T cell Metabolism in Lupus
- PMID: 32257420
- PMCID: PMC7111512
- DOI: 10.20900/immunometab20200009
T cell Metabolism in Lupus
Abstract
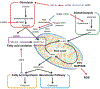
Abnormal T cell responses are central to the development of autoimmunity and organ damage in systemic lupus erythematosus. Following stimulation, naïve T cells undergo rapid proliferation, differentiation and cytokine production. Since the initial report, approximately two decades ago, that engagement of CD28 enhances glycolysis but PD-1 and CTLA-4 decrease it, significant information has been generated which has linked metabolic reprogramming with the fate of differentiating T cell in health and autoimmunity. Herein we summarize how defects in mitochondrial dysfunction, oxidative stress, glycolysis, glutaminolysis and lipid metabolism contribute to pro-inflammatory T cell responses in systemic lupus erythematosus and discuss how metabolic defects can be exploited therapeutically.
Keywords: SLE; T cell metabolism; fatty acid oxidation; glutaminolysis; glycolysis.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Amino Acid Metabolism in Lupus.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 22;12:623844. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.623844. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33692797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
T cell metabolism and possible therapeutic targets in systemic lupus erythematosus: a narrative review.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2022 Aug;44(4):457-470. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2022.2055568. Epub 2022 Mar 30. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2022. PMID: 35352607 Review.
-
[The metabolic regulation in immune cells and pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus ∼toward new therapeutic applications∼].Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2017;40(1):12-20. doi: 10.2177/jsci.40.12. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi. 2017. PMID: 28539549 Review. Japanese.
-
BAFF-R and TACI expression on CD3+ T cells: Interplay among BAFF, APRIL and T helper cytokines profile in systemic lupus erythematosus.Cytokine. 2019 Feb;114:115-127. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2018.11.008. Epub 2018 Nov 19. Cytokine. 2019. PMID: 30467093
-
Metabolism as a key regulator in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus.Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019 Jun;48(6):1142-1145. doi: 10.1016/j.semarthrit.2019.04.006. Epub 2019 Apr 25. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019. PMID: 31056210 Review.
Cited by
-
T Cells in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus.Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2021 Aug;47(3):379-393. doi: 10.1016/j.rdc.2021.04.005. Epub 2021 Jun 16. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2021. PMID: 34215369 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunometabolism at the cornerstone of inflammaging, immunosenescence, and autoimmunity in COVID-19.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Dec 27;12(24):26263-26278. doi: 10.18632/aging.202422. Epub 2020 Dec 27. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 33361522 Free PMC article.
-
Amino Acid Metabolism in Lupus.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 22;12:623844. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.623844. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33692797 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maladaptive T-Cell Metabolic Fitness in Autoimmune Diseases.Cells. 2023 Oct 29;12(21):2541. doi: 10.3390/cells12212541. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37947619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mitochondrial reactive oxygen is critical for IL-12/IL-18-induced IFN-γ production by CD4+ T cells and is regulated by Fas/FasL signaling.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Jun 6;13(6):531. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-04907-5. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 35668079 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Saegusa J, Irino Y, Yoshida M, Tanaka S, Kogata Y, Kageyama G, et al. GC/MS-based metabolomics detects metabolic alterations in serum from SLE patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2014;32(1):148. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
