eIF2B and the Integrated Stress Response: A Structural and Mechanistic View
- PMID: 32200625
- PMCID: PMC7189779
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.0c00132
eIF2B and the Integrated Stress Response: A Structural and Mechanistic View
Abstract
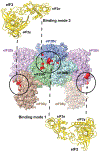
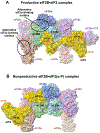
The eukaryotic translation initiation factor eIF2 is a GTPase, which brings the initiator Met-tRNAi to the ribosome as the eIF2-GTP·Met-tRNAi ternary complex (TC). TC regeneration is catalyzed by the guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) eIF2B. eIF2 phosphorylation by several stress-induced kinases converts it into a competitive inhibitor of eIF2B. Inhibition of eIF2B activity lowers cellular TC concentrations, which in turn triggers the integrated stress response (ISR). Depending on its degree of activation and duration, the ISR protects the cell from the stress or can itself induce apoptosis. ISR dysregulation is a causative factor in the pathology of multiple neurodegenerative disorders, while ISR inhibitors are neuroprotective. The realization that eIF2B is a promising therapeutic target has triggered significant interest in its structure and its mechanisms of action and regulation. Recently, four groups published the cryo-electron microscopy structures of eIF2B with its substrate eIF2 and/or its inhibitor, phosphorylated eIF2 [eIF2(α-P)]. While all three structures of the nonproductive eIF2B·eIF2(α-P) complex are similar to each other, there is a sharp disagreement between the published structures of the productive eIF2B·eIF2 complex. One group reports a structure similar to that of the nonproductive complex, whereas two others observe a vastly different eIF2B·eIF2 complex. Here, we discuss the recent reports on the structure, function, and regulation of eIF2B; the preclinical data on the use of ISR inhibitors for the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders; and how the new structural and biochemical information can inform and influence the use of eIF2B as a therapeutic target.
Figures
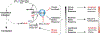
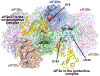
Similar articles
-
eIF2B Mechanisms of Action and Regulation: A Thermodynamic View.Biochemistry. 2018 Mar 6;57(9):1426-1435. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b00957. Epub 2018 Feb 20. Biochemistry. 2018. PMID: 29425030 Free PMC article.
-
Novel mechanisms of eIF2B action and regulation by eIF2α phosphorylation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Nov 16;45(20):11962-11979. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx845. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 29036434 Free PMC article.
-
A C-term truncated EIF2Bγ protein encoded by an intronically polyadenylated isoform introduces unfavorable EIF2Bγ-EIF2γ interactions.Proteins. 2022 Mar;90(3):889-897. doi: 10.1002/prot.26284. Epub 2021 Nov 26. Proteins. 2022. PMID: 34796993
-
Crystal structure of eIF2B and insights into eIF2-eIF2B interactions.FEBS J. 2017 Mar;284(6):868-874. doi: 10.1111/febs.13896. Epub 2016 Sep 29. FEBS J. 2017. PMID: 27627185 Review.
-
Protection of eIF2B from inhibitory phosphorylated eIF2: A viral strategy to maintain mRNA translation during the PKR-triggered integrated stress response.J Biol Chem. 2023 Nov;299(11):105287. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105287. Epub 2023 Sep 22. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37742919 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Defective regulation of the eIF2-eIF2B translational axis underlies depressive-like behavior in mice and correlates with major depressive disorder in humans.Transl Psychiatry. 2024 Oct 1;14(1):397. doi: 10.1038/s41398-024-03128-y. Transl Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 39349438 Free PMC article.
-
Fluorescence Intensity-Based eIF2B's Guanine Nucleotide-Exchange Factor Activity Assay.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2428:187-196. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1975-9_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35171481
-
Non-canonical mRNA translation initiation in cell stress and cancer.NAR Cancer. 2024 May 31;6(2):zcae026. doi: 10.1093/narcan/zcae026. eCollection 2024 Jun. NAR Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38828390 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Move and countermove: the integrated stress response in picorna- and coronavirus-infected cells.Curr Opin Immunol. 2022 Dec;79:102254. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2022.102254. Epub 2022 Sep 28. Curr Opin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36274340 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ReporterSeq reveals genome-wide dynamic modulators of the heat shock response across diverse stressors.Elife. 2021 Jul 5;10:e57376. doi: 10.7554/eLife.57376. Elife. 2021. PMID: 34223816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kashiwagi K, Takahashi M, Nishimoto M, Hiyama TB, Higo T, Umehara T, Sakamoto K, Ito T, and Yokoyama S (2016) Crystal structure of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2B, Nature 531, 122–125. - PubMed
-
- Kashiwagi K, Yokoyama T, Nishimoto M, Takahashi M, Sakamoto A, Yonemochi M, Shirouzu M, and Ito T (2019) Structural basis for eIF2B inhibition in integrated stress response, Science 364, 495–499. - PubMed
-
- Marintchev A, and Wagner G (2004) Translation initiation: structures, mechanisms and evolution, Q Rev Biophys 37, 197–284. - PubMed
-
- Pestova TV, Lorsch JR, and Hellen CUT (2007) The Mechanism of Translation Initiation in Eukaryotes, In Translational Control in Biology and Medicine (Mathews MB, Sonenberg N, Hershey JWB, Ed.), pp 87–128, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring harbor, NY.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

