Identification of Potential Serum Metabolic Biomarkers of Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Widely Targeted Metabolomics Study
- PMID: 32190695
- PMCID: PMC7072115
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/3049098
Identification of Potential Serum Metabolic Biomarkers of Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Widely Targeted Metabolomics Study
Abstract
Background and Objectives. Diabetic kidney disease is a leading cause of chronic kidney disease and end-stage renal disease across the world. Early identification of DKD is vitally important for the effective prevention and control of it. However, the available indicators are doubtful in the early diagnosis of DKD. This study is aimed at determining novel sensitive and specific biomarkers to distinguish DKD from their counterparts effectively based on the widely targeted metabolomics approach. Materials and Method. This case-control study involved 44 T2DM patients. Among them, 24 participants with DKD were defined as the cases and another 20 without DKD were defined as the controls. The ultraperformance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry system was applied for the assessment of the serum metabolic profiles. Comprehensive analysis of metabolomics characteristics was conducted to detect the candidate metabolic biomarkers and assess their capability and feasibility.
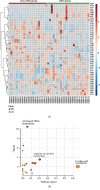
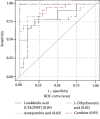
Result: A total of 11 differential metabolites, including Hexadecanoic Acid (C16:0), Linolelaidic Acid (C18:2N6T), Linoleic Acid (C18:2N6C), Trans-4-Hydroxy-L-Proline, 6-Aminocaproic Acid, L-Dihydroorotic Acid, 6-Methylmercaptopurine, Piperidine, Azoxystrobin Acid, Lysopc 20:4, and Cuminaldehyde, were determined as the potential biomarkers for the DKD early identification, based on the multivariable generalized linear regression model and receiver operating characteristic analysis.
Conclusion: Serum metabolites might act as sensitive and specific biomarkers for DKD early detection. Further longitudinal studies are needed to confirm our findings.
Copyright © 2020 Hang Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Urine metabolomics reveals biomarkers and the underlying pathogenesis of diabetic kidney disease.Int Urol Nephrol. 2023 Apr;55(4):1001-1013. doi: 10.1007/s11255-022-03326-x. Epub 2022 Oct 18. Int Urol Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36255506
-
Clinical metabolomics characteristics of diabetic kidney disease: A meta-analysis of 1875 cases with diabetic kidney disease and 4503 controls.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2024 Mar;40(3):e3789. doi: 10.1002/dmrr.3789. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 38501707
-
Serum metabolomics detected by LDI-TOF-MS can be used to distinguish between diabetic patients with and without diabetic kidney disease.FEBS Open Bio. 2023 Oct;13(10):1844-1858. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13683. Epub 2023 Aug 11. FEBS Open Bio. 2023. PMID: 37525631 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomics as a tool for the early diagnosis and prognosis of diabetic kidney disease.Med Res Rev. 2022 Jul;42(4):1518-1544. doi: 10.1002/med.21883. Epub 2022 Mar 10. Med Res Rev. 2022. PMID: 35274315 Review.
-
Metabolomic biomarkers in diabetic kidney diseases--A systematic review.J Diabetes Complications. 2015 Nov-Dec;29(8):1345-51. doi: 10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2015.06.016. Epub 2015 Jul 9. J Diabetes Complications. 2015. PMID: 26253264 Review.
Cited by
-
Application of Metabolomics and Traditional Chinese Medicine for Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Treatment.Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023 Dec 28;16:4269-4282. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S441399. eCollection 2023. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2023. PMID: 38164418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acylcarnitines: Can They Be Biomarkers of Diabetic Nephropathy?Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022 Jan 29;15:247-256. doi: 10.2147/DMSO.S350233. eCollection 2022. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes. 2022. PMID: 35125878 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Untargeted Metabolomic Plasma Profiling of Emirati Dialysis Patients with Diabetes versus Non-Diabetic: A Pilot Study.Biomolecules. 2022 Jul 8;12(7):962. doi: 10.3390/biom12070962. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35883517 Free PMC article.
-
Lipidomics Profiling Reveals Serum Phospholipids Associated with Albuminuria in Early Type 2 Diabetic Kidney Disease.ACS Omega. 2023 Sep 22;8(39):36543-36552. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c05504. eCollection 2023 Oct 3. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37810655 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced Mass Spectrometry-Based Biomarker Identification for Metabolomics of Diabetes Mellitus and Its Complications.Molecules. 2024 May 27;29(11):2530. doi: 10.3390/molecules29112530. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38893405 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

