Principles of fluoride toxicity and the cellular response: a review
- PMID: 32152649
- PMCID: PMC7230026
- DOI: 10.1007/s00204-020-02687-5
Principles of fluoride toxicity and the cellular response: a review
Abstract
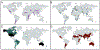
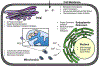
Fluoride is ubiquitously present throughout the world. It is released from minerals, magmatic gas, and industrial processing, and travels in the atmosphere and water. Exposure to low concentrations of fluoride increases overall oral health. Consequently, many countries add fluoride to their public water supply at 0.7-1.5 ppm. Exposure to high concentrations of fluoride, such as in a laboratory setting often exceeding 100 ppm, results in a wide array of toxicity phenotypes. This includes oxidative stress, organelle damage, and apoptosis in single cells, and skeletal and soft tissue damage in multicellular organisms. The mechanism of fluoride toxicity can be broadly attributed to four mechanisms: inhibition of proteins, organelle disruption, altered pH, and electrolyte imbalance. Recently, there has been renewed concern in the public sector as to whether fluoride is safe at the current exposure levels. In this review, we will focus on the impact of fluoride at the chemical, cellular, and multisystem level, as well as how organisms defend against fluoride. We also address public concerns about fluoride toxicity, including whether fluoride has a significant effect on neurodegeneration, diabetes, and the endocrine system.
Keywords: Cell stress; Fluoride; Metal; Toxicity.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
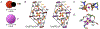
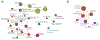
Similar articles
-
Toxic effects of fluoride on organisms.Life Sci. 2018 Apr 1;198:18-24. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2018.02.001. Epub 2018 Feb 9. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29432760 Review.
-
Pulmonary fluorosis: a review.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017 Oct;24(28):22119-22132. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9951-z. Epub 2017 Aug 25. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28840484 Review.
-
A possible mechanism for combined arsenic and fluoride induced cellular and DNA damage in mice.Metallomics. 2012 Jan;4(1):78-90. doi: 10.1039/c1mt00118c. Epub 2011 Oct 10. Metallomics. 2012. PMID: 21986897
-
The effects of fluoride on animals and plants in the south Safi zone.Sci Total Environ. 1984 Sep;38:63-8. doi: 10.1016/0048-9697(84)90208-0. Sci Total Environ. 1984. PMID: 6523125
-
Long-term exposure to low level of fluoride induces apoptosis via p53 pathway in lymphocytes of aluminum smelter workers.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019 Jan;26(3):2671-2680. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-3726-z. Epub 2018 Nov 26. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30478774
Cited by
-
Fluoride in groundwater sources in Ghana: A multifaceted and country-wide review.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 27;10(13):e33744. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e33744. eCollection 2024 Jul 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39044966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sodium Fluoride Exposure Leads to ATP Depletion and Altered RNA Decay in Escherichia coli under Anaerobic Conditions.Microbiol Spectr. 2023 Mar 20;11(2):e0415822. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.04158-22. Online ahead of print. Microbiol Spectr. 2023. PMID: 36939343 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of the Nrf-2 and HO-1 signalling axis is associated with Betaine's abatement of fluoride-induced hepatorenal toxicities in rats.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024 Oct;397(10):7725-7745. doi: 10.1007/s00210-024-03133-4. Epub 2024 May 7. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38713257
-
Voriconazole-Associated Periostitis: New Insights into Pathophysiology and Management.JBMR Plus. 2021 Oct 6;6(2):e10557. doi: 10.1002/jbm4.10557. eCollection 2022 Feb. JBMR Plus. 2021. PMID: 35229058 Free PMC article.
-
Fluoride Intake Through Dental Care Products: A Systematic Review.Front Oral Health. 2022 Jun 10;3:916372. doi: 10.3389/froh.2022.916372. eCollection 2022. Front Oral Health. 2022. PMID: 35757442 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adamek E, Palowska-Goral K, Bober K (2005) In vitro and in vivo effects of fluoride ions on enzyme activity. Ann Acad Med Stetin 51:69–85. - PubMed
-
- Agalakova NI, Gusev GP (2011) Molecular mechanisms of cytotoxicity and apoptosis induced by inorganic fluoride. Int Sch Res Not 2012:16 10.5402/2012/403835 - DOI
-
- Ainsworth NJ (1933) Mottled teeth. Brit Dent J 55:233–250.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

