The Unfolded Protein Response Mediator PERK Governs Myeloid Cell-Driven Immunosuppression in Tumors through Inhibition of STING Signaling
- PMID: 32294407
- PMCID: PMC7207019
- DOI: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.03.004
The Unfolded Protein Response Mediator PERK Governs Myeloid Cell-Driven Immunosuppression in Tumors through Inhibition of STING Signaling
Abstract
The primary mechanisms supporting immunoregulatory polarization of myeloid cells upon infiltration into tumors remain largely unexplored. Elucidation of these signals could enable better strategies to restore protective anti-tumor immunity. Here, we investigated the role of the intrinsic activation of the PKR-like endoplasmic reticulum (ER) kinase (PERK) in the immunoinhibitory actions of tumor-associated myeloid-derived suppressor cells (tumor-MDSCs). PERK signaling increased in tumor-MDSCs, and its deletion transformed MDSCs into myeloid cells that activated CD8+ T cell-mediated immunity against cancer. Tumor-MDSCs lacking PERK exhibited disrupted NRF2-driven antioxidant capacity and impaired mitochondrial respiratory homeostasis. Moreover, reduced NRF2 signaling in PERK-deficient MDSCs elicited cytosolic mitochondrial DNA elevation and, consequently, STING-dependent expression of anti-tumor type I interferon. Reactivation of NRF2 signaling, conditional deletion of STING, or blockade of type I interferon receptor I restored the immunoinhibitory potential of PERK-ablated MDSCs. Our findings demonstrate the pivotal role of PERK in tumor-MDSC functionality and unveil strategies to reprogram immunosuppressive myelopoiesis in tumors to boost cancer immunotherapy.
Keywords: ER stress; MDSCs; NRF2; PERK; STING; tumor immunity; type I IFN; unfolded protein responses.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
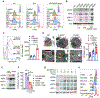
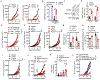
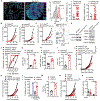
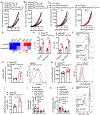
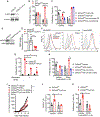
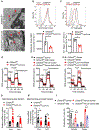
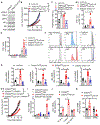
Comment in
-
Reducing Stress PERKs up Anti-tumor Immunity.Immunity. 2020 Apr 14;52(4):575-577. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2020.03.012. Immunity. 2020. PMID: 32294402 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Dual negative roles of C/EBPα in the expansion and pro-tumor functions of MDSCs.Sci Rep. 2017 Oct 25;7(1):14048. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-12968-2. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29070836 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor conditions induce bone marrow expansion of granulocytic, but not monocytic, immunosuppressive leukocytes with increased CXCR2 expression in mice.Eur J Immunol. 2018 Mar;48(3):532-542. doi: 10.1002/eji.201746976. Epub 2017 Dec 8. Eur J Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29120053 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Jagged Immunotherapy Inhibits MDSCs and Overcomes Tumor-Induced Tolerance.Cancer Res. 2017 Oct 15;77(20):5628-5638. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0357. Epub 2017 Sep 13. Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28904063 Free PMC article.
-
Unfolding anti-tumor immunity: ER stress responses sculpt tolerogenic myeloid cells in cancer.J Immunother Cancer. 2017 Jan 17;5:5. doi: 10.1186/s40425-016-0203-4. eCollection 2017. J Immunother Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28105371 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CCR5 in recruitment and activation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in melanoma.Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2017 Aug;66(8):1015-1023. doi: 10.1007/s00262-017-1988-9. Epub 2017 Apr 5. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2017. PMID: 28382399 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging strategies in targeting tumor-resident myeloid cells for cancer immunotherapy.J Hematol Oncol. 2022 Aug 28;15(1):118. doi: 10.1186/s13045-022-01335-y. J Hematol Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36031601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRAPPC1 is essential for the maintenance and differentiation of common myeloid progenitors in mice.EMBO Rep. 2023 Feb 6;24(2):e55503. doi: 10.15252/embr.202255503. Epub 2022 Nov 28. EMBO Rep. 2023. PMID: 36440617 Free PMC article.
-
MDSC: Markers, development, states, and unaddressed complexity.Immunity. 2021 May 11;54(5):875-884. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2021.04.004. Immunity. 2021. PMID: 33979585 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Road of Solid Tumor Survival: From Drug-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress to Drug Resistance.Front Mol Biosci. 2021 Apr 13;8:620514. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.620514. eCollection 2021. Front Mol Biosci. 2021. PMID: 33928116 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer immunotherapy strategies that target the cGAS-STING pathway.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 24;13:996663. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.996663. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36353640 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Atkins C, Liu Q, Minthorn E, Zhang SY, Figueroa DJ, Moss K, Stanley TB, Sanders B, Goetz A, Gaul N, et al. (2013). Characterization of a novel PERK kinase inhibitor with antitumor and antiangiogenic activity. Cancer Res. 73, 1993–2002. - PubMed
-
- Bettigole SE, and Glimcher LH (2015). Endoplasmic reticulum stress in immunity. Annu Rev Immunol 33, 107–138. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

