Pre-Transplant Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Antibodies and Anti-Endothelial Cell Antibodies Predict Graft Function and Allograft Rejection in a Low-Risk Kidney Transplantation Setting
- PMID: 32311853
- PMCID: PMC7169631
- DOI: 10.3343/alm.2020.40.5.398
Pre-Transplant Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Antibodies and Anti-Endothelial Cell Antibodies Predict Graft Function and Allograft Rejection in a Low-Risk Kidney Transplantation Setting
Abstract
Background: Non-HLA antibodies, anti-angiotensin II type 1 receptor antibodies (anti-AT1R) and anti-endothelial cell antibodies (AECA), are known to play a role in allograft rejection. We evaluated the role of both antibodies in predicting post-transplant outcomes in low-risk living donor kidney transplantation (LDKT) recipients.
Methods: In 94 consecutive LDKT recipients who were ABO compatible and negative for pre-transplant HLA donor-specific antibodies, we determined the levels of anti-AT1Rs using an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and the presence of AECAs using a flow cytometric endothelial cell crossmatch (ECXM) assay with pre-transplant sera. Hazard ratio (HR) was calculated to predict post-transplant outcomes.
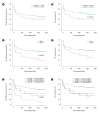
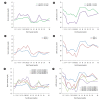
Results: Pre-transplant anti-AT1Rs (≥11.5 U/mL) and AECAs were observed in 36 (38.3%) and 22 recipients (23.4%), respectively; 11 recipients had both. Pre-transplant anti-AT1Rs were a significant risk factor for the development of acute rejection (AR) (HR 2.09; P=0.018), while a positive AECA status was associated with AR or microvascular inflammation only (HR 2.47; P=0.004) throughout the follow-up period. In particular, AECA (+) recipients with ≥11.5 U/mL anti-AT1Rs exhibited a significant effect on creatinine and estimated glomerular filtration rate (P<0.001; P=0.028), although the risk of AR was not significant.
Conclusions: Pre-transplant anti-AT1Rs and AECAs have independent negative effects on post-transplant outcomes in low-risk LDKT recipients. Assessment of both antibodies would be helpful in stratifying the pre-transplant immunological risk, even in low-risk LDKT recipients.
Keywords: Anti-angiotensin II type 1 receptor antibodies; Anti-endothelial cell antibodies; Endothelial cell crossmatch; Kidney transplantation; Low-risk; Non-HLA antibodies; Outcome.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflicts of interest relevant to this paper were reported
Figures
Similar articles
-
Isolated De Novo Antiendothelial Cell Antibodies and Kidney Transplant Rejection.Am J Kidney Dis. 2016 Dec;68(6):933-943. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2016.07.019. Epub 2016 Sep 3. Am J Kidney Dis. 2016. PMID: 27599627
-
Anti-Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor and Anti-Endothelial Cell Antibodies: A Cross-Sectional Analysis of Pathological Findings in Allograft Biopsies.Transplantation. 2017 Mar;101(3):608-615. doi: 10.1097/TP.0000000000001231. Transplantation. 2017. PMID: 27222934 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-transplant Screening for Non-HLA Antibodies: Who should be Tested?Hum Immunol. 2018 Apr;79(4):195-202. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2018.02.001. Epub 2018 Feb 8. Hum Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29428484
-
The significance of angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1 receptor) in renal transplant injury.Adv Clin Exp Med. 2020 May;29(5):629-633. doi: 10.17219/acem/121510. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2020. PMID: 32459402 Review.
-
Angiotensin II type I receptor antibodies in pediatric solid organ transplant.Hum Immunol. 2019 Aug;80(8):568-572. doi: 10.1016/j.humimm.2019.03.016. Epub 2019 Mar 26. Hum Immunol. 2019. PMID: 30926351 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Angiotensin II Type 1 Receptor Antibodies Are Higher in Lupus Nephritis and Vasculitis than Other Glomerulonephritis Patients.Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2022 Sep 24;70(1):23. doi: 10.1007/s00005-022-00660-x. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2022. PMID: 36152104 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances on Biomarkers of Early and Late Kidney Graft Dysfunction.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jul 29;21(15):5404. doi: 10.3390/ijms21155404. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32751357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antigen and Cell-Based Assays for the Detection of Non-HLA Antibodies.Front Immunol. 2022 May 6;13:864671. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.864671. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35603145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Causes of Positive Pretransplant Crossmatches in the Absence of Donor-Specific Anti-Human Leukocyte Antigen Antibodies: A Single-Center Experience.Ann Lab Med. 2021 Jul 1;41(4):429-435. doi: 10.3343/alm.2021.41.4.429. Ann Lab Med. 2021. PMID: 33536364 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Antibodies against Angiotensin II Type-1 Receptor on the Outcome of Kidney Transplantation: A Single-Center Retrospective Study.J Clin Med. 2023 Apr 25;12(9):3112. doi: 10.3390/jcm12093112. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37176553 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Terasaki PI. Humoral theory of transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2003;3:665–73. - PubMed
-
- Opelz G and Collaborative Transplant Study. Non-HLA transplantation immunity revealed by lymphocytotoxic antibodies. Lancet. 2005;365:1570–6. - PubMed
-
- Han F, Lv R, Jin J, Wu J, Chen Y, Wang H, et al. Pre-transplant serum concentrations of anti-endothelial cell antibody in panel reactive antibody negative renal recipients and its impact on acute rejection. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2009;47:1265–9. - PubMed
-
- Breimer ME, Rydberg L, Jackson AM, Lucas DP, Zachary AA, Melancon JK, et al. Multicenter evaluation of a novel endothelial cell crossmatch test in kidney transplantation. Transplantation. 2009;87:549–56. - PubMed
-
- Xavier P, Aires P, Sampaio S, Mendes C, Monteiro M, Alves H, et al. XM-ONE detection of endothelium cell antibodies identifies a subgroup of HLA-antibody negative patients undergoing acute rejection. Transplant Proc. 2011;43:91–4. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

