Non-photopic and photopic visual cycles differentially regulate immediate, early, and late phases of cone photoreceptor-mediated vision
- PMID: 32238432
- PMCID: PMC7212626
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.011374
Non-photopic and photopic visual cycles differentially regulate immediate, early, and late phases of cone photoreceptor-mediated vision
Abstract
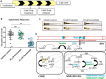
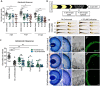
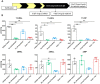
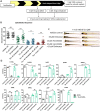
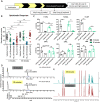
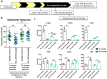
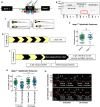
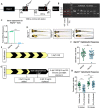
Cone photoreceptors in the retina enable vision over a wide range of light intensities. However, the processes enabling cone vision in bright light (i.e. photopic vision) are not adequately understood. Chromophore regeneration of cone photopigments may require the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) and/or retinal Müller glia. In the RPE, isomerization of all-trans-retinyl esters to 11-cis-retinol is mediated by the retinoid isomerohydrolase Rpe65. A putative alternative retinoid isomerase, dihydroceramide desaturase-1 (DES1), is expressed in RPE and Müller cells. The retinol-isomerase activities of Rpe65 and Des1 are inhibited by emixustat and fenretinide, respectively. Here, we tested the effects of these visual cycle inhibitors on immediate, early, and late phases of cone photopic vision. In zebrafish larvae raised under cyclic light conditions, fenretinide impaired late cone photopic vision, while the emixustat-treated zebrafish unexpectedly had normal vision. In contrast, emixustat-treated larvae raised under extensive dark-adaptation displayed significantly attenuated immediate photopic vision concomitant with significantly reduced 11-cis-retinaldehyde (11cRAL). Following 30 min of light, early photopic vision was recovered, despite 11cRAL levels remaining significantly reduced. Defects in immediate cone photopic vision were rescued in emixustat- or fenretinide-treated larvae following exogenous 9-cis-retinaldehyde supplementation. Genetic knockout of Des1 (degs1) or retinaldehyde-binding protein 1b (rlbp1b) did not eliminate photopic vision in zebrafish. Our findings define molecular and temporal requirements of the nonphotopic or photopic visual cycles for mediating vision in bright light.
Keywords: Rpe65; chemical biology; cone-based visual behavior; pharmacology; retina; vision; visual cycle; vitamin A; zebrafish.
© 2020 Ward et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
Similar articles
-
cis Retinol oxidation regulates photoreceptor access to the retina visual cycle and cone pigment regeneration.J Physiol. 2016 Nov 15;594(22):6753-6765. doi: 10.1113/JP272831. Epub 2016 Aug 2. J Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27385534 Free PMC article.
-
An alternative isomerohydrolase in the retinal Müller cells of a cone-dominant species.FEBS J. 2011 Aug;278(16):2913-26. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-4658.2011.08216.x. Epub 2011 Jul 1. FEBS J. 2011. PMID: 21676174 Free PMC article.
-
Conditional deletion of Des1 in the mouse retina does not impair the visual cycle in cones.FASEB J. 2019 Apr;33(4):5782-5792. doi: 10.1096/fj.201802493R. Epub 2019 Jan 15. FASEB J. 2019. PMID: 30645148 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin A and Vision.Subcell Biochem. 2016;81:231-259. doi: 10.1007/978-94-024-0945-1_9. Subcell Biochem. 2016. PMID: 27830507 Review.
-
Vitamin A metabolism in rod and cone visual cycles.Annu Rev Nutr. 2012 Aug 21;32:125-45. doi: 10.1146/annurev-nutr-071811-150748. Annu Rev Nutr. 2012. PMID: 22809103 Review.
Cited by
-
Shedding new light on the generation of the visual chromophore.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020 Aug 18;117(33):19629-19638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2008211117. Epub 2020 Aug 5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2020. PMID: 32759209 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolutionary Constraint on Visual and Nonvisual Mammalian Opsins.J Biol Rhythms. 2021 Apr;36(2):109-126. doi: 10.1177/0748730421999870. Epub 2021 Mar 25. J Biol Rhythms. 2021. PMID: 33765865 Free PMC article.
-
Retinoids in the visual cycle: role of the retinal G protein-coupled receptor.J Lipid Res. 2021;62:100040. doi: 10.1194/jlr.TR120000850. Epub 2021 Feb 6. J Lipid Res. 2021. PMID: 32493732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disturbed retinoid metabolism upon loss of rlbp1a impairs cone function and leads to subretinal lipid deposits and photoreceptor degeneration in the zebrafish retina.Elife. 2021 Oct 20;10:e71473. doi: 10.7554/eLife.71473. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34668483 Free PMC article.
-
Pathways and disease-causing alterations in visual chromophore production for vertebrate vision.J Biol Chem. 2021 Jan-Jun;296:100072. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.014405. Epub 2020 Nov 23. J Biol Chem. 2021. PMID: 33187985 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Saari J. C. (2016) Vitamin A and Vision. In The Biochemistry of Retinoid Signaling II: Subcellular Biochemistry (Asson-Batres M. and Rochette-Egly C. eds), vol 81, pp. 231–259, Springer, Dordrecht
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

