Synthesis and evaluation of a prodrug of 5-aminosalicylic acid for the treatment of ulcerative colitis
- PMID: 32133064
- PMCID: PMC7043877
- DOI: 10.22038/IJBMS.2019.13991
Synthesis and evaluation of a prodrug of 5-aminosalicylic acid for the treatment of ulcerative colitis
Abstract
Objectives: This study is aimed to design and synthesize a prodrug of 5-aminosalicylic acid and evaluate its ameliorative effect on experimental ulcerative colitis (UC).
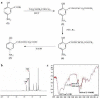
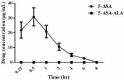
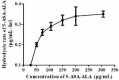
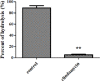
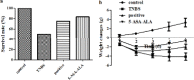
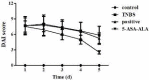
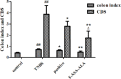
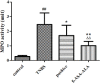
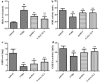
Materials and methods: 5-Aminosalicylic acid-alanine (5-ASA-ALA) was synthesized and characterized. Its stability study was conducted in rat plasma and in the gastrointestinal tract environment, its transport characteristic was assessed using the Caco-2 cells. Its colon-targeting property was evaluated by the pharmacokinetic study, and incubation studies. A series of indicators were used to investigate its therapeutic effect on experimental colitis, including the survival rate and body weight of mice, the disease activity index (DAI), the colonic damage score and colon index, the myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity and the levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), total superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione (GSH) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) in colonic tissues.
Results: 5-ASA-ALA was barely absorbed in the Caco-2 monolayer or into the rat blood. It was remarkably stable when incubated in the upper gastrointestinal tract, while gradually hydrolyzed in the colon of rats. When orally administered to mice, 5-ASA-ALA had significantly greater therapeutic effect on colitis than the positive control.
Conclusion: 5-ASA-ALA is demonstrated to be a promising oral colon-targeting prodrug of 5-ASA and has potential application in UC treatment.
Keywords: 5-Aminosalicylic acid; Anti-inflammation; Colon targeting; Prodrug; Ulcerative colitis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Colon-targeting mutual prodrugs of 5-aminosalicylic acid and butyrate for the treatment of ulcerative colitis.RSC Adv. 2018 Jan 11;8(5):2561-2574. doi: 10.1039/c7ra13011b. eCollection 2018 Jan 9. RSC Adv. 2018. PMID: 35541446 Free PMC article.
-
The Attenuation of Scutellariae radix Extract on Oxidative Stress for Colon Injury in Lipopolysaccharide-induced RAW264.7 Cell and 2,4,6-trinitrobenzene Sulfonic Acid-induced Ulcerative Colitis Rats.Pharmacogn Mag. 2016 Apr-Jun;12(46):153-9. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.177913. Pharmacogn Mag. 2016. PMID: 27076753 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, colon-targeted studies and pharmacological evaluation of an anti-ulcerative colitis drug 4-Aminosalicylic acid-β-O-glucoside.Eur J Med Chem. 2016 Jan 27;108:486-494. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2015.12.021. Epub 2015 Dec 15. Eur J Med Chem. 2016. PMID: 26717200
-
N,N'-Bis(5-aminosalicyl)-L-cystine is a potential colon-specific 5-aminosalicylic acid prodrug with dual therapeutic effects in experimental colitis.J Pharm Sci. 2009 Jan;98(1):159-68. doi: 10.1002/jps.21404. J Pharm Sci. 2009. PMID: 18399548
-
5-Aminosalicylic acid, a specific drug for ulcerative colitis.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2015 Aug;50(8):933-41. doi: 10.3109/00365521.2015.1018937. Epub 2015 Mar 2. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25733192 Review.
Cited by
-
Myeloperoxidase Inhibitory and Antioxidant Activities of (E)-2-Hydroxy-α-aminocinnamic Acids Obtained through Microwave-Assisted Synthesis.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 May 27;14(6):513. doi: 10.3390/ph14060513. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34071735 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect and mechanism insight of purified Antarctic kill phospholipids against mice ulcerative colitis combined with bioinformatics.Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2023 Apr 5;13(1):11. doi: 10.1007/s13659-023-00375-2. Nat Prod Bioprospect. 2023. PMID: 37016023 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis of a novel PEGylated colon-specific azo-based 4- aminosalicylic acid prodrug.Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020 Jun;23(6):781-787. doi: 10.22038/ijbms.2020.41152.9736. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32695295 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-inflammatory Effect of a Novel Pectin Polysaccharide From Rubus chingii Hu on Colitis Mice.Front Nutr. 2022 Apr 29;9:868657. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.868657. eCollection 2022. Front Nutr. 2022. PMID: 35571944 Free PMC article.
-
Comparable Toxicity of Surface-Modified TiO2 Nanoparticles: An In Vivo Experimental Study on Reproductive Toxicity in Rats.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Feb 13;13(2):231. doi: 10.3390/antiox13020231. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38397829 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Das R, Pal S. Modified hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose: efficient matrix for controlled release of 5-amino salicylic acid. Int J Biol Macromol. 2015;77:207–213. - PubMed
-
- Katz S. Update in medical therapy of ulcerative colitis-newer concepts and therapies. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2005;39:557–569. - PubMed
-
- Xiao B, Merlin D. Oral colon-specific therapeutic approaches toward treatment of inflammatory bowel disease. Expert Opin Drug Delv. 2012;9:1393–1407. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
