Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Cancer: Breakthrough and Challenges of Targeted Therapy
- PMID: 32244867
- PMCID: PMC7140093
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12030731
Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in Cancer: Breakthrough and Challenges of Targeted Therapy
Abstract
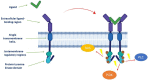
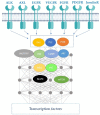
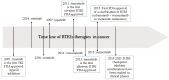
Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are key regulatory signaling proteins governing cancer cell growth and metastasis. During the last two decades, several molecules targeting RTKs were used in oncology as a first or second line therapy in different types of cancer. However, their effectiveness is limited by the appearance of resistance or adverse effects. In this review, we summarize the main features of RTKs and their inhibitors (RTKIs), their current use in oncology, and mechanisms of resistance. We also describe the technological advances of artificial intelligence, chemoproteomics, and microfluidics in elaborating powerful strategies that could be used in providing more efficient and selective small molecules inhibitors of RTKs. Finally, we discuss the interest of therapeutic combination of different RTKIs or with other molecules for personalized treatments, and the challenge for effective combination with less toxic and off-target effects.
Keywords: cancer; oncology; pharmacology; tyrosine kinase inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cyclooxygenase inhibitors potentiate receptor tyrosine kinase therapies in bladder cancer cells in vitro.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018 Jun 13;12:1727-1742. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S158518. eCollection 2018. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2018. PMID: 29942116 Free PMC article.
-
Activation and function of receptor tyrosine kinases in human clear cell renal cell carcinomas.BMC Cancer. 2019 Nov 5;19(1):1044. doi: 10.1186/s12885-019-6159-2. BMC Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31690270 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular toxicity of tyrosine kinase inhibitors during cancer treatment: Potential involvement of TRPM7.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Feb 3;10:1002438. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2023.1002438. eCollection 2023. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 36818331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Phosphorylation Pattern-Based Multidrug Combination Is an Effective Approach for Personalized Cancer Treatment.Mol Cancer Ther. 2016 Oct;15(10):2508-2520. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-15-0735. Epub 2016 Jul 25. Mol Cancer Ther. 2016. PMID: 27458140
-
Receptor tyrosine kinases and cancer: oncogenic mechanisms and therapeutic approaches.Oncogene. 2021 Jun;40(24):4079-4093. doi: 10.1038/s41388-021-01841-2. Epub 2021 Jun 2. Oncogene. 2021. PMID: 34079087 Review.
Cited by
-
Cancer Bioenergetics and Tumor Microenvironments-Enhancing Chemotherapeutics and Targeting Resistant Niches through Nanosystems.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jul 28;15(15):3836. doi: 10.3390/cancers15153836. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37568652 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decoding Oncofusions: Unveiling Mechanisms, Clinical Impact, and Prospects for Personalized Cancer Therapies.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jul 19;15(14):3678. doi: 10.3390/cancers15143678. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37509339 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Editorial: Insight in cancer genetics: 2022.Front Oncol. 2022 Jul 26;12:988310. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.988310. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35957906 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Polydatin Reduces Cardiotoxicity and Enhances the Anticancer Effects of Sunitinib by Decreasing Pro-Oxidative Stress, Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines, and NLRP3 Inflammasome Expression.Front Oncol. 2021 Jun 11;11:680758. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.680758. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34178667 Free PMC article.
-
Amuvatinib Blocks SARS-CoV-2 Infection at the Entry Step of the Viral Life Cycle.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Jun 15;11(3):e0510522. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.05105-22. Epub 2023 Mar 30. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36995225 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

