Mechanisms of mitochondrial dysfunction and their impact on age-related macular degeneration
- PMID: 32298788
- PMCID: PMC7650008
- DOI: 10.1016/j.preteyeres.2020.100858
Mechanisms of mitochondrial dysfunction and their impact on age-related macular degeneration
Abstract
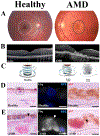
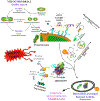
Oxidative stress-induced damage to the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) is considered to be a key factor in age-related macular degeneration (AMD) pathology. RPE cells are constantly exposed to oxidative stress that may lead to the accumulation of damaged cellular proteins, lipids, nucleic acids, and cellular organelles, including mitochondria. The ubiquitin-proteasome and the lysosomal/autophagy pathways are the two major proteolytic systems to remove damaged proteins and organelles. There is increasing evidence that proteostasis is disturbed in RPE as evidenced by lysosomal lipofuscin and extracellular drusen accumulation in AMD. Nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor-2 (NFE2L2) and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1 alpha (PGC-1α) are master transcription factors in the regulation of antioxidant enzymes, clearance systems, and biogenesis of mitochondria. The precise cause of RPE degeneration and the onset and progression of AMD are not fully understood. However, mitochondria dysfunction, increased reactive oxygen species (ROS) production, and mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) damage are observed together with increased protein aggregation and inflammation in AMD. In contrast, functional mitochondria prevent RPE cells damage and suppress inflammation. Here, we will discuss the role of mitochondria in RPE degeneration and AMD pathology focused on mtDNA damage and repair, autophagy/mitophagy signaling, and regulation of inflammation. Mitochondria are putative therapeutic targets to prevent or treat AMD.
Keywords: Age-related macular degeneration; Aggregation; Aging; Autophagy; Clearance; Degeneration; Mitochondria; Mitophagy; Retina; Retinal pigment epithelium.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

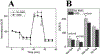


Similar articles
-
Loss of NRF-2 and PGC-1α genes leads to retinal pigment epithelium damage resembling dry age-related macular degeneration.Redox Biol. 2019 Jan;20:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2018.09.011. Epub 2018 Sep 14. Redox Biol. 2019. PMID: 30253279 Free PMC article.
-
Mitophagy in the Retinal Pigment Epithelium of Dry Age-Related Macular Degeneration Investigated in the NFE2L2/PGC-1α-/- Mouse Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Mar 13;21(6):1976. doi: 10.3390/ijms21061976. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32183173 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial damage and clearance in retinal pigment epithelial cells.Acta Ophthalmol. 2024 Mar;102 Suppl 282:3-53. doi: 10.1111/aos.16661. Acta Ophthalmol. 2024. PMID: 38467968
-
Potential of Telomerase in Age-Related Macular Degeneration-Involvement of Senescence, DNA Damage Response and Autophagy and a Key Role of PGC-1α.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 3;22(13):7194. doi: 10.3390/ijms22137194. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34281248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dysfunctional Autophagy, Proteostasis, and Mitochondria as a Prelude to Age-Related Macular Degeneration.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 15;24(10):8763. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108763. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240109 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
m6A-Mediated Upregulation of Imprinted in Prader-Willi Syndrome Induces Aberrant Apical-Basal Polarization and Oxidative Damage in RPE Cells.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024 Feb 1;65(2):10. doi: 10.1167/iovs.65.2.10. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2024. PMID: 38315495 Free PMC article.
-
Mitophagy: An Emerging Target in Ocular Pathology.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021 Mar 1;62(3):22. doi: 10.1167/iovs.62.3.22. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2021. PMID: 33724294 Free PMC article. Review.
-
E3 ubiquitin ligase Herc3 deficiency leads to accumulation of subretinal microglia and retinal neurodegeneration.Sci Rep. 2024 Feb 6;14(1):3010. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-53731-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38321224 Free PMC article.
-
RIP140-Mediated NF-κB Inflammatory Pathway Promotes Metabolic Dysregulation in Retinal Pigment Epithelium Cells.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022 Nov 21;44(11):5788-5801. doi: 10.3390/cimb44110393. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 36421677 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid Droplet Accumulation Promotes RPE Dysfunction.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 4;23(3):1790. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031790. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163712 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alaimo A, Liñares GG, Bujjamer JM, Gorojod RM, Alcon SP, Martínez JH, Baldessari A, Grecco HE, Kotler ML, 2019. Toxicity of blue led light and A2E is associated to mitochondrial dynamics impairment in ARPE-19 cells: implications for age-related macular degeneration. Arch. Toxicol 93, 1401–1415. - PubMed
-
- Allio R, Donega S, Galtier N, Nabholz B, 2017. Large variation in the ratio of mitochondrial to nuclear mutation rate across animals: implications for genetic diversity and the use of mitochondrial DNA as a molecular marker. Mol. Biol. Evol 34, 2762–2772. - PubMed
-
- Ames BN, Shigenaga MK, 1992. Oxidants are a major contributor to aging. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci 21, 85–96. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

