Overexpression of Murine Rnaset2 in a Colon Syngeneic Mouse Carcinoma Model Leads to Rebalance of Intra-Tumor M1/M2 Macrophage Ratio, Activation of T Cells, Delayed Tumor Growth, and Rejection
- PMID: 32197460
- PMCID: PMC7140044
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12030717
Overexpression of Murine Rnaset2 in a Colon Syngeneic Mouse Carcinoma Model Leads to Rebalance of Intra-Tumor M1/M2 Macrophage Ratio, Activation of T Cells, Delayed Tumor Growth, and Rejection
Abstract
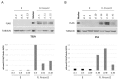
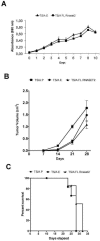
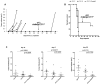
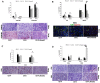
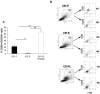
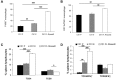
Human RNASET2 acts as a powerful oncosuppressor protein in in vivo xenograft-based murine models of human cancer. Secretion of RNASET2 in the tumor microenvironment seems involved in tumor suppression, following recruitment of M1-polarized macrophages. Here, we report a murine Rnaset2-based syngeneic in vivo assay. BALB/c mice were injected with parental, empty vector-transfected or murine Rnaset2-overexpressing mouse C51 or TS/A syngeneic cells and tumor growth pattern and immune cells distribution in tumor mass were investigated. Compared to control cells, mouse Rnaset2-expressing C51 cells showed strong delayed tumor growth. CD86+ M1 macrophages were massively recruited in Rnaset2-expressing C51-derived tumors, with concomitant inhibition of MDSCs and CD206+ M2 macrophages recruitment. At later times, a relevant expansion of intra-tumor CD8+ T cells was also observed. After re-challenge with C51 parental cells, most mice previously injected with Rnaset2-expressing C51 cells still rejected C51 tumor cells, suggesting a Rnaset2-mediated T cell adaptive immune memory response. These results point at T2 RNases as evolutionary conserved oncosuppressors endowed with the ability to inhibit cancer growth in vivo through rebalance of intra-tumor M1/M2 macrophage ratio and concomitant recruitment of adaptive anti-tumor CD8+ T cells.
Keywords: C51 colon carcinoma; M1/M2 macrophage ratio; RNASET2; TNFα-producing M1 macrophages; immune T cell responses.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The human RNASET2 protein affects the polarization pattern of human macrophages in vitro.Immunol Lett. 2018 Nov;203:102-111. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2018.09.005. Epub 2018 Sep 12. Immunol Lett. 2018. PMID: 30218741
-
Human recombinant RNASET2-induced inflammatory response and connective tissue remodeling in the medicinal leech.Cell Tissue Res. 2017 May;368(2):337-351. doi: 10.1007/s00441-016-2557-9. Epub 2017 Jan 9. Cell Tissue Res. 2017. PMID: 28070637
-
Ribonuclease T2 from Aspergillus fumigatus promotes T helper type 2 responses through M2 polarization of macrophages.Int J Mol Med. 2020 Aug;46(2):718-728. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4613. Epub 2020 May 21. Int J Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 32468025 Free PMC article.
-
Innate Immune Response Regulation by the Human RNASET2 Tumor Suppressor Gene.Front Immunol. 2019 Nov 5;10:2587. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02587. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31749812 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human RNASET2: A Highly Pleiotropic and Evolutionary Conserved Tumor Suppressor Gene Involved in the Control of Ovarian Cancer Pathogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 13;23(16):9074. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169074. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012339 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Tumor Growth Suppression of Pancreatic Cancer Orthotopic Xenograft Model by CEA-Targeting CAR-T Cells.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jan 18;15(3):601. doi: 10.3390/cancers15030601. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36765558 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Therapy as Target Therapy against Colon Cancer Stem Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 3;24(9):8163. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098163. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175871 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epididymal RNase T2 contributes to astheno-teratozoospermia and intergenerational metabolic disorder through epididymosome-sperm interaction.BMC Med. 2023 Nov 22;21(1):453. doi: 10.1186/s12916-023-03158-1. BMC Med. 2023. PMID: 37993934 Free PMC article.
-
The Potential Role of the T2 Ribonucleases in TME-Based Cancer Therapy.Biomedicines. 2023 Aug 1;11(8):2160. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11082160. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37626657 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tumor-Associated Macrophages (TAMs) in Colorectal Cancer (CRC): From Mechanism to Therapy and Prognosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 6;22(16):8470. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168470. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445193 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Acquati F., Bertilaccio S., Grimaldi A., Monti L., Cinquetti R., Bonetti P., Lualdi M., Vidalino L., Fabbri M., Sacco M.G., et al. Microenvironmental control of malignancy exerted by RNASET2, a widely conserved extracellular RNase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2011;108:1104–1109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1013746108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Acquati F., Lualdi M., Bertilaccio S., Monti L., Turconi G., Fabbri M., Grimaldi A., Anselmo A., Inforzato A., Collotta A., et al. Loss of function of Ribonuclease T2, an ancient and phylogenetically conserved RNase, plays a crucial role in ovarian tumorigenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2013;110:8140–8145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1222079110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Lualdi M., Pedrini E., Rea K., Monti L., Scaldaferri D., Gariboldi M., Camporeale A., Ghia P., Monti E., Tomassetti A., et al. Pleiotropic modes of action in tumor cells of RNASET2, an evolutionary highly conserved extracellular RNase. Oncotarget. 2015;6:7851–7865. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3490. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

