Immunodomination of Serotype-Specific CD4+ T-Cell Epitopes Contributed to the Biased Immune Responses Induced by a Tetravalent Measles-Vectored Dengue Vaccine
- PMID: 32300346
- PMCID: PMC7145397
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00546
Immunodomination of Serotype-Specific CD4+ T-Cell Epitopes Contributed to the Biased Immune Responses Induced by a Tetravalent Measles-Vectored Dengue Vaccine
Abstract
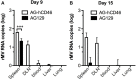
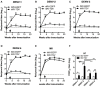
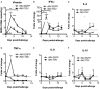
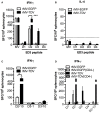
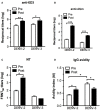
Dengue is an emerging mosquito-borne disease, and the use of prophylactic vaccines is still limited. We previously developed a tetravalent dengue vaccine (rMV-TDV) by a recombinant measles virus (MV) vector expressing envelope protein domain III (ED3). In this study, we used dengue-susceptible AG129 mice to evaluate the protective and/or pathogenic immune responses induced by rMV-TDV. Consistent with the previous study, rMV-TDV-immunized mice developed a significant neutralizing antibody response against all serotypes of DENV, as well as a significant IFN-γ response biased to DENV-3, compared to the vector controls. We further demonstrated that this DENV-3-specific IFN-γ response was dominated by one CD4+ T-cell epitope located in E349-363. After DENV-2 challenge, rMV-TDV-immunized mice showed a significantly lower viremia and no inflammatory cytokine increase compared to the vector controls, which had an ~100 times higher viremia and a significant increase in IFN-γ and TNF-α. As a correlate of protection, a robust memory IFN-γ response specific to DENV-2 was boosted in rMV-TDV-immunized mice after challenge. This result suggested that pre-existing DENV-3-dominated T-cell responses did not cross-react, but a DENV-2-specific IFN-γ response, which was undetectable during immunization, was recalled. Interestingly, this recalled T-cell response recognized the epitope in the same position as the E349-363 but in the DENV-2 serotype. This result suggested that immunodomination occurred in the CD4+ T-cell epitopes between dengue serotypes after rMV-TDV vaccination and resulted in a DENV-3-dominated CD4+ T-cell response. Although the significant increase in IgG against both DENV-2 and -3 suggested that cross-reactive antibody responses were boosted, the increased neutralizing antibodies and IgG avidity still remained DENV-2 specific, consistent with the serotype-specific T cell response post challenge. Our data reveal that immunodomination caused a biased T-cell response to one of the dengue serotypes after tetravalent dengue vaccination and highlight the roles of cross-reactive T cells in dengue protection.
Keywords: AG129 mice; dengue; dengue vaccine; envelope protein; immunodominance; recombinant measles virus.
Copyright © 2020 Lin, Chen, Hsiao, Yan, Chiang, Chen, Hu, Wu and Pan.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The Immunodominance Change and Protection of CD4+ T-Cell Responses Elicited by an Envelope Protein Domain III-Based Tetravalent Dengue Vaccine in Mice.PLoS One. 2015 Dec 29;10(12):e0145717. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145717. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26714037 Free PMC article.
-
A Dengue Virus Serotype 1 mRNA-LNP Vaccine Elicits Protective Immune Responses.J Virol. 2021 May 24;95(12):e02482-20. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02482-20. Print 2021 May 24. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33762420 Free PMC article.
-
A tetravalent virus-like particle vaccine designed to display domain III of dengue envelope proteins induces multi-serotype neutralizing antibodies in mice and macaques which confer protection against antibody dependent enhancement in AG129 mice.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018 Jan 8;12(1):e0006191. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006191. eCollection 2018 Jan. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018. PMID: 29309412 Free PMC article.
-
A recombinant, chimeric tetravalent dengue vaccine candidate based on a dengue virus serotype 2 backbone.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2016;15(4):497-508. doi: 10.1586/14760584.2016.1128328. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2016. PMID: 26635182 Review.
-
Cross-Reactive T Cell Immunity to Dengue and Zika Viruses: New Insights Into Vaccine Development.Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 11;10:1316. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01316. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31244855 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dengue mouse models for evaluating pathogenesis and countermeasures.Curr Opin Virol. 2020 Aug;43:50-58. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2020.09.001. Epub 2020 Sep 17. Curr Opin Virol. 2020. PMID: 32950933 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Versatility of live-attenuated measles viruses as platform technology for recombinant vaccines.NPJ Vaccines. 2022 Oct 15;7(1):119. doi: 10.1038/s41541-022-00543-4. NPJ Vaccines. 2022. PMID: 36243743 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Animal models for COVID-19: advances, gaps and perspectives.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Jul 7;7(1):220. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01087-8. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022. PMID: 35798699 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO Dengue: Guidelines for Diagnosis, Treatment, Prevention and Control. World Health Organization; (2009). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

