A randomized proof-of-mechanism trial applying the 'fast-fail' approach to evaluating κ-opioid antagonism as a treatment for anhedonia
- PMID: 32231295
- PMCID: PMC9949770
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-020-0806-7
A randomized proof-of-mechanism trial applying the 'fast-fail' approach to evaluating κ-opioid antagonism as a treatment for anhedonia
Abstract
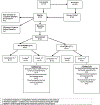
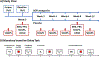
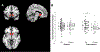
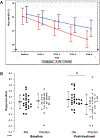
The National Institute of Mental Health (NIMH) 'fast-fail' approach seeks to improve too-often-misleading early-phase drug development methods by incorporating biomarker-based proof-of-mechanism (POM) testing in phase 2a. This first comprehensive application of the fast-fail approach evaluated the potential of κ-opioid receptor (KOR) antagonism for treating anhedonia with a POM study determining whether robust target engagement favorably impacts the brain circuitry hypothesized to mediate clinical effects. Here we report the results from a multicenter, 8-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial in patients with anhedonia and a mood or anxiety disorder (selective KOR antagonist (JNJ-67953964, 10 mg; n = 45) and placebo (n = 44)). JNJ-67953964 significantly increased functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) ventral striatum activation during reward anticipation (primary outcome) as compared to placebo (baseline-adjusted mean: JNJ-67953964, 0.72 (s.d. = 0.67); placebo, 0.33 (s.d. = 0.68); F(1,86) = 5.58, P < 0.01; effect size = 0.58 (95% confidence interval, 0.13-0.99)). JNJ-67953964, generally well tolerated, was not associated with any serious adverse events. This study supports proceeding with assessment of the clinical impact of target engagement and serves as a model for implementing the 'fast-fail' approach.
Figures
Comment in
-
A precision medicine-based, 'fast-fail' approach for psychiatry.Nat Med. 2020 May;26(5):653-654. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-0854-z. Nat Med. 2020. PMID: 32405056 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Selective kappa-opioid antagonism ameliorates anhedonic behavior: evidence from the Fast-fail Trial in Mood and Anxiety Spectrum Disorders (FAST-MAS).Neuropsychopharmacology. 2020 Sep;45(10):1656-1663. doi: 10.1038/s41386-020-0738-4. Epub 2020 Jun 16. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2020. PMID: 32544925 Free PMC article.
-
Double-blind, placebo-controlled, proof-of-concept trial of a kappa-selective opioid receptor antagonist augmentation in treatment-resistant depression.Ann Clin Psychiatry. 2020 Feb;32(4):18-26. doi: 10.12788/acp.0003. Ann Clin Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 33125454
-
The kappa opioid receptor antagonist aticaprant reverses behavioral effects from unpredictable chronic mild stress in male mice.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2020 Dec;237(12):3715-3728. doi: 10.1007/s00213-020-05649-y. Epub 2020 Sep 7. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2020. PMID: 32894343 Free PMC article.
-
Aticaprant, a kappa opioid receptor antagonist, and the recovered 'interest and pleasure' in the concept of major depressive disorder.Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024 Jul 6. doi: 10.1007/s00406-024-01851-7. Online ahead of print. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38969753 Review.
-
Preclinical and clinical efficacy of kappa opioid receptor antagonists for depression: A systematic review.J Affect Disord. 2024 Oct 1;362:816-827. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2024.07.030. Epub 2024 Jul 15. J Affect Disord. 2024. PMID: 39019223 Review.
Cited by
-
Drug targeting in psychiatric disorders - how to overcome the loss in translation?Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024 Mar;23(3):218-231. doi: 10.1038/s41573-023-00847-7. Epub 2023 Dec 19. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2024. PMID: 38114612 Review.
-
Mediation of the behavioral effects of ketamine and (2R,6R)-hydroxynorketamine in mice by kappa opioid receptors.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022 Jul;239(7):2309-2316. doi: 10.1007/s00213-022-06118-4. Epub 2022 Apr 23. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2022. PMID: 35459958
-
Probabilistic Reinforcement Learning and Anhedonia.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2022;58:355-377. doi: 10.1007/7854_2022_349. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35435644 Free PMC article.
-
Psychological Treatments for Anhedonia.Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2022;58:491-513. doi: 10.1007/7854_2021_291. Curr Top Behav Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 34935116 Review.
-
Peptide Kappa Opioid Receptor Ligands and Their Potential for Drug Development.Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2022;271:197-220. doi: 10.1007/164_2021_519. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 34463847 Review.
References
-
- Denys D, de Geus F. Predictors of pharmacotherapy response in anxiety disorders. Curr Psychiatry Rep 7(4), 252–7 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Rush AJ, Trivedi MH, Wisniewski SR, Nierenberg AA, Stewart JW, Warden D, Niederehe G, Thase ME, Lavori PW, Lebowitz BD, McGrath PJ, Rosenbaum JF, Sackeim HA, Kupfer DJ, Luther J, Fava M. Acute and longer-term outcomes in depressed outpatients requiring one or several treatment steps: a STAR*D report. Am J Psychiatry 163(11),1905–17 (2006). - PubMed
-
- Insel TR, Wang PS. The STAR*D trial: revealing the need for better treatments. Psychiatr Serv 60(11), 1466–7 (2009) - PubMed
-
- National Advisory Mental Health Workgroup. From Discovery to Cure: Accelerating the Development of New and Personalized Interventions for Mental Illness Washington, DC: NIMH. (2010).
-
- Paul SM, Mytelka DS, Dunwiddie CT, et al. How to improve R&D productivity: the pharmaceutical industry’s grand challenge. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9(3), 203–214 (2010). - PubMed
METHODS ONLY REFERENCES
-
- American Psychiatric Association (2000). Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (4th ed., Text Revision). Washington, DC. (2009).
-
- Sheehan DV, Lecrubier Y, Sheehan KH, Amorim P, Janavs J, Weiller E, Hergueta T, Baer R, Dunbar GC. The Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (M.I.N.I.): the development and validation of a structured diagnostic psychiatric interview for DSM-IV and ICD-10. J Clin Psychiatry 59 Suppl 20, 22–33 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Posner K Columbia-Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS) http://www.cssrs.columbia.edu (2011).
-
- Jenkinson M, Bannister P, Brady M, Smith S. Improved optimization for the robust and accurate linear registration and motion correction of brain images. Neuroimage 17(2), 825–41 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Jenkinson M, Smith S. A global optimisation method for robust affine registration of brain images. Med Image Anal 5(2), 143–56 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

