Updated efficacy results from the JAVELIN Renal 101 trial: first-line avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma
- PMID: 32339648
- PMCID: PMC8436592
- DOI: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.04.010
Updated efficacy results from the JAVELIN Renal 101 trial: first-line avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma
Abstract
Background: The phase 3 JAVELIN Renal 101 trial (NCT02684006) demonstrated significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS) with first-line avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib in advanced renal cell carcinoma (aRCC). We report updated efficacy data from the second interim analysis.
Patients and methods: Treatment-naive patients with aRCC were randomized (1 : 1) to receive avelumab (10 mg/kg) intravenously every 2 weeks plus axitinib (5 mg) orally twice daily or sunitinib (50 mg) orally once daily for 4 weeks (6-week cycle). The two independent primary end points were PFS and overall survival (OS) among patients with programmed death ligand 1-positive (PD-L1+) tumors. Key secondary end points were OS and PFS in the overall population.
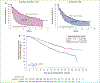
Results: Of 886 patients, 442 were randomized to the avelumab plus axitinib arm and 444 to the sunitinib arm; 270 and 290 had PD-L1+ tumors, respectively. After a minimum follow-up of 13 months (data cut-off 28 January 2019), PFS was significantly longer in the avelumab plus axitinib arm than in the sunitinib arm {PD-L1+ population: hazard ratio (HR) 0.62 [95% confidence interval (CI) 0.490-0.777]}; one-sided P < 0.0001; median 13.8 (95% CI 10.1-20.7) versus 7.0 months (95% CI 5.7-9.6); overall population: HR 0.69 (95% CI 0.574-0.825); one-sided P < 0.0001; median 13.3 (95% CI 11.1-15.3) versus 8.0 months (95% CI 6.7-9.8)]. OS data were immature [PD-L1+ population: HR 0.828 (95% CI 0.596-1.151); one-sided P = 0.1301; overall population: HR 0.796 (95% CI 0.616-1.027); one-sided P = 0.0392].
Conclusion: Among patients with previously untreated aRCC, treatment with avelumab plus axitinib continued to result in a statistically significant improvement in PFS versus sunitinib; OS data were still immature.
Clinical trial number: NCT02684006.
Keywords: PD-L1; avelumab; axitinib; immune checkpoint inhibitor; phase 3; renal cell carcinoma.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure TKC reports the following: Research (institutional and personal): AstraZeneca, Alexion, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb/ER Squibb and sons LLC, Cerulean, Eisai, Foundation Medicine Inc., Exelixis, Ipsen, Tracon, Genentech, Roche, Roche Products Limited, F. Hoffmann-La Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, Lilly, Merck, Novartis, Peloton, Pfizer, Prometheus Labs, Corvus, Calithera, Analysis Group, Sanofi/Aventis, Takeda. Honoraria: AstraZeneca, Alexion, Sanofi/Aventis, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb/ER Squibb and sons LLC, Cerulean, Eisai, Foundation Medicine Inc., Exelixis, Genentech, Roche, Roche Products Limited, F. Hoffmann-La Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Novartis, Peloton, Pfizer, EMD Serono, Prometheus Labs, Corvus, Ipsen, Up-to-Date, NCCN, Analysis Group, NCCN, Michael J. Hennessy (MJH) Associates, Inc (Healthcare Communications Company with several brands such as OncLive, PeerView, and PER), Research to Practice, Lpath, Kidney Cancer Journal, Clinical Care Options, PlatformQ, Navinata Healthcare, Harborside Press, American Society of Medical Oncology, New England Journal of Medicine, The Lancet Oncology, Heron Therapeutics, Lilly. Consulting or Advisory Role: AstraZeneca, Alexion, Sanofi/Aventis, Bayer, Bristol-Myers Squibb/ER Squibb and sons LLC, Cerulean, Eisai, Foundation Medicine Inc., Exelixis, Genentech, Heron Therapeutics, Lilly, Roche, GlaxoSmithKline, Merck, Novartis, Peloton, Pfizer, EMD Serono, Prometheus Labs, Corvus, Ipsen, Up-to-Date, NCCN, Analysis Group, Pionyr, Tempest. Stock ownership: Pionyr, Tempest. Other present or past leadership roles: Director of GU Oncology Division at Dana-Farber and past President of Medical Staff at Dana-Farber, member of NCCN Kidney Panel and the GU Steering Committee, past chairman of the Kidney Cancer Association Medical and Scientific Steering Committee. Patents, royalties or other intellectual properties: International Patent Application No. PCT/US2018/12209, entitled ‘PBRM1 Biomarkers Predictive of Anti-Immune Checkpoint Response’, filed 3 January 2018, claiming