Pyruvate Kinase M2 and Cancer: The Role of PKM2 in Promoting Tumorigenesis
- PMID: 32195169
- PMCID: PMC7061896
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2020.00159
Pyruvate Kinase M2 and Cancer: The Role of PKM2 in Promoting Tumorigenesis
Abstract
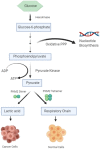
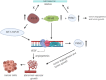
Pyruvate kinase plays a pivotal role in regulating cell metabolism. The final and rate-limiting step of glycolysis is the conversion of Phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP) to Pyruvate, which is catalyzed by Pyruvate Kinase. There are four isomeric, tissue-specific forms of Pyruvate Kinase found in mammals: PKL, PKR, PKM1, and PKM2. PKM1 and PKM2 are formed bya single mRNA transcript of the PKM gene by alternative splicing. The oligomers of PKM2 exist in high activity tetramer and low activity dimer forms. The dimer PKM2 regulates the rate-limiting step of glycolysis that shifts the glucose metabolism from the normal respiratory chain to lactate production in tumor cells. Besides its role as a metabolic regulator, it also acts as protein kinase, which contributes to tumorigenesis. This review is focused on the metabolic role of pyruvate kinase M2 in normal cells vs. cancerous cells and its regulation at the transcriptional level. The review also highlights the role of PKM2 as a potential diagnostic marker and as a therapeutic target in cancer treatment.
Keywords: anaerobic glycolysis; angiogenesis; cancer metabolism; chemotherapy; pyruvate kinase M2.
Copyright © 2020 Zahra, Dey, Ashish, Mishra and Pandey.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The cysteine residue at 424th of pyruvate kinase M2 is crucial for tetramerization and responsiveness to oxidative stress.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Jun 11;526(4):973-977. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.03.182. Epub 2020 Apr 12. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 32295714
-
A short review on cross-link between pyruvate kinase (PKM2) and Glioblastoma Multiforme.Metab Brain Dis. 2021 Jun;36(5):751-765. doi: 10.1007/s11011-021-00690-y. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Metab Brain Dis. 2021. PMID: 33651273 Review.
-
NEK2 Promotes Aerobic Glycolysis in Multiple Myeloma Through Regulating Splicing of Pyruvate Kinase.J Hematol Oncol. 2017 Jan 13;10(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13045-017-0392-4. J Hematol Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28086949 Free PMC article.
-
Sam68 promotes aerobic glycolysis in colorectal cancer by regulating PKM2 alternative splicing.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Apr;8(7):459. doi: 10.21037/atm.2020.03.108. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32395503 Free PMC article.
-
Pyruvate kinase: Function, regulation and role in cancer.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015 Jul;43:43-51. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.08.004. Epub 2015 Aug 13. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26277545 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pyruvate Kinase Differentially Alters Metabolic Signatures during Head and Neck Carcinogenesis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 23;24(23):16639. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316639. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38068962 Free PMC article.
-
Osthole increases the radiosensitivity of hepatoma cells by inhibiting GSK-3β/AMPK/mTOR pathway-controlled glycolysis.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023 Apr;396(4):683-692. doi: 10.1007/s00210-022-02347-8. Epub 2022 Nov 29. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36445387
-
Oxidative stress regulation and related metabolic pathways in epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer stem cells.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Nov 28;14(1):342. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03571-6. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 38017510 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Functions and modulation of PKM2 activity by human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein (Review).Oncol Lett. 2022 Nov 14;25(1):7. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13593. eCollection 2023 Jan. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 36478899 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Smooth Muscle Cell-Specific PKM2 (Pyruvate Kinase Muscle 2) Promotes Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Switching and Neointimal Hyperplasia.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021 May 5;41(5):1724-1737. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.121.316021. Epub 2021 Mar 11. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2021. PMID: 33691477 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

