Changes in the gene mutation profiles of circulating tumor DNA detected using CAPP-Seq in neoadjuvant chemotherapy-treated advanced ovarian cancer
- PMID: 32218822
- PMCID: PMC7068231
- DOI: 10.3892/ol.2020.11356
Changes in the gene mutation profiles of circulating tumor DNA detected using CAPP-Seq in neoadjuvant chemotherapy-treated advanced ovarian cancer
Abstract
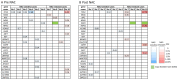
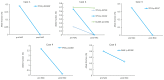
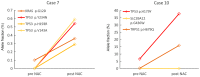
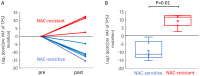
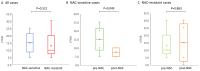
Cancer Personalized Profiling by deep Sequencing (CAPP-Seq) is a novel ultrasensitive next-generation sequencing-based approach that is used to detect circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA). The aim of the present study was to compare the gene mutation profiles and blood tumor mutation burden (bTMB) measured between pre- and post-neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC), utilizing CAPP-seq for plasma ctDNA in patients with advanced ovarian cancer. The current study included 10 patients (6 NAC-sensitive and 4 NAC-resistant) clinically diagnosed as having stage III or IV ovarian cancer and were administered NAC between May 2017 and February 2019. The plasma ctDNA samples were collected at pre- and post-NAC, and comprehensive gene mutation analysis was performed using CAPP-seq. In 5 out of 6 NAC-sensitive cases, the variant allele frequency (VAF) of non-synonymous somatic mutations decreased following NAC. In 2 out of the 4 NAC-resistant cases, the VAF of non-synonymous somatic mutations increased, and new somatic mutations emerged following NAC. In regard to TP53 mutation, the rate of TP53 mutation in the NAC-resistant cases was significantly higher compared with NAC-sensitive cases. Finally, the bTMB decreased significantly after NAC treatment in the NAC-sensitive cases, even though there were no significant differences in the pretreatment bTMB levels between the NAC-sensitive and NAC-resistant cases. These results indicated that gene mutation can be profiled and monitored using liquid biopsy-based CAPP-Seq in patients with advanced ovarian cancer with NAC treatment, and TP53 mutation in the ctDNA and bTMB may be novel biomarkers that can be used for patient monitoring during NAC treatment.
Keywords: CAncer Personalized Profiling by deep sequencing; circulating tumor DNA; liquid biopsy; neoadjuvant chemotherapy; ovarian cancer.
Copyright: © Noguchi et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Liquid biopsy-based comprehensive gene mutation profiling for gynecological cancer using CAncer Personalized Profiling by deep Sequencing.Sci Rep. 2019 Jul 18;9(1):10426. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-47030-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 31320709 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive gene mutation analysis of liquid biopsy samples from patients with metastatic colorectal cancer to the ovary: A case report.Oncol Lett. 2018 Nov;16(5):6431-6436. doi: 10.3892/ol.2018.9467. Epub 2018 Sep 20. Oncol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30405780 Free PMC article.
-
[Analysis of the feasibility and prognostic value of circulating tumor DNA in detecting gene mutations in small cell lung cancer].Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020 Dec 8;100(45):3614-3621. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112137-20200504-01412. Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 33333686 Chinese.
-
Potential clinical utility of ultrasensitive circulating tumor DNA detection with CAPP-Seq.Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2015 Jun;15(6):715-9. doi: 10.1586/14737159.2015.1019476. Epub 2015 Mar 16. Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2015. PMID: 25773944 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Using the neoadjuvant chemotherapy paradigm to develop precision therapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer.Urol Oncol. 2016 Oct;34(10):469-76. doi: 10.1016/j.urolonc.2016.05.012. Epub 2016 Jun 15. Urol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27317490 Review.
Cited by
-
Recent Advances in Integrative Multi-Omics Research in Breast and Ovarian Cancer.J Pers Med. 2021 Feb 19;11(2):149. doi: 10.3390/jpm11020149. J Pers Med. 2021. PMID: 33669749 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Copy Number Variation of Circulating Tumor DNA (ctDNA) Detected Using NIPT in Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy-Treated Ovarian Cancer Patients.Front Genet. 2022 Jul 22;13:938985. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.938985. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35938032 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation analysis of circulating tumor DNA and paired ascites and tumor tissues in ovarian cancer.Exp Ther Med. 2022 Jun 30;24(3):542. doi: 10.3892/etm.2022.11479. eCollection 2022 Sep. Exp Ther Med. 2022. PMID: 35978934 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Tumor DNA Is a Variant of Liquid Biopsy with Predictive and Prognostic Clinical Value in Breast Cancer Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Dec 2;24(23):17073. doi: 10.3390/ijms242317073. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38069396 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome Sequencing and Apoptotic Markers to Assess Treatment Response of Lacrimal Gland Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma to Intra-Arterial Cytoreductive Chemotherapy.Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2022 Mar-Apr 01;38(2):e44-e47. doi: 10.1097/IOP.0000000000002079. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2022. PMID: 34798653 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chi DS, Eisenhauer EL, Zivanovic O, Sonoda Y, Abu-Rustum NR, Levine DA, Guile MW, Bristow RE, Aghajanian C, Barakat RR. Improved progression-free and overall survival in advanced ovarian cancer as a result of a change in surgical paradigm. Gynecol Oncol. 2009;114:26–31. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2009.03.018. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fagotti A, Ferrandina G, Vizzielli G, Fanfani F, Gallotta V, Chiantera V, Costantini B, Margariti PA, Gueli Alletti S, Cosentino F, et al. Phase III randomised clinical trial comparing primary surgery versus neoadjuvant chemotherapy in advanced epithelial ovarian cancer with high tumour load (SCORPION trial): Final analysis of peri-operative outcome. Eur J Cancer. 2016;59:22–33. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2016.01.017. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kehoe S, Hook J, Nankivell M, Jayson GC, Kitchener H, Lopes T, Luesley D, Perren T, Bannoo S, Mascarenhas M, et al. Primary chemotherapy versus primary surgery for newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer (CHORUS): An open-label, randomised, controlled, non-inferiority trial. Lancet. 2015;386:249–257. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)62223-6. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
