Serum albumin cysteine trioxidation is a potential oxidative stress biomarker of type 2 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 32296090
- PMCID: PMC7160123
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-62341-z
Serum albumin cysteine trioxidation is a potential oxidative stress biomarker of type 2 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
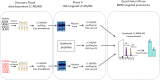
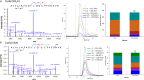
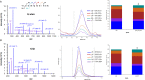
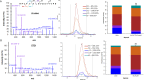
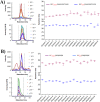
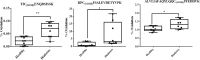
Metabolic disorders in T2DM generate multiple sources of free radicals and oxidative stress that accelerate nonenzymatic degenerative protein modifications (DPMs) such as protein oxidation, disrupt redox signaling and physiological function, and remain a major risk factor for clinical diabetic vascular complications. In order to identify potential oxidative biomarkers in the blood plasma of patients with T2DM, we used LC-MS/MS-based proteomics to profile plasma samples from patients with T2DM and healthy controls. The results showed that human serum albumin (HSA) is damaged by irreversible cysteine trioxidation, which can be a potential oxidative stress biomarker for the early diagnosis of T2DM. The quantitative detection of site-specific thiol trioxidation is technically challenging; thus, we developed a sensitive and selective LC-MS/MS workflow that has been used to discover and quantify three unique thiol-trioxidized HSA peptides, ALVLIAFAQYLQQC(SO3H)PFEDHVK (m/z 1241.13), YIC(SO3H)ENQDSISSK (m/z 717.80) and RPC(SO3H)FSALEVDETYVPK (m/z 951.45), in 16 individual samples of healthy controls (n = 8) and individuals with diabetes (n = 8). Targeted quantitative analysis using multiple reaction monitoring mass spectrometry revealed impairment of the peptides with m/z 1241.13, m/z 717.80 and m/z 951.45, with significance (P < 0.02, P < 0.002 and P < 0.03), in individuals with diabetes. The results demonstrated that a set of three HSA thiol-trioxidized peptides, which are irreversibly oxidatively damaged in HSA in the plasma of patients with T2DM, can be important indicators and potential biomarkers of oxidative stress in T2DM.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Albumin Oxidation and Albumin Glycation Discordance During Type 2 Diabetes Therapy: Biological and Clinical Implications.Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2024 Jun;22(5):372-384. doi: 10.1089/met.2023.0275. Epub 2024 May 2. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2024. PMID: 38696648
-
Quantification of Specific Glycation Sites in Human Serum Albumin as Prospective Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Biomarkers.Protein Pept Lett. 2017;24(10):887-896. doi: 10.2174/0929866524666170202124120. Protein Pept Lett. 2017. PMID: 28155619
-
Oxidised Met147 of human serum albumin is a biomarker of oxidative stress, reflecting glycaemic fluctuations and hypoglycaemia in diabetes.Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 14;10(1):268. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-57095-2. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 31937809 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Implications Associated With the Posttranslational Modification-Induced Functional Impairment of Albumin in Oxidative Stress-Related Diseases.J Pharm Sci. 2017 Sep;106(9):2195-2203. doi: 10.1016/j.xphs.2017.03.002. Epub 2017 Mar 14. J Pharm Sci. 2017. PMID: 28302542 Review.
-
Activity-Based Sensing for Site-Specific Proteomic Analysis of Cysteine Oxidation.Acc Chem Res. 2020 Jan 21;53(1):20-31. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.9b00562. Epub 2019 Dec 23. Acc Chem Res. 2020. PMID: 31869209 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
N-Acetylcysteine and Other Sulfur-Donors as a Preventative and Adjunct Therapy for COVID-19.Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2022 Aug 10;2022:4555490. doi: 10.1155/2022/4555490. eCollection 2022. Adv Pharmacol Pharm Sci. 2022. PMID: 35992575 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Extracellular Vesicle Proteome of Breast Cancer Patients with and Without Cognitive Impairment Following Anthracycline-based Chemotherapy: An Exploratory Study.Biomark Insights. 2021 May 24;16:11772719211018204. doi: 10.1177/11772719211018204. eCollection 2021. Biomark Insights. 2021. PMID: 34103887 Free PMC article.
-
Methylglyoxal Forms Diverse Mercaptomethylimidazole Crosslinks with Thiol and Guanidine Pairs in Endogenous Metabolites and Proteins.ACS Chem Biol. 2021 Nov 19;16(11):2453-2461. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.1c00553. Epub 2021 Sep 28. ACS Chem Biol. 2021. PMID: 34581579 Free PMC article.
-
Biomonitoring of Ambient Outdoor Air Pollutant Exposure in Humans Using Targeted Serum Albumin Adductomics.Chem Res Toxicol. 2021 Apr 19;34(4):1183-1196. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.1c00055. Epub 2021 Apr 1. Chem Res Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33793228 Free PMC article.
-
Trioxidized cysteine and aging: a molecular binomial that extends far beyond classical proteinopathic paradigms.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Jul 25;16(15):11484-11490. doi: 10.18632/aging.206036. Epub 2024 Jul 25. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 39058307 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Esposito K, et al. Inflammatory cytokine concentrations are acutely increased by hyperglycemia in humans: role of oxidative stress. Circulation. 2002;106:2067–2072. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000034509.14906.AE. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

