Fyn Kinase: A Potential Therapeutic Target in Acute Kidney Injury
- PMID: 32336052
- PMCID: PMC7216742
- DOI: 10.4062/biomolther.2019.214
Fyn Kinase: A Potential Therapeutic Target in Acute Kidney Injury
Abstract
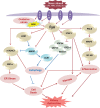
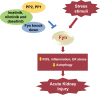
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common disease with a complex pathophysiology which significantly contributes to the development of chronic kidney disease and end stage kidney failure. Preventing AKI can consequently reduce mortality, morbidity, and healthcare burden. However, there are no effective drugs in use for either prevention or treatment of AKI. Developing therapeutic agents with pleiotropic effects covering multiple pathophysiological pathways are likely to be more effective in attenuating AKI. Fyn, a nonreceptor tyrosine kinase, has been acknowledged to integrate multiple injurious stimuli in the kidney. Limited studies have shown increased Fyn transcription level and activation under experimental AKI. Activated Fyn kinase propagates various downstream signaling pathways associated to the progression of AKI, such as oxidative stress, inflammation, endoplasmic reticulum stress, as well as autophagy dysfunction. The versatility of Fyn kinase in mediating various pathophysiological pathways suggests that its inhibition can be a potential strategy in attenuating AKI.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Autophagy; ER stress; Fyn kinase; Inflammation; Oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declared no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CO-Releasing Molecule-2 Prevents Acute Kidney Injury through Suppression of ROS-Fyn-ER Stress Signaling in Mouse Model.Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021 Jul 6;2021:9947772. doi: 10.1155/2021/9947772. eCollection 2021. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021. PMID: 34326922 Free PMC article.
-
Src Family Kinases: A Potential Therapeutic Target for Acute Kidney Injury.Biomolecules. 2022 Jul 14;12(7):984. doi: 10.3390/biom12070984. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35883540 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Small molecules as a source for acute kidney injury therapy.Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Sep;237:108169. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108169. Epub 2022 Mar 17. Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 35306111 Review.
-
Pathophysiological Role of Organelle Stress/Crosstalk in AKI-to-CKD Transition.Semin Nephrol. 2019 Nov;39(6):581-588. doi: 10.1016/j.semnephrol.2019.10.007. Semin Nephrol. 2019. PMID: 31836040 Review.
-
Carbon monoxide releasing molecule-2 protects mice against acute kidney injury through inhibition of ER stress.Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018 Sep;22(5):567-575. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2018.22.5.567. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 30181703 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Advances in the expression and function of Fyn in different human tumors.Clin Transl Oncol. 2023 Oct;25(10):2852-2860. doi: 10.1007/s12094-023-03167-9. Epub 2023 Apr 24. Clin Transl Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37093456 Review.
-
Implication of Nanoparticles to Combat Chronic Liver and Kidney Diseases: Progress and Perspectives.Biomolecules. 2022 Sep 21;12(10):1337. doi: 10.3390/biom12101337. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36291548 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prospects for Protective Potential of Moringa oleifera against Kidney Diseases.Plants (Basel). 2021 Dec 20;10(12):2818. doi: 10.3390/plants10122818. Plants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34961289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the CDKL1-SOX11 signaling axis in acute kidney injury.Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024 Sep 1;327(3):F426-F434. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00147.2024. Epub 2024 Jul 11. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38991010
-
Deficiency of Nuclear Receptor Coactivator 3 Aggravates Diabetic Kidney Disease by Impairing Podocyte Autophagy.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 May;11(19):e2308378. doi: 10.1002/advs.202308378. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38483947 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

