B7-33, a Functionally Selective Relaxin Receptor 1 Agonist, Attenuates Myocardial Infarction-Related Adverse Cardiac Remodeling in Mice
- PMID: 32295457
- PMCID: PMC7428518
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.119.015748
B7-33, a Functionally Selective Relaxin Receptor 1 Agonist, Attenuates Myocardial Infarction-Related Adverse Cardiac Remodeling in Mice
Abstract
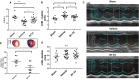
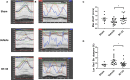
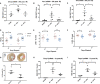
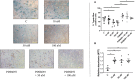
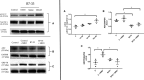
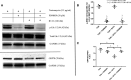
Background Human relaxin-2 is a peptide hormone capable of pleiotropic effects in several organ systems. Its recombinant formulation (serelaxin) has been demonstrated to reduce infarct size and prevent excessive scar formation in animal models of cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury. B7-33, a synthetically designed peptide analogous to B-chain of relaxin-2, invokes signaling at relaxin family peptide receptor 1 (cognate receptor for relaxin-2) by preferentially phosphorylating the mitogen-activated protein kinase extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2. We sought to investigate the effects of B7-33 treatment post ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Methods and Results Adult male CD1 mice were subjected to ischemia-reperfusion via ligation of left anterior descending artery for 30 minutes, followed by 24 hours or 7 days of reperfusion. Echocardiography was performed to assess cardiac function, and cardiac tissue was stained to determine infarct size at 24 hours. B7-33 significantly reduced infarct size (21.99% versus 45.32%; P=0.02) and preserved fractional shortening (29% versus 23%; P=0.02) compared with vehicle. The difference in fractional shortening further increased at 7 days post myocardial infarction (29% versus 20% for B7-33 and vehicle groups, respectively). In vitro, primary cardiomyocytes were isolated from adult hearts and subjected to simulated ischemia-reperfusion injury (simulated ischemia reoxygenation). B7-33 (50 and 100 nmol/L) improved cell survival and reduced the expression of GRP78 (glucose regulated protein), an endoplasmic reticulum stress marker. Subsequently, B7-33 (100 nmol/L) reduced tunicamycin (2.5 μg/mL) induced upregulation of GRP78 in an extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2-dependent manner. Conclusions B7-33 confers acute cardioprotection and limits myocardial infarction-related adverse remodeling in mice by attenuating cardiomyocyte death and endoplasmic reticulum stress as well as preserving cardiac function.
Keywords: adverse cardiac remodeling; echocardiography; endoplasmic reticulum stress; myocardial infarction; relaxin.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Reperfusion therapy with recombinant human relaxin-2 (Serelaxin) attenuates myocardial infarct size and NLRP3 inflammasome following ischemia/reperfusion injury via eNOS-dependent mechanism.Cardiovasc Res. 2017 May 1;113(6):609-619. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvw246. Cardiovasc Res. 2017. PMID: 28073832
-
Cardioprotection by post-conditioning with exogenous triiodothyronine in isolated perfused rat hearts and isolated adult rat cardiomyocytes.Basic Res Cardiol. 2021 Apr 19;116(1):27. doi: 10.1007/s00395-021-00868-6. Basic Res Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33876304 Free PMC article.
-
Relaxin mitigates microvascular damage and inflammation following cardiac ischemia-reperfusion.Basic Res Cardiol. 2019 Jun 19;114(4):30. doi: 10.1007/s00395-019-0739-9. Basic Res Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 31218471
-
The role of aldosterone inhibitors in cardiac ischemia-reperfusion injury.Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2021 Jan;99(1):18-29. doi: 10.1139/cjpp-2020-0276. Epub 2020 Aug 15. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 32799671 Review.
-
Angiotensin 1-7 increases cardiac tolerance to ischemia/reperfusion and mitigates adverse remodeling of the heart-The signaling mechanism.Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2024 Jun;38(3):489-501. doi: 10.1111/fcp.12983. Epub 2024 Feb 4. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38311344 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances on Drug Development and Emerging Therapeutic Agents Through Targeting Cellular Homeostasis for Ageing and Cardiovascular Disease.Front Aging. 2022 Apr 25;3:888190. doi: 10.3389/fragi.2022.888190. eCollection 2022. Front Aging. 2022. PMID: 35821839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic treatment with serelaxin mitigates adverse remodeling in a murine model of ischemic heart failure and modulates bioactive sphingolipid signaling.Sci Rep. 2022 May 25;12(1):8897. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12930-x. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35614179 Free PMC article.
-
RNA nanotherapeutics with fibrosis overexpression and retention for MASH treatment.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 27;15(1):7263. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51571-8. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39191801 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac Gene Therapy With Relaxin Receptor 1 Overexpression Protects Against Acute Myocardial Infarction.JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2021 Dec 22;7(1):53-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2021.10.012. eCollection 2022 Jan. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2021. PMID: 35128209 Free PMC article.
-
A Lipidated Single-B-Chain Derivative of Relaxin Exhibits Improved In Vitro Serum Stability without Altering Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 1;24(7):6616. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076616. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047588 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Valle Raleigh J, Mauro AG, Devarakonda T, Marchetti C, He J, Kim E, Filippone S, Das A, Toldo S, Abbate A, et al. Reperfusion therapy with recombinant human relaxin‐2 (serelaxin) attenuates myocardial infarct size and NLRP3 inflammasome following ischemia/reperfusion injury via eNOS‐dependent mechanism. Cardiovasc Res. 2017;2:1–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

