Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms Responsible for Beneficial Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Product "Exo-d-MAPPS" in Attenuation of Chronic Airway Inflammation
- PMID: 32257769
- PMCID: PMC7109559
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/3153891
Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms Responsible for Beneficial Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Product "Exo-d-MAPPS" in Attenuation of Chronic Airway Inflammation
Abstract
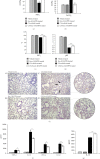
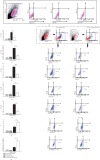
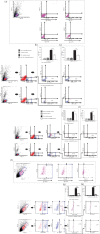
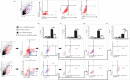
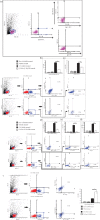
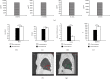
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), due to their potential for differentiation into alveolar epithelial cells and their immunosuppressive characteristics, are considered a new therapeutic agent in cell-based therapy of inflammatory lung disorders, including chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). Since most of the MSC-mediated beneficent effects were the consequence of their paracrine action, herewith, we investigated the effects of a newly designed MSC-derived product "Exosome-derived Multiple Allogeneic Protein Paracrine Signaling (Exo-d-MAPPS)" in the attenuation of chronic airway inflammation by using an animal model of COPD (induced by chronic exposure to cigarette smoke (CS)) and clinical data obtained from Exo-d-MAPPS-treated COPD patients. Exo-d-MAPPS contains a high concentration of immunomodulatory factors which are capable of attenuating chronic airway inflammation, including soluble TNF receptors I and II, IL-1 receptor antagonist, and soluble receptor for advanced glycation end products. Accordingly, Exo-d-MAPPS significantly improved respiratory function, downregulated serum levels of inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-12, and IFN-γ), increased serum concentration of immunosuppressive IL-10, and attenuated chronic airway inflammation in CS-exposed mice. The cellular makeup of the lungs revealed that Exo-d-MAPPS treatment attenuated the production of inflammatory cytokines in lung-infiltrated macrophages, neutrophils, and natural killer and natural killer T cells and alleviated the antigen-presenting properties of lung-infiltrated macrophages and dendritic cells (DCs). Additionally, Exo-d-MAPPS promoted the expansion of immunosuppressive IL-10-producing alternatively activated macrophages, regulatory DCs, and CD4+FoxP3+T regulatory cells in inflamed lungs which resulted in the attenuation of chronic airway inflammation. In a similar manner, as it was observed in an animal model, Exo-d-MAPPS treatment significantly improved the pulmonary status and quality of life of COPD patients. Importantly, Exo-d-MAPPS was well tolerated since none of the 30 COPD patients reported any adverse effects after Exo-d-MAPPS administration. In summing up, we believe that Exo-d-MAPPS could be considered a potentially new therapeutic agent in the treatment of chronic inflammatory lung diseases whose efficacy should be further explored in large clinical trials.
Copyright © 2020 Carl Randall Harrell et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
"Derived Multiple Allogeneic Protein Paracrine Signaling (d-MAPPS)" Enhances T Cell-Driven Immune Response to Murine Mammary Carcinoma.Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2022 Jun 15;2022:3655595. doi: 10.1155/2022/3655595. eCollection 2022. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2022. PMID: 35757015 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes derived from adipose-derived stem cells alleviate cigarette smoke-induced lung inflammation and injury by inhibiting alveolar macrophages pyroptosis.Respir Res. 2022 Jan 11;23(1):5. doi: 10.1186/s12931-022-01926-w. Respir Res. 2022. PMID: 35016678 Free PMC article.
-
Protective role of mesenchymal stem cells and mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes in cigarette smoke-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in mice.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019 Dec 15;385:114788. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2019.114788. Epub 2019 Oct 31. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2019. PMID: 31678243 Free PMC article.
-
The role of Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist in mesenchymal stem cell-based tissue repair and regeneration.Biofactors. 2020 Mar;46(2):263-275. doi: 10.1002/biof.1587. Epub 2019 Nov 22. Biofactors. 2020. PMID: 31755595 Review.
-
Therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes for allergic airway inflammation.Cell Immunol. 2024 Mar-Apr;397-398:104813. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2024.104813. Epub 2024 Feb 15. Cell Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38364454 Review.
Cited by
-
Promising Therapeutic Functions of Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived-Exosome in Asthma.Can Respir J. 2022 Dec 20;2022:1485719. doi: 10.1155/2022/1485719. eCollection 2022. Can Respir J. 2022. PMID: 36582191 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Potential of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in Bone Regeneration.J Clin Med. 2023 Jun 29;12(13):4385. doi: 10.3390/jcm12134385. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 37445420 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intestine epithelial cell-derived extracellular vesicles alleviate inflammation induced by Clostridioides difficile TcdB through the activity of TGF-β1.Mol Cell Toxicol. 2022 Jul 30:1-11. doi: 10.1007/s13273-022-00280-8. Online ahead of print. Mol Cell Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35967466 Free PMC article.
-
Prospect of Mesenchymal Stem-Cell-Conditioned Medium in the Treatment of Acute Pancreatitis: A Systematic Review.Biomedicines. 2023 Aug 23;11(9):2343. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11092343. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37760784 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of mesenchymal stem cells in attenuating inflammatory bowel disease through ubiquitination.Front Immunol. 2024 Aug 9;15:1423069. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1423069. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39185411 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Pauwels R. A., Buist A. S., Calverley P. M. A., Jenkins C. R., Hurd S. S., behalf of the GOLD Scientific Committee Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: NHLBI/WHO Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) workshop summary. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2001;163(5):1256–1276. doi: 10.1164/ajrccm.163.5.2101039. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

