Alpha-Lipoic Acid Ameliorates Radiation-Induced Salivary Gland Injury by Preserving Parasympathetic Innervation in Rats
- PMID: 32218158
- PMCID: PMC7178006
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21072260
Alpha-Lipoic Acid Ameliorates Radiation-Induced Salivary Gland Injury by Preserving Parasympathetic Innervation in Rats
Abstract
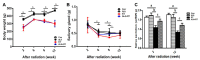
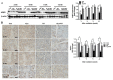
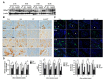
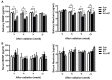
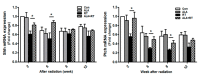
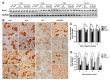
Radiation therapy is a standard treatment for patients with head and neck cancer. However, radiation exposure to the head and neck induces salivary gland (SG) dysfunction. Alpha lipoic acid (ALA) has been reported to reduce radiation-induced toxicity in normal tissues. In this study, we investigated the effect of ALA on radiation-induced SG dysfunction. Male Sprague-Dawley rats were assigned to the following treatment groups: control, ALA only (100 mg/kg, intraperitoneally), irradiation only, and ALA administration 24 h or 30 min prior to irradiation. The neck area, including SGs, was irradiated evenly at 2 Gy/min (total dose, 18 Gy) using a photon 6 MV linear accelerator. The rats were sacrificed at 2, 6, 8, and 12 weeks after irradiation. Radiation decreased SG weight, saliva secretion, AQP5 expression, parasympathetic innervation (GFRα2 and AchE expression), regeneration potentials (Shh and Ptch expression), salivary trophic factor levels (brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurturin), and stem cell expression (Sca-1). These features were restored by treatment with ALA. This study demonstrated that ALA can rescue radiation-induced hyposalivation by preserving parasympathetic innervation and regenerative potentials.
Keywords: Alpha lipoic acid; parasympathetic innervation; radiation therapy; salivary gland; xerostomia.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protective effects of alpha lipoic acid on radiation-induced salivary gland injury in rats.Oncotarget. 2016 May 17;7(20):29143-53. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8661. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27072584 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effect of Alpha-Lipoic Acid on Salivary Dysfunction in a Mouse Model of Radioiodine Therapy-Induced Sialoadenitis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 10;21(11):4136. doi: 10.3390/ijms21114136. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32531940 Free PMC article.
-
Alpha lipoic acid attenuates radiation-induced thyroid injury in rats.PLoS One. 2014 Nov 17;9(11):e112253. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0112253. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25401725 Free PMC article.
-
Acquired salivary dysfunction. Drugs and radiation.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998 Apr 15;842:132-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1998.tb09641.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1998. PMID: 9599303 Review.
-
Effects of head and neck radiotherapy on major salivary glands--animal studies and human implications.In Vivo. 2003 Jul-Aug;17(4):369-75. In Vivo. 2003. PMID: 12929593 Review.
Cited by
-
Radioprotective effects and mechanism of HL-003 on radiation-induced salivary gland damage in mice.Sci Rep. 2022 May 19;12(1):8419. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12581-y. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35589816 Free PMC article.
-
Aquaporins in Glandular Secretion.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023;1398:225-249. doi: 10.1007/978-981-19-7415-1_16. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2023. PMID: 36717498
-
Experimental Animal Model Systems for Understanding Salivary Secretory Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 10;21(22):8423. doi: 10.3390/ijms21228423. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33182571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artesunate Combined With Metformin Ameliorate on Diabetes-Induced Xerostomia by Mitigating Superior Salivatory Nucleus and Salivary Glands Injury in Type 2 Diabetic Rats via the PI3K/AKT Pathway.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 20;12:774674. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.774674. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34987398 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the Function of Aquaporins in Gastrointestinal Fluid Absorption and Secretion in Health and Disease.Cells. 2023 Aug 29;12(17):2170. doi: 10.3390/cells12172170. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37681902 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Jellema A.P., Slotman B.J., Doornaert P., Leemans C.R., Langendijk J.A. Impact of radiation-induced xerostomia on quality of life after primary radiotherapy among patients with head and neck cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007;69:751–760. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2007.04.021. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

