Small heat-shock proteins and their role in mechanical stress
- PMID: 32253742
- PMCID: PMC7332611
- DOI: 10.1007/s12192-020-01095-z
Small heat-shock proteins and their role in mechanical stress
Abstract
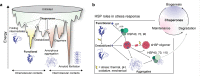
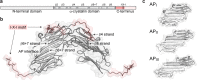
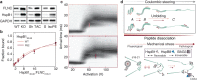
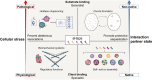
The ability of cells to respond to stress is central to health. Stress can damage folded proteins, which are vulnerable to even minor changes in cellular conditions. To maintain proteostasis, cells have developed an intricate network in which molecular chaperones are key players. The small heat-shock proteins (sHSPs) are a widespread family of molecular chaperones, and some sHSPs are prominent in muscle, where cells and proteins must withstand high levels of applied force. sHSPs have long been thought to act as general interceptors of protein aggregation. However, evidence is accumulating that points to a more specific role for sHSPs in protecting proteins from mechanical stress. Here, we briefly introduce the sHSPs and outline the evidence for their role in responses to mechanical stress. We suggest that sHSPs interact with mechanosensitive proteins to regulate physiological extension and contraction cycles. It is likely that further study of these interactions - enabled by the development of experimental methodologies that allow protein contacts to be studied under the application of mechanical force - will expand our understanding of the activity and functions of sHSPs, and of the roles played by chaperones in general.
Keywords: Cardiomyocytes; FLNC; Filamin C; HspB8; Mechanical stress; Mechanosensing; Molecular chaperones; Monodispersity; Muscle; Polydispersity; Proteostasis; Small heat-shock proteins; sHSPs.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Studying heat shock proteins through single-molecule mechanical manipulation.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2020 Jul;25(4):615-628. doi: 10.1007/s12192-020-01096-y. Epub 2020 Apr 6. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2020. PMID: 32253740 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The function of small heat-shock proteins and their implication in proteostasis.Essays Biochem. 2016 Oct 15;60(2):163-172. doi: 10.1042/EBC20160010. Essays Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27744332 Review.
-
The Diverse Functions of Small Heat Shock Proteins in the Proteostasis Network.J Mol Biol. 2022 Jan 15;434(1):167157. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167157. Epub 2021 Jul 14. J Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34271010 Review.
-
Duplicate divergence of two bacterial small heat shock proteins reduces the demand for Hsp70 in refolding of substrates.PLoS Genet. 2019 Oct 25;15(10):e1008479. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1008479. eCollection 2019 Oct. PLoS Genet. 2019. PMID: 31652260 Free PMC article.
-
Medical implications of understanding the functions of human small heat shock proteins.Expert Rev Proteomics. 2015 Jun;12(3):295-308. doi: 10.1586/14789450.2015.1039993. Epub 2015 Apr 27. Expert Rev Proteomics. 2015. PMID: 25915440 Review.
Cited by
-
The role of heat shock proteins in the pathogenesis of heart failure (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2023 Nov;52(5):106. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2023.5309. Epub 2023 Sep 29. Int J Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37772383 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Shear Stress Modulates Osteoblast Cell and Nucleus Morphology and Volume.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 7;21(21):8361. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218361. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33171812 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic response differences between 2D and 3D tumor models of magnetic hyperthermia.Nanoscale Adv. 2021 May 5;3(13):3663-3680. doi: 10.1039/d1na00224d. eCollection 2021 Jun 30. Nanoscale Adv. 2021. PMID: 36133021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Homozygous expression of the myofibrillar myopathy-associated p.W2710X filamin C variant reveals major pathomechanisms of sarcomeric lesion formation.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2020 Sep 4;8(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s40478-020-01001-9. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2020. PMID: 32887649 Free PMC article.
-
Function and Fiber-Type Specific Distribution of Hsp60 and αB-Crystallin in Skeletal Muscles: Role of Physical Exercise.Biology (Basel). 2021 Jan 21;10(2):77. doi: 10.3390/biology10020077. Biology (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33494467 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

