ARV-825-induced BRD4 protein degradation as a therapy for thyroid carcinoma
- PMID: 32163373
- PMCID: PMC7093165
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.102910
ARV-825-induced BRD4 protein degradation as a therapy for thyroid carcinoma
Abstract
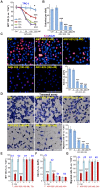
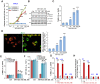
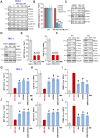
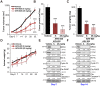
Bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) is overexpressed in thyroid carcinoma, represents as an important therapeutic target. ARV-825 is a novel cereblon-based PROTAC (Proteolysis Targeting Chsimera) compound. It can induce fast and sustained BRD4 protein degradation. Its potential effect in human thyroid carcinoma cells was studied here. In TPC-1 cells and primary human thyroid carcinoma cells, ARV-825 potently inhibited cell viability, proliferation and migration. Furthermore, ARV-825 induced robust apoptosis activation in the thyroid carcinoma cells. ARV-825 induced BRD4 protein degradation and downregulation of its targets, including c-Myc, Bcl-xL and cyclin D1 in thyroid carcinoma cells. It was significantly more potent in inhibiting thyroid carcinoma cells than the known small molecule BRD4 inhibitors. In vivo studies demonstrated that ARV-825 oral administration potently suppressed TPC-1 xenograft tumor growth in severe combined immunodeficient mice. BRD4 protein degradation as well as c-Myc, Bcl-xL and cyclin D1 downregulation were detected in ARV-825-treated TPC-1 tumor tissues. Taken together, ARV-825 induces BRD4 protein degradation and inhibits thyroid carcinoma cell growth in vitro and in vivo.
Keywords: ARV-825; BRD4; c-Myc; proteolysis targeting chimera; thyroid carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
AZD5153, a novel BRD4 inhibitor, suppresses human thyroid carcinoma cell growth in vitro and in vivo.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018 May 15;499(3):531-537. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.03.184. Epub 2018 Mar 31. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018. PMID: 29596834
-
Novel BET protein proteolysis-targeting chimera exerts superior lethal activity than bromodomain inhibitor (BETi) against post-myeloproliferative neoplasm secondary (s) AML cells.Leukemia. 2017 Sep;31(9):1951-1961. doi: 10.1038/leu.2016.393. Epub 2017 Feb 2. Leukemia. 2017. PMID: 28042144 Free PMC article.
-
Hijacking the E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Cereblon to Efficiently Target BRD4.Chem Biol. 2015 Jun 18;22(6):755-63. doi: 10.1016/j.chembiol.2015.05.009. Epub 2015 Jun 4. Chem Biol. 2015. PMID: 26051217 Free PMC article.
-
Bromodomain Protein-directed Agents and MYC in Small Cell Lung Cancer.Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2024;24(9):930-940. doi: 10.2174/0115680096272757231211113206. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 38275056 Review.
-
An updated patent review of BRD4 degraders.Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2024 Oct;34(10):929-951. doi: 10.1080/13543776.2024.2400166. Epub 2024 Sep 4. Expert Opin Ther Pat. 2024. PMID: 39219068 Review.
Cited by
-
Gene Editing with CRISPR/Cas Methodology and Thyroid Cancer: Where Are We?Cancers (Basel). 2022 Feb 8;14(3):844. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030844. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35159110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Conception to Development: Investigating PROTACs Features for Improved Cell Permeability and Successful Protein Degradation.Front Chem. 2021 Apr 20;9:672267. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.672267. eCollection 2021. Front Chem. 2021. PMID: 33959589 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of the Small-molecule BRD4 Degrader CFT-2718 in Small-cell Lung Cancer and Pancreatic Cancer Models.Mol Cancer Ther. 2021 Aug;20(8):1367-1377. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-20-0831. Epub 2021 May 27. Mol Cancer Ther. 2021. PMID: 34045230 Free PMC article.
-
Cereblon-Recruiting PROTACs: Will New Drugs Have to Face Old Challenges?Pharmaceutics. 2023 Mar 2;15(3):812. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15030812. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 36986673 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PROTAC Beyond Cancer- Exploring the New Therapeutic Potential of Proteolysis Targeting Chimeras.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(23):2050-2073. doi: 10.2174/0115680266309968240621072550. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38963108 Review.
References
-
- Vuong HG, Altibi AM, Abdelhamid AH, Ngoc PU, Quan VD, Tantawi MY, Elfil M, Vu TL, Elgebaly A, Oishi N, Nakazawa T, Hirayama K, Katoh R, et al.. The changing characteristics and molecular profiles of papillary thyroid carcinoma over time: a systematic review. Oncotarget. 2017; 8:10637–49. 10.18632/oncotarget.12885 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

