Influence of adiposity, insulin resistance, and intrahepatic triglyceride content on insulin kinetics
- PMID: 32191646
- PMCID: PMC7260030
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI136756
Influence of adiposity, insulin resistance, and intrahepatic triglyceride content on insulin kinetics
Abstract
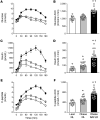
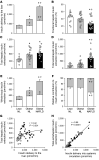
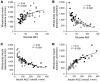
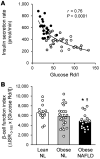
BACKGROUNDInsulin is a key regulator of metabolic function. The effects of excess adiposity, insulin resistance, and hepatic steatosis on the complex integration of insulin secretion and hepatic and extrahepatic tissue extraction are not clear.METHODSA hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp and a 3-hour oral glucose tolerance test were performed to evaluate insulin sensitivity and insulin kinetics after glucose ingestion in 3 groups: (a) lean subjects with normal intrahepatic triglyceride (IHTG) and glucose tolerance (lean-NL; n = 14), (b) obese subjects with normal IHTG and glucose tolerance (obese-NL; n = 24), and (c) obese subjects with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and prediabetes (obese-NAFLD; n = 22).RESULTSInsulin sensitivity progressively decreased and insulin secretion progressively increased from the lean-NL to the obese-NL to the obese-NAFLD groups. Fractional hepatic insulin extraction progressively decreased from the lean-NL to the obese-NL to the obese-NAFLD groups, whereas total hepatic insulin extraction (molar amount removed) was greater in the obese-NL and obese-NAFLD subjects than in the lean-NL subjects. Insulin appearance in the systemic circulation and extrahepatic insulin extraction progressively increased from the lean-NL to the obese-NL to the obese-NAFLD groups. Total hepatic insulin extraction plateaued at high rates of insulin delivery, whereas the relationship between systemic insulin appearance and total extrahepatic extraction was linear.CONCLUSIONHyperinsulinemia after glucose ingestion in obese-NL and obese-NAFLD is due to an increase in insulin secretion, without a decrease in total hepatic or extrahepatic insulin extraction. However, the liver's maximum capacity to remove insulin is limited because of a saturable extraction process. The increase in insulin delivery to the liver and extrahepatic tissues in obese-NAFLD is unable to compensate for the increase in insulin resistance, resulting in impaired glucose homeostasis.TRIAL REGISTRATIONClinicalTrials.gov NCT02706262.FUNDINGNIH grants DK56341 (Nutrition Obesity Research Center), DK052574 (Digestive Disease Research Center), RR024992 (Clinical and Translational Science Award), and T32 DK007120 (a T32 Ruth L. Kirschstein National Research Service Award); the American Diabetes Foundation (1-18-ICTS-119); Janssen Research & Development; and the Pershing Square Foundation.
Keywords: Endocrinology; Metabolism; Obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Insulin resistance drives hepatic de novo lipogenesis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease.J Clin Invest. 2020 Mar 2;130(3):1453-1460. doi: 10.1172/JCI134165. J Clin Invest. 2020. PMID: 31805015 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Associations Among Adipose Tissue Immunology, Inflammation, Exosomes and Insulin Sensitivity in People With Obesity and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Gastroenterology. 2021 Sep;161(3):968-981.e12. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2021.05.008. Epub 2021 May 15. Gastroenterology. 2021. PMID: 34004161 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Adipose Tissue Fibrogenesis, Not Impaired Expandability, Is Associated With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease.Hepatology. 2021 Sep;74(3):1287-1299. doi: 10.1002/hep.31822. Epub 2021 Jun 22. Hepatology. 2021. PMID: 33743554 Free PMC article.
-
A review of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in non-obese and lean individuals.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Jun;36(6):1497-1507. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15353. Epub 2020 Dec 15. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 33217052 Review.
-
Fructose as a key player in the development of fatty liver disease.World J Gastroenterol. 2013 Feb 28;19(8):1166-72. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v19.i8.1166. World J Gastroenterol. 2013. PMID: 23482247 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Critical Evaluation of Indices Used to Assess β-Cell Function.Diabetes. 2024 Mar 1;73(3):391-400. doi: 10.2337/db23-0613. Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 38015795
-
Current Options and Future Directions for NAFLD and NASH Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 15;22(14):7571. doi: 10.3390/ijms22147571. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34299189 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Impaired plasma glucose clearance is a key determinant of fasting hyperglycemia in people with obesity.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2024 Mar;32(3):540-546. doi: 10.1002/oby.23963. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2024. PMID: 38228469
-
Therapeutic opportunities for pancreatic β-cell ER stress in diabetes mellitus.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021 Aug;17(8):455-467. doi: 10.1038/s41574-021-00510-4. Epub 2021 Jun 23. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2021. PMID: 34163039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The influence of steroidal implants and manganese sulfate supplementation on growth performance, trace mineral status, hepatic gene expression, hepatic enzyme activity, and circulating metabolites in feedlot steers.J Anim Sci. 2024 Jan 3;102:skae062. doi: 10.1093/jas/skae062. J Anim Sci. 2024. PMID: 38456567 Free PMC article.