priority to U.S. Provisional Patent Application No. 62/445,094, filed 11 January 2017; International Patent Application No. PCT/US2018/058430, entitled ‘Biomarkers of Clinical Response and Benefit to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy’, filed 31 October 2018, claiming priority to U.S. Provisional Patent Application No. 62/581,175, filed 3 November 2017. Medical writing and editorial assistance support may have been funded by Communications companies funded by pharmaceutical companies (ClinicalThinking, Envision Pharma Group, Fishawack). RJM reports personal fees and other from Pfizer during the conduct of the study; personal fees and other from Genentech/Roche, personal fees from Incyte, other from Bristol-Myers Squibb, personal fees and other from Novartis, personal fees and other from Exelixis, personal fees and other from Eisai, personal fees from Merck, outside the submitted work. BIR reports grants and personal fees from Pfizer during the conduct of the study, grants and personal fees from Merck (MSD), grants and personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, personal fees from Novartis, grants and personal fees from GNE/Roche, personal fees from Exelixis, personal fees from Peloton, outside the submitted work. JH reports grants and personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, MSD, Novartis, and Neon Therapeutics; personal fees from Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, Bayer, Immunocore, Seattle Genetics, Gadeta B.V., Celsius Therapeutics, and AstraZeneca/MedImmune, outside the submitted work. MTC reports personal fees from Eisai, grants and personal fees from EMD Serono, grants from Pfizer, personal fees from Genentech and AstraZeneca, grants from Exelixis and Janssen, other from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Roche, and Merck, outside the submitted work. BV reports personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, personal fees and nonfinancial support from Merck Serono Dohme (MSD), personal fees from EUSA Pharma, personal fees and nonfinancial support from Ipsen, during the conduct of the study. CK reports personal fees from Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Eisai, Ipsen, Astellas, and EMD Serono, outside the submitted work. GG-M and MU have nothing to disclose. JLL reports grants, personal fees, and other from Pfizer Korea and Ipsen Korea, personal fees and other from Janssen and Sanofi Aventis, personal fees from Novartis Korea, and personal fees and other from Astellas Korea and Bristol-Myers Squibb Korea, outside the submitted work. M-OG reports grants and personal fees from Novartis and Bristol-Myers Squibb, personal fees from Pfizer, Bayer HealthCare, Astellas, Intuitive Surgical, Sanofi Aventis, Hexal, APOGEPHA, Amgen, AstraZeneca, MSD, Janssen Cilag, Ono Pharma, Ipsen Pharma, Medac, and Merck, outside the submitted work. HG reports personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Astellas, Pfizer, AstraZeneca, Ipsen, Roche, and MSD, outside the submitted work. MS reports grants, personal fees, and nonfinancial support from Pfizer; personal fees and nonfinancial support from Roche; and personal fees from Novartis, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Ipsen, Exelixis, Eisai, Astellas, and EUSA Pharma, outside the submitted work. JL reports grants and personal fees from Achilles Therapeutics, MSD, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Nektar, Novartis, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, and Immunocore; personal fees from AstraZeneca, Boston Biomedical, Eisai, EUSA Pharma, GlaxoSmithKline, Ipsen, Imugene, Incyte, iOnctura, Kymab, Merck Serono, Pierre Fabre, Secarna, Vitaccess, and Covance; and grants from Aveo and Pharmacyclics, outside the submitted work. MBA reports personal fees from Pfizer, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Merck, Roche, Exelixis, Eisai, Novartis, Alexion, Boehringer Ingelheim, Nektar, and X4 Pharmaceuticals, outside the submitted work. SKP has received honoraria from Astellas Pharma, Medivation, and Novartis; and fees for a consulting or advisory role from Aveo, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Exelixis, Genentech, Myriad Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, and Pfizer. JW, MM, SK, PC, AC, CF, BH, and AdP are employees of Pfizer. LA reports personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Ipsen, Peloton Therapeutics, Roche, MSD, and Novartis, outside the submitted work.
