Role of Connexins 30, 36, and 43 in Brain Tumors, Neurodegenerative Diseases, and Neuroprotection
- PMID: 32244528
- PMCID: PMC7226843
- DOI: 10.3390/cells9040846
Role of Connexins 30, 36, and 43 in Brain Tumors, Neurodegenerative Diseases, and Neuroprotection
Abstract
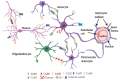
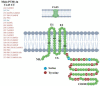
Gap junction (GJ) channels and their connexins (Cxs) are complex proteins that have essential functions in cell communication processes in the central nervous system (CNS). Neurons, astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, and microglial cells express an extraordinary repertory of Cxs that are important for cell to cell communication and diffusion of metabolites, ions, neurotransmitters, and gliotransmitters. GJs and Cxs not only contribute to the normal function of the CNS but also the pathological progress of several diseases, such as cancer and neurodegenerative diseases. Besides, they have important roles in mediating neuroprotection by internal or external molecules. However, regulation of Cx expression by epigenetic mechanisms has not been fully elucidated. In this review, we provide an overview of the known mechanisms that regulate the expression of the most abundant Cxs in the central nervous system, Cx30, Cx36, and Cx43, and their role in brain cancer, CNS disorders, and neuroprotection. Initially, we focus on describing the Cx gene structure and how this is regulated by epigenetic mechanisms. Then, the posttranslational modifications that mediate the activity and stability of Cxs are reviewed. Finally, the role of GJs and Cxs in glioblastoma, Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and Huntington's diseases, and neuroprotection are analyzed with the aim of shedding light in the possibility of using Cx regulators as potential therapeutic molecules.
Keywords: astrocytes; connexins; epigenetics; gap junctions; microglia; neurodegenerative diseases; neurons; neuroprotection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The roles of connexins and gap junctions in the progression of cancer.Cell Commun Signal. 2023 Jan 13;21(1):8. doi: 10.1186/s12964-022-01009-9. Cell Commun Signal. 2023. PMID: 36639804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Connexin 43/47 channels are important for astrocyte/ oligodendrocyte cross-talk in myelination and demyelination.J Biosci. 2018 Dec;43(5):1055-1068. doi: 10.1007/s12038-018-9811-0. J Biosci. 2018. PMID: 30541963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functional Roles of Connexins and Gap Junctions in Osteo-Chondral Cellular Components.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 19;24(4):4156. doi: 10.3390/ijms24044156. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835567 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Connexins-mediated glia networking impacts myelination and remyelination in the central nervous system.Mol Neurobiol. 2014 Jun;49(3):1460-71. doi: 10.1007/s12035-013-8625-1. Epub 2014 Jan 7. Mol Neurobiol. 2014. PMID: 24395132 Review.
-
Functional analysis of hemichannels and gap-junctional channels formed by connexins 43 and 46.Mol Vis. 2010 Jul 15;16:1343-52. Mol Vis. 2010. PMID: 20664797 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
DNA methylation of imprint control regions associated with Alzheimer's disease in non-Hispanic Blacks and non-Hispanic Whites.Clin Epigenetics. 2024 Apr 25;16(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s13148-024-01672-4. Clin Epigenetics. 2024. PMID: 38658973 Free PMC article.
-
Fascin-1 limits myosin activity in microglia to control mechanical characterization of the injured spinal cord.J Neuroinflammation. 2024 Apr 10;21(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s12974-024-03089-5. J Neuroinflammation. 2024. PMID: 38600569 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of astroglial hemichannels ameliorates infrasonic noise induced short-term learning and memory impairment.Behav Brain Funct. 2023 Dec 18;19(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s12993-023-00226-7. Behav Brain Funct. 2023. PMID: 38110991 Free PMC article.
-
The Key Role of Astrocytes in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Their Commitment to Glutamate Excitotoxicity.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 21;24(20):15430. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015430. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37895110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotection of Retinal Ganglion Cells Suppresses Microglia Activation in a Mouse Model of Glaucoma.Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023 Jun 1;64(7):24. doi: 10.1167/iovs.64.7.24. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2023. PMID: 37318444 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

