Crosstalk of lncRNA and Cellular Metabolism and Their Regulatory Mechanism in Cancer
- PMID: 32331347
- PMCID: PMC7215767
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21082947
Crosstalk of lncRNA and Cellular Metabolism and Their Regulatory Mechanism in Cancer
Abstract
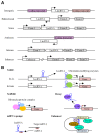
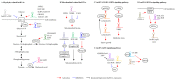
The imbalanced regulation of metabolic homeostasis and energy production is highly associated with inflammation, tumor growth, metastasis and cancer progression. Both glycolysis and oxidative phosphorylation maintain metabolic homeostasis and energy production in cells. Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) are a class of non-protein-coding transcripts longer than 200 nucleotides. Furthermore, lncRNAs can function as either tumor suppressors or oncogenes in cancer. Dysregulated lncRNAs reportedly regulate cancer hallmarks such as tumor growth, metabolism and metastasis. Accordingly, uncovering the interaction between lncRNAs and cellular metabolism has become a necessity when attempting to identify effective therapeutic and preventive strategies in cancer progression. This review summarizes important knowledge of the actions of known lncRNAs-mediated cancer metabolism.
Keywords: cancer; glycolysis; lncRNA; mitochondria; therapeutic target.
Conflict of interest statement
The author have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glycolysis-associated lncRNAs in cancer energy metabolism and immune microenvironment: a magic key.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 13;15:1456636. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1456636. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39346921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
How long noncoding RNAs enforce their will on mitochondrial activity: regulation of mitochondrial respiration, reactive oxygen species production, apoptosis, and metabolic reprogramming in cancer.Curr Genet. 2018 Feb;64(1):163-172. doi: 10.1007/s00294-017-0744-1. Epub 2017 Sep 6. Curr Genet. 2018. PMID: 28879612 Review.
-
The effects of mitochondria-associated long noncoding RNAs in cancer mitochondria: New players in an old arena.Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2018 Nov;131:76-82. doi: 10.1016/j.critrevonc.2018.08.005. Epub 2018 Aug 27. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2018. PMID: 30293709 Review.
-
Regulation of aerobic glycolysis by long non-coding RNAs in cancer.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016 Oct 7;479(1):28-32. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.09.007. Epub 2016 Sep 3. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016. PMID: 27596968 Review.
-
The emerging regulatory roles of long non-coding RNAs implicated in cancer metabolism.Mol Ther. 2021 Jul 7;29(7):2209-2218. doi: 10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.03.017. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Mol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33775912 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel long non-coding RNA CYB561-5 promotes aerobic glycolysis and tumorigenesis by interacting with basigin in non-small cell lung cancer.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Mar;26(5):1402-1412. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17057. Epub 2022 Jan 22. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35064752 Free PMC article.
-
Glycolysis-associated lncRNAs in cancer energy metabolism and immune microenvironment: a magic key.Front Immunol. 2024 Sep 13;15:1456636. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1456636. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39346921 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploration of the Long Noncoding RNAs Involved in the Crosstalk between M2 Macrophages and Tumor Metabolism in Lung Cancer.Genet Res (Camb). 2023 Jan 25;2023:4512820. doi: 10.1155/2023/4512820. eCollection 2023. Genet Res (Camb). 2023. PMID: 36741921 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Roles of LINC00665 in Human Cancers.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Mar 9;10:839177. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.839177. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35356290 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Transcriptome profiling of lncRNA and co-expression network in the vaginal epithelial tissue of women with lubrication disorders.PeerJ. 2021 Nov 10;9:e12485. doi: 10.7717/peerj.12485. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34824921 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stine Z.E., Walton Z.E., Altman B.J., Hsieh A.L., Dang C.V. MYC, Metabolism, and Cancer. Cancer Discov. 2015;5:1024–1039. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-0507. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

