Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay: Pathologies and the Potential for Novel Therapeutics
- PMID: 32213869
- PMCID: PMC7140085
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12030765
Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay: Pathologies and the Potential for Novel Therapeutics
Abstract
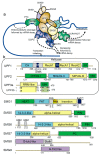
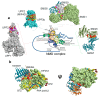
Nonsense-mediated messenger RNA (mRNA) decay (NMD) is a surveillance pathway used by cells to control the quality mRNAs and to fine-tune transcript abundance. NMD plays an important role in cell cycle regulation, cell viability, DNA damage response, while also serving as a barrier to virus infection. Disturbance of this control mechanism caused by genetic mutations or dys-regulation of the NMD pathway can lead to pathologies, including neurological disorders, immune diseases and cancers. The role of NMD in cancer development is complex, acting as both a promoter and a barrier to tumour progression. Cancer cells can exploit NMD for the downregulation of key tumour suppressor genes, or tumours adjust NMD activity to adapt to an aggressive immune microenvironment. The latter case might provide an avenue for therapeutic intervention as NMD inhibition has been shown to lead to the production of neoantigens that stimulate an immune system attack on tumours. For this reason, understanding the biology and co-option pathways of NMD is important for the development of novel therapeutic agents. Inhibitors, whose design can make use of the many structures available for NMD study, will play a crucial role in characterizing and providing diverse therapeutic options for this pathway in cancer and other diseases.
Keywords: Cancer; NMD inhibition; Neoantigens; Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay; Premature termination codon.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nonsense-mediated mRNA Decay and Cancer.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2018 Feb;48:44-50. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2017.10.007. Epub 2017 Nov 7. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2018. PMID: 29121514 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nonsense-Mediated mRNA Decay in Human Health and Diseases: Current Understanding, Regulatory Mechanisms and Future Perspectives.Mol Biotechnol. 2024 Sep 12. doi: 10.1007/s12033-024-01267-7. Online ahead of print. Mol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39264527 Review.
-
Deciphering the nonsense-mediated mRNA decay pathway to identify cancer cell vulnerabilities for effective cancer therapy.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Dec 1;40(1):376. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02192-2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34852841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Antisense suppression of the nonsense mediated decay factor Upf3b as a potential treatment for diseases caused by nonsense mutations.Genome Biol. 2018 Jan 15;19(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s13059-017-1386-9. Genome Biol. 2018. PMID: 29334995 Free PMC article.
-
Arginine CGA codons as a source of nonsense mutations: a possible role in multivariant gene expression, control of mRNA quality, and aging.Mol Genet Genomics. 2017 Oct;292(5):1013-1026. doi: 10.1007/s00438-017-1328-y. Epub 2017 May 18. Mol Genet Genomics. 2017. PMID: 28523359
Cited by
-
Retinoic acid-induced 1 gene haploinsufficiency alters lipid metabolism and causes autophagy defects in Smith-Magenis syndrome.Cell Death Dis. 2022 Nov 21;13(11):981. doi: 10.1038/s41419-022-05410-7. Cell Death Dis. 2022. PMID: 36411275 Free PMC article.
-
An Alternatively Spliced Variant of METTL3 Mediates Tumor Suppression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Genes (Basel). 2022 Apr 11;13(4):669. doi: 10.3390/genes13040669. Genes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35456475 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin D inhibits osteosarcoma by reprogramming nonsense-mediated RNA decay and SNAI2-mediated epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition.Front Oncol. 2023 May 9;13:1188641. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1188641. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2023. PMID: 37228489 Free PMC article.
-
A Novel Four-Gene Signature Based on Nonsense-Mediated RNA Decay for Predicting Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Bioinformatics Analysis and Functional Validation.J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024 Apr 23;11:747-766. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S450711. eCollection 2024. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2024. PMID: 38680213 Free PMC article.
-
Recoding of Nonsense Mutation as a Pharmacological Strategy.Biomedicines. 2023 Feb 22;11(3):659. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030659. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36979640 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

