Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV) Small Noncoding RNAs Antisense to the VZV Latency-Encoded Transcript VLT Enhance Viral Replication
- PMID: 32295909
- PMCID: PMC7307171
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00123-20
Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV) Small Noncoding RNAs Antisense to the VZV Latency-Encoded Transcript VLT Enhance Viral Replication
Abstract
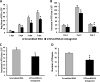
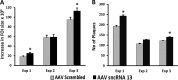
Small noncoding RNAs (sncRNA), including microRNA (miR), are expressed by many viruses to provide an additional layer of gene expression regulation. Our work has shown that varicella-zoster virus (VZV; also called human herpesvirus 3 [HHV3]), the human alphaherpesvirus causing varicella and herpes zoster, expresses 24 virally encoded sncRNA (VZVsncRNA) in infected cells. Here, we demonstrate that several VZVsncRNA can modulate VZV growth, including four VZVsncRNA (VZVsncRNA10, -11, -12, and -13) that are antisense to VLT, a transcript made in lytic infections and associated with VZV latency. The influence on productive VZV growth and spread was assessed in epithelial cells transfected with locked nucleotide analog antagonists (LNAA). LNAA to the four VZVsncRNA antisense to VLT significantly reduced viral spread and progeny titers of infectious virus, suggesting that these sncRNA promoted lytic infection. The LNAA to VZVsncRNA12, encoded in the leader to ORF61, also significantly increased the levels of VLT transcripts. Conversely, overexpression of VZVsncRNA13 using adeno-associated virus consistently increased VZV spread and progeny titers. These results suggest that sncRNA antisense to VZV may regulate VZV growth, possibly by affecting VLT expression. Transfection of LNAA to VZVsncRNA14 and VZVsncRNA9 decreased and increased VZV growth, respectively, while LNAA to three other VZVsncRNA had no significant effects on replication. These data strongly support the conclusion that VZV replication is modulated by multiple virally encoded sncRNA, revealing an additional layer of complexity of VZV regulation of lytic infections. This may inform the development of novel anti-sncRNA-based therapies for treatment of VZV diseases.IMPORTANCE Varicella-zoster virus (VZV) causes herpes zoster, a major health issue in the aging and immunocompromised populations. Small noncoding RNAs (sncRNA) are recognized as important actors in modulating gene expression. This study extends our previous work and shows that four VZVsncRNA clustering in and near ORF61 and antisense to the latency-associated transcript of VZV can positively influence productive VZV infection. The ability of multiple exogenous small oligonucleotides targeting VZVsncRNA to inhibit VZV replication strengthens the possibility that they may inform development of novel treatments for painful herpes zoster.
Keywords: herpes zoster; noncoding RNA; varicella-zoster virus.
Copyright © 2020 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
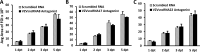
Similar articles
-
Locked-nucleotide antagonists to varicella zoster virus small non-coding RNA block viral growth and have potential as an anti-viral therapy.Antiviral Res. 2021 Sep;193:105144. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2021.105144. Epub 2021 Jul 22. Antiviral Res. 2021. PMID: 34303746 Free PMC article.
-
Studies of Infection and Experimental Reactivation by Recombinant VZV with Mutations in Virally-Encoded Small Non-Coding RNA.Viruses. 2022 May 10;14(5):1015. doi: 10.3390/v14051015. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35632756 Free PMC article.
-
Varicella-Zoster Virus Expresses Multiple Small Noncoding RNAs.J Virol. 2017 Nov 30;91(24):e01710-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01710-17. Print 2017 Dec 15. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 29021397 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Issues in Varicella-Zoster Virus Latency.Viruses. 2021 Oct 7;13(10):2018. doi: 10.3390/v13102018. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34696448 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Aspects of Varicella-Zoster Virus Latency.Viruses. 2018 Jun 28;10(7):349. doi: 10.3390/v10070349. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 29958408 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Locked-nucleotide antagonists to varicella zoster virus small non-coding RNA block viral growth and have potential as an anti-viral therapy.Antiviral Res. 2021 Sep;193:105144. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2021.105144. Epub 2021 Jul 22. Antiviral Res. 2021. PMID: 34303746 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of keratin 15 is required for varicella-zoster virus replication in keratinocytes and is attenuated in the live attenuated vOka vaccine strain.Virol J. 2024 Oct 9;21(1):253. doi: 10.1186/s12985-024-02514-8. Virol J. 2024. PMID: 39385182 Free PMC article.
-
Noncoding RNAs: the crucial role of programmed cell death in osteoporosis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 May 10;12:1409662. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1409662. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38799506 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Studies of Infection and Experimental Reactivation by Recombinant VZV with Mutations in Virally-Encoded Small Non-Coding RNA.Viruses. 2022 May 10;14(5):1015. doi: 10.3390/v14051015. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35632756 Free PMC article.
-
miRNAs: Targets to Investigate Herpesvirus Infection Associated with Neurological Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 1;24(21):15876. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115876. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958855 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

