MiRNA profiles in blood plasma from mother-child duos in human biobanks and the implication of sample quality: Circulating miRNAs as potential early markers of child health
- PMID: 32240265
- PMCID: PMC7117735
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0231040
MiRNA profiles in blood plasma from mother-child duos in human biobanks and the implication of sample quality: Circulating miRNAs as potential early markers of child health
Abstract
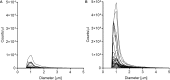
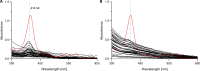
Background: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been linked to several diseases and to regulation of almost every biological process. This together with their stability while freely circulating in blood suggests that they could serve as minimal-invasive biomarkers for a wide range of diseases. Successful miRNA-based biomarker discovery in plasma is dependent on controlling sources of preanalytical variation, such as cellular contamination and hemolysis, as they can be major causes of altered miRNA expression levels. Analysis of plasma quality is therefore a crucial step for the best output when searching for novel miRNA biomarkers.
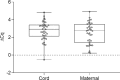
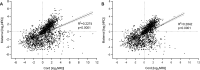
Methods: Plasma quality was assessed by three different methods in samples from mother-child duos (maternal and cord blood, N = 2x38), with collection and storage methods comparable to large cohort study biobanks. Total RNA was isolated and the expression profiles of 201 miRNAs was obtained by qPCR to identify differentially expressed miRNAs in cord and maternal plasma samples.
Results: All three methods for quality assurance indicate that the plasma samples used in this study are of high quality with very low levels of contamination, suitable for analysis of circulating miRNAs. We identified 19 significantly differentially expressed miRNAs between cord and maternal plasma samples (paired t-tests, FDR<0.05, and fold change>±1.5), and we observed low correlation of miRNA transcript levels between cord and maternal samples throughout our dataset.
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that good quality plasma samples suitable for miRNA profiling can be achieved from samples collected and stored by large biobanks. Incorporation of extensive quality control measures, such as those established here, would be beneficial for future projects. The overall low correlation of miRNA expression between cord and maternal samples is an interesting observation, and promising for our future studies on identification of miRNA-based biomarkers in cord blood plasma, considering that these samples were collected at term and some exchange of blood components between cord and maternal blood frequently occur.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Impact of long-term storage and freeze-thawing on eight circulating microRNAs in plasma samples.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 14;15(1):e0227648. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227648. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31935258 Free PMC article.
-
Study of the preanalytical variables affecting the measurement of clinically relevant free-circulating microRNAs: focus on sample matrix, platelet depletion, and storage conditions.Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2020 Feb 15;30(1):010703. doi: 10.11613/BM.2020.010703. Epub 2019 Dec 15. Biochem Med (Zagreb). 2020. PMID: 31839723 Free PMC article.
-
"Future-Proofing" Blood Processing for Measurement of Circulating miRNAs in Samples from Biobanks and Prospective Clinical Trials.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2018 Feb;27(2):208-218. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-17-0657. Epub 2017 Dec 18. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2018. PMID: 29254935 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic review investigating the association of microRNAs with human abdominal aortic aneurysms.Atherosclerosis. 2017 Jun;261:78-89. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2017.03.010. Epub 2017 Mar 8. Atherosclerosis. 2017. PMID: 28347473 Review.
-
Circulating microRNAs as novel biomarkers for bone diseases - Complex signatures for multifactorial diseases?Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2016 Sep 5;432:83-95. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2015.10.015. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2016. PMID: 26525415 Review.
Cited by
-
Expressions of mitochondria-related genes in pregnant women with subclinical hypothyroidism, and expressions of miRNAs in maternal and cord blood.Thyroid Res. 2023 Sep 18;16(1):38. doi: 10.1186/s13044-023-00180-6. Thyroid Res. 2023. PMID: 37723507 Free PMC article.
-
Blood miRNA levels associated with ADHD traits in children across six European birth cohorts.BMC Psychiatry. 2023 Sep 25;23(1):696. doi: 10.1186/s12888-023-05199-5. BMC Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37749515 Free PMC article.
-
Differentially Expressed Extracellular Vesicle, Exosome and Non-Exosome miRNA Profile in High and Low Tick-Resistant Beef Cattle.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021 Dec 17;11:780424. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2021.780424. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34976862 Free PMC article.
-
Improving the Diagnostic Potential of Extracellular miRNAs Coupled to Multiomics Data by Exploiting the Power of Artificial Intelligence.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jun 9;13:888414. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.888414. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35756065 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