Figures
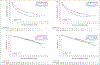



Comment in
-
Are we ready to accept intermediate outcome measures in clinical cancer trials?Ann Oncol. 2020 Aug;31(8):973-975. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.05.017. Epub 2020 May 23. Ann Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32454069 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of avelumab plus axitinib in elderly patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: extended follow-up results from JAVELIN Renal 101.ESMO Open. 2022 Apr;7(2):100450. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2022.100450. Epub 2022 Apr 6. ESMO Open. 2022. PMID: 35397432 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Avelumab plus Axitinib versus Sunitinib for Advanced Renal-Cell Carcinoma.N Engl J Med. 2019 Mar 21;380(12):1103-1115. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1816047. Epub 2019 Feb 16. N Engl J Med. 2019. PMID: 30779531 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Extended follow-up from JAVELIN Renal 101: subgroup analysis of avelumab plus axitinib versus sunitinib by the International Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma Database Consortium risk group in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma.ESMO Open. 2023 Jun;8(3):101210. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2023.101210. Epub 2023 Apr 25. ESMO Open. 2023. PMID: 37104931 Free PMC article.
-
Avelumab and axitinib in the treatment of renal cell carcinoma: safety and efficacy.Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2020 May;20(5):343-354. doi: 10.1080/14737140.2020.1756780. Epub 2020 May 7. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2020. PMID: 32293937 Review.
-
Pembrolizumab in advanced renal cell carcinoma: a meta-analysis providing level 1a evidence.Curr Probl Cancer. 2022 Aug;46(4):100875. doi: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2022.100875. Epub 2022 Jun 1. Curr Probl Cancer. 2022. PMID: 35679628 Review.
Cited by
-
Molecular insight into renal cancer and latest therapeutic approaches to tackle it: an updated review.Med Oncol. 2023 Nov 13;40(12):355. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02225-0. Med Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37955787 Review.
-
Efficacy of combination therapy with pembrolizumab and axitinib for metastatic renal collecting duct cell carcinoma: A report on two cases.IJU Case Rep. 2022 Sep 26;5(6):438-441. doi: 10.1002/iju5.12504. eCollection 2022 Nov. IJU Case Rep. 2022. PMID: 36341193 Free PMC article.
-
Management of Immune-Related Adverse Events from Immune-Checkpoint Inhibitors in Advanced or Metastatic Renal Cell Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Sep 8;14(18):4369. doi: 10.3390/cancers14184369. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36139530 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy and safety of avelumab plus axitinib in elderly patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma: extended follow-up results from JAVELIN Renal 101.ESMO Open. 2022 Apr;7(2):100450. doi: 10.1016/j.esmoop.2022.100450. Epub 2022 Apr 6. ESMO Open. 2022. PMID: 35397432 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Increasing cure rates of solid tumors by immune checkpoint inhibitors.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2023 Jan 16;12(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s40164-023-00372-8. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36647169 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Choueiri TK, Motzer RJ. Systemic therapy for metastatic renal-cell carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2017;376:354–366. - PubMed
-
- Inlyta (Axitinib) [Prescribing Information]. New York, NY: Pfizer; 2018.
-
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology: kidney cancer. Available at https://www.nccn.org/professionals/physician_gls/PDF/kidney.pdf. Accessed December 10, 2019. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

