Paracrine orchestration of intestinal tumorigenesis by a mesenchymal niche
- PMID: 32322056
- PMCID: PMC7490650
- DOI: 10.1038/s41586-020-2166-3
Paracrine orchestration of intestinal tumorigenesis by a mesenchymal niche
Abstract
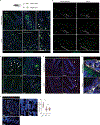
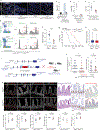
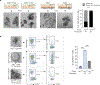
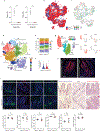
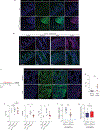
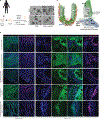
The initiation of an intestinal tumour is a probabilistic process that depends on the competition between mutant and normal epithelial stem cells in crypts1. Intestinal stem cells are closely associated with a diverse but poorly characterized network of mesenchymal cell types2,3. However, whether the physiological mesenchymal microenvironment of mutant stem cells affects tumour initiation remains unknown. Here we provide in vivo evidence that the mesenchymal niche controls tumour initiation in trans. By characterizing the heterogeneity of the intestinal mesenchyme using single-cell RNA-sequencing analysis, we identified a population of rare pericryptal Ptgs2-expressing fibroblasts that constitutively process arachidonic acid into highly labile prostaglandin E2 (PGE2). Specific ablation of Ptgs2 in fibroblasts was sufficient to prevent tumour initiation in two different models of sporadic, autochthonous tumorigenesis. Mechanistically, single-cell RNA-sequencing analyses of a mesenchymal niche model showed that fibroblast-derived PGE2 drives the expansion οf a population of Sca-1+ reserve-like stem cells. These express a strong regenerative/tumorigenic program, driven by the Hippo pathway effector Yap. In vivo, Yap is indispensable for Sca-1+ cell expansion and early tumour initiation and displays a nuclear localization in both mouse and human adenomas. Using organoid experiments, we identified a molecular mechanism whereby PGE2 promotes Yap dephosphorylation, nuclear translocation and transcriptional activity by signalling through the receptor Ptger4. Epithelial-specific ablation of Ptger4 misdirected the regenerative reprogramming of stem cells and prevented Sca-1+ cell expansion and sporadic tumour initiation in mutant mice, thereby demonstrating the robust paracrine control of tumour-initiating stem cells by PGE2-Ptger4. Analyses of patient-derived organoids established that PGE2-PTGER4 also regulates stem-cell function in humans. Our study demonstrates that initiation of colorectal cancer is orchestrated by the mesenchymal niche and reveals a mechanism by which rare pericryptal Ptgs2-expressing fibroblasts exert paracrine control over tumour-initiating stem cells via the druggable PGE2-Ptger4-Yap signalling axis.
Figures




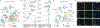


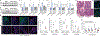
Comment in
-
Fibroblasts orchestrate tumour initiation.Nat Rev Cancer. 2020 Jun;20(6):301. doi: 10.1038/s41568-020-0264-z. Nat Rev Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32317743 No abstract available.
-
Fibroblasts fuel intestinal tumorigenesis.Cell Res. 2020 Aug;30(8):635-636. doi: 10.1038/s41422-020-0340-7. Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 32494022 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Prostaglandin E2 Activates YAP and a Positive-Signaling Loop to Promote Colon Regeneration After Colitis but Also Carcinogenesis in Mice.Gastroenterology. 2017 Feb;152(3):616-630. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2016.11.005. Epub 2016 Nov 15. Gastroenterology. 2017. PMID: 27864128 Free PMC article.
-
Yap-dependent reprogramming of Lgr5(+) stem cells drives intestinal regeneration and cancer.Nature. 2015 Oct 29;526(7575):715-8. doi: 10.1038/nature15382. Epub 2015 Oct 21. Nature. 2015. PMID: 26503053
-
Prostaglandin E2 Promotes Colorectal Cancer Stem Cell Expansion and Metastasis in Mice.Gastroenterology. 2015 Dec;149(7):1884-1895.e4. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2015.07.064. Epub 2015 Aug 7. Gastroenterology. 2015. PMID: 26261008 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular Interactions in the Intestinal Stem Cell Niche.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2019 Feb;67(1):19-26. doi: 10.1007/s00005-018-0524-8. Epub 2018 Sep 21. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2019. PMID: 30242440 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inflammatory cues acting on the adult intestinal stem cells and the early onset of cancer (review).Int J Oncol. 2014 Sep;45(3):959-68. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2014.2490. Epub 2014 Jun 10. Int J Oncol. 2014. PMID: 24920319 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Liquid chromatography coupled to high-resolution mass spectrometry metabolomics: A useful tool for investigating tumor secretome based on a three-dimensional co-culture model.PLoS One. 2022 Sep 21;17(9):e0274623. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0274623. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36129929 Free PMC article.
-
Aspirin in the Prevention of Colorectal Neoplasia.Annu Rev Med. 2021 Jan 27;72:415-430. doi: 10.1146/annurev-med-060319-120913. Epub 2020 Oct 9. Annu Rev Med. 2021. PMID: 33035431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IL-13-programmed airway tuft cells produce PGE2, which promotes CFTR-dependent mucociliary function.JCI Insight. 2022 Jul 8;7(13):e159832. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.159832. JCI Insight. 2022. PMID: 35608904 Free PMC article.
-
Roles of polyunsaturated fatty acids, from mediators to membranes.J Lipid Res. 2020 Aug;61(8):1150-1160. doi: 10.1194/jlr.R120000800. Epub 2020 Jun 2. J Lipid Res. 2020. PMID: 32487545 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the aryl hydrocarbon receptor in stem cells to improve the use of food as medicine.Curr Stem Cell Rep. 2020 Dec;6(4):109-118. doi: 10.1007/s40778-020-00184-0. Epub 2021 Jan 5. Curr Stem Cell Rep. 2020. PMID: 34395177 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vermeulen L & Snippert HJ Stem cell dynamics in homeostasis and cancer of the intestine. Nat. Rev. Cancer 14, 468–480 (2014). - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

