Temporal profiles of viral load in posterior oropharyngeal saliva samples and serum antibody responses during infection by SARS-CoV-2: an observational cohort study
- PMID: 32213337
- PMCID: PMC7158907
- DOI: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30196-1
Temporal profiles of viral load in posterior oropharyngeal saliva samples and serum antibody responses during infection by SARS-CoV-2: an observational cohort study
Abstract
Background: Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) causes severe community and nosocomial outbreaks. Comprehensive data for serial respiratory viral load and serum antibody responses from patients infected with severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) are not yet available. Nasopharyngeal and throat swabs are usually obtained for serial viral load monitoring of respiratory infections but gathering these specimens can cause discomfort for patients and put health-care workers at risk. We aimed to ascertain the serial respiratory viral load of SARS-CoV-2 in posterior oropharyngeal (deep throat) saliva samples from patients with COVID-19, and serum antibody responses.
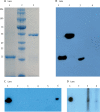
Methods: We did a cohort study at two hospitals in Hong Kong. We included patients with laboratory-confirmed COVID-19. We obtained samples of blood, urine, posterior oropharyngeal saliva, and rectal swabs. Serial viral load was ascertained by reverse transcriptase quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR). Antibody levels against the SARS-CoV-2 internal nucleoprotein (NP) and surface spike protein receptor binding domain (RBD) were measured using EIA. Whole-genome sequencing was done to identify possible mutations arising during infection.
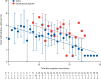
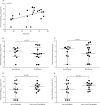
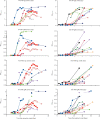
Findings: Between Jan 22, 2020, and Feb 12, 2020, 30 patients were screened for inclusion, of whom 23 were included (median age 62 years [range 37-75]). The median viral load in posterior oropharyngeal saliva or other respiratory specimens at presentation was 5·2 log10 copies per mL (IQR 4·1-7·0). Salivary viral load was highest during the first week after symptom onset and subsequently declined with time (slope -0·15, 95% CI -0·19 to -0·11; R2=0·71). In one patient, viral RNA was detected 25 days after symptom onset. Older age was correlated with higher viral load (Spearman's ρ=0·48, 95% CI 0·074-0·75; p=0·020). For 16 patients with serum samples available 14 days or longer after symptom onset, rates of seropositivity were 94% for anti-NP IgG (n=15), 88% for anti-NP IgM (n=14), 100% for anti-RBD IgG (n=16), and 94% for anti-RBD IgM (n=15). Anti-SARS-CoV-2-NP or anti-SARS-CoV-2-RBD IgG levels correlated with virus neutralisation titre (R2>0·9). No genome mutations were detected on serial samples.
Interpretation: Posterior oropharyngeal saliva samples are a non-invasive specimen more acceptable to patients and health-care workers. Unlike severe acute respiratory syndrome, patients with COVID-19 had the highest viral load near presentation, which could account for the fast-spreading nature of this epidemic. This finding emphasises the importance of stringent infection control and early use of potent antiviral agents, alone or in combination, for high-risk individuals. Serological assay can complement RT-qPCR for diagnosis.
Funding: Richard and Carol Yu, May Tam Mak Mei Yin, The Shaw Foundation Hong Kong, Michael Tong, Marina Lee, Government Consultancy Service, and Sanming Project of Medicine.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
SARS-CoV-2: virus dynamics and host response.Lancet Infect Dis. 2020 May;20(5):515-516. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30235-8. Epub 2020 Mar 23. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32213336 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
SARS-CoV-2 shedding and seroconversion among passengers quarantined after disembarking a cruise ship: a case series.Lancet Infect Dis. 2020 Sep;20(9):1051-1060. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30364-9. Epub 2020 Jun 12. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32539986 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody tests for identification of current and past infection with SARS-CoV-2.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jun 25;6(6):CD013652. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013652. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2022 Nov 17;11:CD013652. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013652.pub2. PMID: 32584464 Free PMC article. Updated.
-
Prospective Study Comparing Deep Throat Saliva With Other Respiratory Tract Specimens in the Diagnosis of Novel Coronavirus Disease 2019.J Infect Dis. 2020 Oct 13;222(10):1612-1619. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jiaa487. J Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 32738137 Free PMC article.
-
[SARS-CoV-2 and Microbiological Diagnostic Dynamics in COVID-19 Pandemic].Mikrobiyol Bul. 2020 Jul;54(3):497-509. doi: 10.5578/mb.69839. Mikrobiyol Bul. 2020. PMID: 32755524 Review. Turkish.
-
New COVID-19 saliva-based test: How good is it compared with the current nasopharyngeal or throat swab test?J Chin Med Assoc. 2020 Oct;83(10):891-894. doi: 10.1097/JCMA.0000000000000396. J Chin Med Assoc. 2020. PMID: 32773584 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Perioral Aerosol Sequestration Suction Device Effectively Reduces Biological Cross-Contamination in Dental Procedures.Eur J Dent. 2021 May;15(2):340-346. doi: 10.1055/s-0041-1724152. Epub 2021 Mar 12. Eur J Dent. 2021. PMID: 33711845 Free PMC article.
-
Serological profiles of pan-coronavirus-specific responses in COVID-19 patients using a multiplexed electro-chemiluminescence-based testing platform.PLoS One. 2021 Jun 3;16(6):e0252628. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0252628. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34081747 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 serology in nephrology healthcare workers.Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2021 Sep;133(17-18):923-930. doi: 10.1007/s00508-021-01848-5. Epub 2021 Apr 9. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2021. PMID: 33835265 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Risk of rapid evolutionary escape from biomedical interventions targeting SARS-CoV-2 spike protein.PLoS One. 2021 Apr 28;16(4):e0250780. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0250780. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 33909660 Free PMC article.
-
SARS-CoV-2 presented moderately during two episodes of the infection with lack of antibody responses.Virus Res. 2021 Jul 2;299:198421. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2021.198421. Epub 2021 Apr 6. Virus Res. 2021. PMID: 33836204 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

