Pro-Inflammatory Effects of NX-3 Toxin Are Comparable to Deoxynivalenol and not Modulated by the Co-Occurring Pro-Oxidant Aurofusarin
- PMID: 32326355
- PMCID: PMC7232499
- DOI: 10.3390/microorganisms8040603
Pro-Inflammatory Effects of NX-3 Toxin Are Comparable to Deoxynivalenol and not Modulated by the Co-Occurring Pro-Oxidant Aurofusarin
Abstract
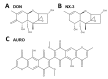
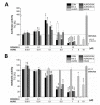
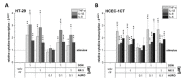
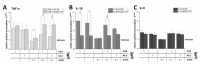
The type A trichothecene NX-3, produced by certain Fusarium graminearum strains, is similar to the mycotoxin deoxynivalenol (DON), with the exception that it lacks the carbonyl moiety at the C-8 position. NX-3 inhibits protein biosynthesis and induces cytotoxicity to a similar extent as DON, but so far, immunomodulatory effects have not been assessed. In the present study, we investigated the impact of NX-3 on the activity of the nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway in direct comparison to DON. Under pro-inflammatory conditions (IL-1β treatment), the impact on cytokine mRNA levels of NF-κB downstream genes was studied in human colon cell lines, comparing noncancer (HCEC-1CT) and cancer cells (HT-29). In addition, potential combinatory effects with the co-occurring Fusarium secondary metabolite aurofusarin (AURO), a dimeric naphthoquinone known to induce oxidative stress, were investigated. NX-3 and DON (1 μM, 20 h) significantly activated a NF-κB regulated reporter gene to a similar extent. Both trichothecenes also enhanced transcript levels of the known NF-κB-dependent pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-8, IL-6, TNF-α and IL-1β. Comparing the colon cancer HT-29 and noncancer HCEC-1CT cells, significant differences in cytokine signaling were identified. In contrast, AURO did not affect NF-κB pathway activity and respective cytokine expression levels at the tested concentration. Despite its pro-oxidant potency, the combination with AURO did not significantly affect the immunomodulatory effects of the tested trichothecenes. Taken together, the present study reveals comparable potency of DON and NX-3 with respect to immunomodulatory and pro-inflammatory potential. Consequently, not only DON but also NX-3 should be considered as factors contributing to intestinal inflammatory processes.
Keywords: NF-κB; combinatory effects; food safety; intestinal inflammation; mycotoxin; trichothecene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Suppression of Trichothecene-Mediated Immune Response by the Fusarium Secondary Metabolite Butenolide in Human Colon Epithelial Cells.Front Nutr. 2020 Aug 6;7:127. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2020.00127. eCollection 2020. Front Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32850941 Free PMC article.
-
Influence of deoxynivalenol on NF-kappaB activation and IL-8 secretion in human intestinal Caco-2 cells.Toxicol Lett. 2008 Apr 1;177(3):205-14. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2008.01.018. Epub 2008 Feb 8. Toxicol Lett. 2008. PMID: 18343055
-
Impact of glutathione modulation on the toxicity of the Fusarium mycotoxins deoxynivalenol (DON), NX-3 and butenolide in human liver cells.Toxicol Lett. 2018 Dec 15;299:104-117. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2018.09.007. Epub 2018 Sep 20. Toxicol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30244016
-
Intestinal toxicity of the new type A trichothecenes, NX and 3ANX.Chemosphere. 2022 Feb;288(Pt 1):132415. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132415. Epub 2021 Sep 29. Chemosphere. 2022. PMID: 34600008
-
Oxidative stress-mediated cytotoxicity and metabolism of T-2 toxin and deoxynivalenol in animals and humans: an update.Arch Toxicol. 2014 Jul;88(7):1309-26. doi: 10.1007/s00204-014-1280-0. Epub 2014 Jun 4. Arch Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24894432 Review.
Cited by
-
Detoxification and Excretion of Trichothecenes in Transgenic Arabidopsisthaliana Expressing Fusarium graminearum Trichothecene 3-O-acetyltransferase.Toxins (Basel). 2021 Apr 29;13(5):320. doi: 10.3390/toxins13050320. Toxins (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33946742 Free PMC article.
-
Anthocyanin-Rich Berry Extracts Affect SN-38-Induced Response: A Comparison of Non-Tumorigenic HCEC-1CT and HCT116 Colon Carcinoma Cells.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Jul 15;13(7):846. doi: 10.3390/antiox13070846. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061915 Free PMC article.
-
Combinatory Exposure to Urolithin A, Alternariol, and Deoxynivalenol Affects Colon Cancer Metabolism and Epithelial Barrier Integrity in vitro.Front Nutr. 2022 Jun 24;9:882222. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.882222. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35811943 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Fusarium graminearum NA3 Population Produces High Levels of Mycotoxins in Wheat and Barley.Toxins (Basel). 2024 Sep 20;16(9):408. doi: 10.3390/toxins16090408. Toxins (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39330866 Free PMC article.
-
Fusarium: Mycotoxins, Taxonomy, Pathogenicity.Microorganisms. 2020 Sep 12;8(9):1404. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8091404. Microorganisms. 2020. PMID: 32932595 Free PMC article.
References
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

