Interactions between DksA and Stress-Responsive Alternative Sigma Factors Control Inorganic Polyphosphate Accumulation in Escherichia coli
- PMID: 32341074
- PMCID: PMC7317045
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00133-20
Interactions between DksA and Stress-Responsive Alternative Sigma Factors Control Inorganic Polyphosphate Accumulation in Escherichia coli
Abstract
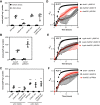
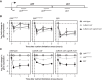
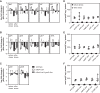
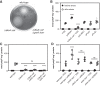
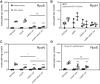
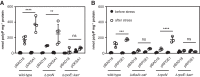
Bacteria synthesize inorganic polyphosphate (polyP) in response to a variety of different stress conditions. polyP protects bacteria by acting as a protein-stabilizing chaperone, metal chelator, or regulator of protein function, among other mechanisms. However, little is known about how stress signals are transmitted in the cell to lead to increased polyP accumulation. Previous work in the model enterobacterium Escherichia coli has indicated that the RNA polymerase-binding regulatory protein DksA is required for polyP synthesis in response to nutrient limitation stress. In this work, I set out to characterize the role of DksA in polyP regulation in more detail. I found that overexpression of DksA increases cellular polyP content (explaining the long-mysterious phenotype of dksA overexpression rescuing growth of a dnaK mutant at high temperatures) and characterized the roles of known functional residues of DksA in this process, finding that binding to RNA polymerase is required but that none of the other functions of DksA appear to be necessary. Transcriptomics revealed genome-wide transcriptional changes upon nutrient limitation, many of which were affected by DksA, and follow-up experiments identified complex interactions between DksA and the stress-sensing alternative sigma factors FliA, RpoN, and RpoE that impact polyP production, indicating that regulation of polyP synthesis is deeply entwined in the multifactorial stress response network of E. coliIMPORTANCE Inorganic polyphosphate (polyP) is an evolutionarily ancient, widely conserved biopolymer required for stress resistance and pathogenesis in diverse bacteria, but we do not understand how its synthesis is regulated. In this work, I gained new insights into this process by characterizing the role of the transcriptional regulator DksA in polyP regulation in Escherichia coli and identifying previously unknown links between polyP synthesis and the stress-responsive alternative sigma factors FliA, RpoN, and RpoE.
Keywords: polyphosphate; sigma factors; stress response; stringent response.
Copyright © 2020 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inorganic Polyphosphate Accumulation in Escherichia coli Is Regulated by DksA but Not by (p)ppGpp.J Bacteriol. 2019 Apr 9;201(9):e00664-18. doi: 10.1128/JB.00664-18. Print 2019 May 1. J Bacteriol. 2019. PMID: 30745375 Free PMC article.
-
The role of nitrogen-responsive regulators in controlling inorganic polyphosphate synthesis in Escherichia coli.Microbiology (Reading). 2022 Apr;168(4):001185. doi: 10.1099/mic.0.001185. Microbiology (Reading). 2022. PMID: 35482529 Free PMC article.
-
DksA and ppGpp Regulate the σS Stress Response by Activating Promoters for the Small RNA DsrA and the Anti-Adapter Protein IraP.J Bacteriol. 2017 Dec 20;200(2):e00463-17. doi: 10.1128/JB.00463-17. Print 2018 Jan 15. J Bacteriol. 2017. PMID: 29061665 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional switching in Escherichia coli during stress and starvation by modulation of sigma activity.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2010 Sep;34(5):646-57. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00223.x. Epub 2010 Apr 14. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2010. PMID: 20491934 Review.
-
Inorganic polyphosphate regulates responses of Escherichia coli to nutritional stringencies, environmental stresses and survival in the stationary phase.Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 1999;23:183-95. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-58444-2_9. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 1999. PMID: 10448677 Review.
Cited by
-
The Phosin PptA Plays a Negative Role in the Regulation of Antibiotic Production in Streptomyces lividans.Antibiotics (Basel). 2021 Mar 20;10(3):325. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics10030325. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33804592 Free PMC article.
-
Ppx1 putative exopolyphosphatase is essential for polyphosphate accumulation in Lacticaseibacillus paracasei.Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024 May 21;90(5):e0229023. doi: 10.1128/aem.02290-23. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38619267 Free PMC article.
-
Inorganic polyphosphate and the stringent response coordinately control cell division and cell morphology in Escherichia coli.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 12:2024.09.11.612536. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.11.612536. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: mBio. 2025 Feb 5;16(2):e0351124. doi: 10.1128/mbio.03511-24. PMID: 39314361 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
The role of metals in hypothiocyanite resistance in Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2024 Aug 22;206(8):e0009824. doi: 10.1128/jb.00098-24. Epub 2024 Jul 17. J Bacteriol. 2024. PMID: 39016617 Free PMC article.
-
The DnaK/DnaJ Chaperone System Enables RNA Polymerase-DksA Complex Formation in Salmonella Experiencing Oxidative Stress.mBio. 2021 May 11;12(3):e03443-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.03443-20. mBio. 2021. PMID: 33975942 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

