Rapidly increasing cumulative incidence of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in the European Union/European Economic Area and the United Kingdom, 1 January to 15 March 2020
- PMID: 32186277
- PMCID: PMC7096777
- DOI: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.11.2000285
Rapidly increasing cumulative incidence of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) in the European Union/European Economic Area and the United Kingdom, 1 January to 15 March 2020
Abstract
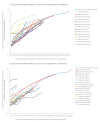
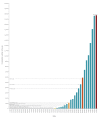
The cumulative incidence of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) cases is showing similar trends in European Union/European Economic Area countries and the United Kingdom confirming that, while at a different stage depending on the country, the COVID-19 pandemic is progressing rapidly in all countries. Based on the experience from Italy, countries, hospitals and intensive care units should increase their preparedness for a surge of patients with COVID-19 who will require healthcare, and in particular intensive care.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2, COVID-19, coronavirus disease; coronavirus, EU/EEA, United Kingdom, Europe.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Estimating number of cases and spread of coronavirus disease (COVID-19) using critical care admissions, United Kingdom, February to March 2020.Euro Surveill. 2020 May;25(18):2000632. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.18.2000632. Euro Surveill. 2020. PMID: 32400358 Free PMC article.
-
Indications for healthcare surge capacity in European countries facing an exponential increase in coronavirus disease (COVID-19) cases, March 2020.Euro Surveill. 2020 Apr;25(13):2000323. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.13.2000323. Euro Surveill. 2020. PMID: 32265003 Free PMC article.
-
Roll-out of SARS-CoV-2 testing for healthcare workers at a large NHS Foundation Trust in the United Kingdom, March 2020.Euro Surveill. 2020 Apr;25(14):2000433. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.14.2000433. Euro Surveill. 2020. PMID: 32290904 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 pandemic - an African perspective.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020 Dec;9(1):1300-1308. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1775132. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020. PMID: 32458760 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regional COVID-19 Network for Coordination of SARS-CoV-2 outbreak in Veneto, Italy.J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2020 Sep;34(9):2341-2345. doi: 10.1053/j.jvca.2020.05.005. Epub 2020 May 15. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2020. PMID: 32425461 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Lived experience of Iranian pre-hospital medical staff during the COVID-19 pandemic: a descriptive phenomenological study.Front Psychol. 2023 Dec 21;14:1230892. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1230892. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 38235282 Free PMC article.
-
Hand Trauma and Reconstructive Microsurgery during the COVID-19 Emergency in the Marche Region (Italy): What Has Changed?Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Nov 21;11(23):3006. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11233006. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38063574 Free PMC article.
-
Information networks for COVID-19 according to race/ethnicity.Inf Technol Manag. 2023;24(2):147-157. doi: 10.1007/s10799-022-00360-0. Epub 2022 Apr 23. Inf Technol Manag. 2023. PMID: 37124836 Free PMC article.
-
A Retrospective Population Study of 385 191 Positive Real-Time Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction Tests For SARS-CoV-2 from a Single Laboratory in Katowice, Poland from April 2020 to July 2022.Med Sci Monit. 2023 Jan 2;29:e938872. doi: 10.12659/MSM.938872. Med Sci Monit. 2023. PMID: 36636983 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology and clinical features of SARS-CoV-2 infection in hospitalized children across four waves in Hungary: A retrospective, comparative study from March 2020 to December 2021.Health Sci Rep. 2022 Nov 21;5(6):e937. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.937. eCollection 2022 Nov. Health Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36425898 Free PMC article.
References
-
- European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC). Novel coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic: increased transmission in the EU/EEA and the UK – sixth update, 12 March 2020. ECDC: Stockholm; 2020. Available from: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/RRA-sixth-updat...
-
- Bernard Stoecklin S, Rolland P, Silue Y, Mailles A, Campese C, Simondon A, et al. Investigation Team First cases of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in France: surveillance, investigations and control measures, January 2020. Euro Surveill. 2020;25(6):2000094. 10.2807/1560-7917.ES.2020.25.6.2000094 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO Director-General's opening remarks at the media briefing on COVID-19 - 11 March 2020. World Health Organization: Geneva; 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/dg/speeches/detail/who-director-general-s-opening-re...
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) technical guidance: Surveillance and case definitions. Geneva: WHO; 2020. Available from: https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/technica...
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

