound by alloantibodies. Human HLA-specific monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have been instrumental for this purpose but are largely lacking for HLA class II. In this study, we isolated single HLA-DR-specific memory B cells from peripheral blood of immunized individuals (n = 3) using HLA class II tetramers to generate recombinant human HLA-DR antigen-reactive mAbs (n = 5). Comparison of the amino acid composition of the reactive HLA alleles in relation to the antibody reactivity patterns led to identification of 3 configurations, 70Q 73A, 31F 32Y 37Y, and 14K 25Q recognized, respectively, by HLA-DRB1*01:01, HLA-DRB1*04:01, and HLA-DRB1*07:01 antigen-reactive mAbs. The first 2 correspond to eplets 70QA and 31FYY and can now be considered antibody verified. The latter indicates that eplet 25Q needs to be redefined before being considered as antibody verified. Generation and reactivity analysis of human HLA-DR mAbs allowed for identification of amino acid configurations corresponding to known eplets, whereas the other patterns may be used to redefine eplets with similar, but not identical predicted amino acid composition.
Keywords: alloantibody; basic (laboratory) research / science; histocompatibility; immunogenetics; major histocompatibility complex (MHC); recipient selection; sensitization.
© 2020 The Authors. American Journal of Transplantation published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript have no conflicts of interest to disclose as described by the
Figures
Similar articles
-
Antibody verification of HLA class I and class II eplets by human monoclonal HLA antibodies.HLA. 2024 Jan;103(1):e15345. doi: 10.1111/tan.15345. HLA. 2024. PMID: 38239050
-
A Comprehensive Evaluation of the Antibody-Verified Status of Eplets Listed in the HLA Epitope Registry.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 28;12:800946. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.800946. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35154076 Free PMC article.
-
HLA-DQ-Specific Recombinant Human Monoclonal Antibodies Allow for In-Depth Analysis of HLA-DQ Epitopes.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 7;12:761893. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.761893. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35069533 Free PMC article.
-
Matchmaker, matchmaker make me a match: Opportunities and challenges in optimizing compatibility of HLA eplets in transplantation.Int J Immunogenet. 2021 Apr;48(2):135-144. doi: 10.1111/iji.12525. Epub 2021 Jan 10. Int J Immunogenet. 2021. PMID: 33426788 Review.
-
Anti-HLA Antibody: The Role of Epitopes in Organ Transplantation.Exp Clin Transplant. 2019 Jan;17(Suppl 1):38-42. doi: 10.6002/ect.MESOT2018.L41. Exp Clin Transplant. 2019. PMID: 30777521 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of an immunogenicity score for HLA-DQ eplets: A conceptual study.HLA. 2021 Jan;97(1):30-43. doi: 10.1111/tan.14110. Epub 2020 Oct 28. HLA. 2021. PMID: 33068062 Free PMC article.
-
Site-directed mutagenesis of HLA molecules reveals the functional epitope of a human HLA-A1/A36-specific monoclonal antibody.HLA. 2023 Feb;101(2):138-142. doi: 10.1111/tan.14895. Epub 2022 Nov 25. HLA. 2023. PMID: 36401817 Free PMC article.
-
Memory B Cells in Pregnancy Sensitization.Front Immunol. 2021 Jun 30;12:688987. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.688987. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34276679 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Anti-HLA Class II Antibodies Are the Most Resistant to Desensitization in Crossmatch-positive Living-donor Kidney Transplantations: A Patient Series.Transplant Direct. 2024 Aug 29;10(9):e1695. doi: 10.1097/TXD.0000000000001695. eCollection 2024 Sep. Transplant Direct. 2024. PMID: 39220218 Free PMC article.
-
Qualitative, rather than quantitative, differences between HLA-DQ alleles affect HLA-DQ immunogenicity in organ transplantation.HLA. 2024 Apr;103(4):e15455. doi: 10.1111/tan.15455. HLA. 2024. PMID: 38575370
References
-
- Loupy A, Lefaucheur C, Vernerey D, et al. Complement‐binding anti‐HLA antibodies and kidney‐allograft survival. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(13):1215‐1226. - PubMed
-
- Duquesnoy RJ, Marrari M, Mulder A, da Mata Sousa LCD, da Silva AS, do Monte SJH. First report on the antibody verification of HLA‐ABC epitopes recorded in the website‐based HLA Epitope Registry. Tissue Antigens. 2014;83(6):391‐400. - PubMed
-
- Duquesnoy RJ, Marrari M, Tambur AR, et al. First report on the antibody verification of HLA‐DR, HLA‐DQ and HLA‐DP epitopes recorded in the HLA Epitope Registry. Hum Immunol. 2014;75(11):1097‐1103. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

