Creation of different bioluminescence resonance energy transfer based biosensors with high affinity to VEGF
- PMID: 32214330
- PMCID: PMC7098639
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0230344
Creation of different bioluminescence resonance energy transfer based biosensors with high affinity to VEGF
Abstract
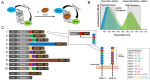
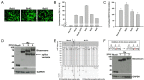
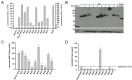
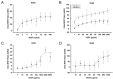
In age-related macular degeneration (AMD) or diabetic retinopathy (DR), hypoxia and inflammatory processes lead to an upregulation of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) expression and thereby to pathological neovascularisation with incorrectly formed vessels prone to damage, thus increasing the vascular permeability and the risk of bleeding and oedema in the retina. State of the art treatment is the repeated intraocular injection of anti-VEGF molecules. For developing improved individualized treatment approaches, a minimally invasive, repeatable method for in vivo quantification of VEGF in the eye is necessary. Therefore, we designed single molecule eBRET2 VEGF biosensors by directly fusing a Renilla luciferase mutant (Rluc8) N-terminal and a green fluorescent protein (GFP2) C-terminal to a VEGF binding domain. In total, 10 different VEGF biosensors (Re01- Re10) were generated based on either single domains or full length of VEGF receptor 1 or 2 extracellular regions as VEGF binding domains. Full length expression of the biosensors in HEK293-T cells was verified via Western Blot employing an anti-Rluc8-IgG. Expression of alternative splice variants was eliminated through the deletion of the donor splice site by introduction of a silent point mutation. In all ten biosensors the energy transfer from the Rluc8 to the GFP2 occurs and generates a measurable eBRET2 ratio. Four biosensors show a relevant change of the BRET ratio (ΔBR) after VEGF binding. Furthermore, each biosensor shows a unique detection range for VEGF quantification and especially Re06 and Re07 have a high sensitivity in the range of in vivo VEGF concentrations in the eye, previously measured by invasive methods. In conclusion, we generated several eBRET2 biosensors that are suitable for VEGF quantification in vitro and could identify two eBRET2 biosensors, which may be suitable for non-invasive in vivo VEGF quantification with an implantable device.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have read the journal's policy and have the following competing interests: The authors would like to declare the following patents/patent applications associated with this research: TW, KS and BL have a patent pending on the method for measurement and control of intraocular VEGF concentration (EP 3211422 A1, WO 2017/144416 pending). This does not alter our adherence to all the PLOS ONE policies on sharing data and materials
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quantification of the vascular endothelial growth factor with a bioluminescence resonance energy transfer (BRET) based single molecule biosensor.Biosens Bioelectron. 2016 Dec 15;86:609-615. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2016.07.058. Epub 2016 Jul 19. Biosens Bioelectron. 2016. PMID: 27459244
-
Comparison of enhanced bioluminescence energy transfer donors for protease biosensors.Anal Biochem. 2012 May 15;424(2):206-10. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2012.02.028. Epub 2012 Mar 1. Anal Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22387387
-
Detection of the Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor with a Novel Bioluminescence Resonance Energy Transfer Pair Using a Two-Component System.Sensors (Basel). 2017 Jan 13;17(1):145. doi: 10.3390/s17010145. Sensors (Basel). 2017. PMID: 28098756 Free PMC article.
-
A Review: Proteomics in Retinal Artery Occlusion, Retinal Vein Occlusion, Diabetic Retinopathy and Acquired Macular Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Apr 28;18(5):907. doi: 10.3390/ijms18050907. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28452939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Role of VEGF in diseases of the retina].Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2015 Mar;90 Suppl 1:3-5. doi: 10.1016/S0365-6691(15)30002-2. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2015. PMID: 25925044 Review. Spanish.
Cited by
-
Ways into Understanding HIF Inhibition.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jan 5;13(1):159. doi: 10.3390/cancers13010159. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33466454 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Coelenterazine-Dependent Luciferases as a Powerful Analytical Tool for Research and Biomedical Applications.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 10;21(20):7465. doi: 10.3390/ijms21207465. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33050422 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bourne RRA, Flaxman SR, Braithwaite T, Cicinelli MV, Das A, Jonas JB et al. Magnitude, temporal trends, and projections of the global prevalence of blindness and distance and near vision impairment: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The Lancet Global Health 2017; 5(9):e888–e897. 10.1016/S2214-109X(17)30293-0 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

