Pseudorabies Virus Infection of Epithelial Cells Leads to Persistent but Aberrant Activation of the NF-κB Pathway, Inhibiting Hallmark NF-κB-Induced Proinflammatory Gene Expression
- PMID: 32132236
- PMCID: PMC7199412
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00196-20
Pseudorabies Virus Infection of Epithelial Cells Leads to Persistent but Aberrant Activation of the NF-κB Pathway, Inhibiting Hallmark NF-κB-Induced Proinflammatory Gene Expression
Abstract
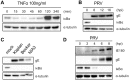
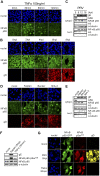
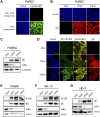
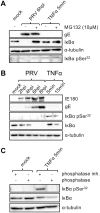
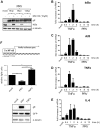
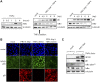
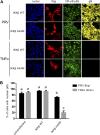
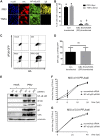
The nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) is a potent transcription factor, activation of which typically results in robust proinflammatory signaling and triggering of fast negative feedback modulators to avoid excessive inflammatory responses. Here, we report that infection of epithelial cells, including primary porcine respiratory epithelial cells, with the porcine alphaherpesvirus pseudorabies virus (PRV) results in the gradual and persistent activation of NF-κB, illustrated by proteasome-dependent degradation of the inhibitory NF-κB regulator IκB and nuclear translocation and phosphorylation of the NF-κB subunit p65. PRV-induced persistent activation of NF-κB does not result in expression of negative feedback loop genes, like the gene for IκBα or A20, and does not trigger expression of prototypical proinflammatory genes, like the gene for tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) or interleukin-6 (IL-6). In addition, PRV infection inhibits TNF-α-induced canonical NF-κB activation. Hence, PRV infection triggers persistent NF-κB activation in an unorthodox way and dramatically modulates the NF-κB signaling axis, preventing typical proinflammatory gene expression and the responsiveness of cells to canonical NF-κB signaling, which may aid the virus in modulating early proinflammatory responses in the infected host.IMPORTANCE The NF-κB transcription factor is activated via different key inflammatory pathways and typically results in the fast expression of several proinflammatory genes as well as negative feedback loop genes to prevent excessive inflammation. In the current report, we describe that infection of cells with the porcine alphaherpesvirus pseudorabies virus (PRV) triggers a gradual and persistent aberrant activation of NF-κB, which does not result in expression of hallmark proinflammatory or negative feedback loop genes. In addition, although PRV-induced NF-κB activation shares some mechanistic features with canonical NF-κB activation, it also shows remarkable differences; e.g., it is largely independent of the canonical IκB kinase (IKK) and even renders infected cells resistant to canonical NF-κB activation by the inflammatory cytokine TNF-α. Aberrant PRV-induced NF-κB activation may therefore paradoxically serve as a viral immune evasion strategy and may represent an important tool to unravel currently unknown mechanisms and consequences of NF-κB activation.
Keywords: NF-κB; evasion; herpes; innate; pseudorabies virus.
Copyright © 2020 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pseudorabies Virus Infection Triggers NF-κB Activation via the DNA Damage Response but Actively Inhibits NF-κB-Dependent Gene Expression.J Virol. 2021 Nov 23;95(24):e0166621. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01666-21. Epub 2021 Oct 6. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34613805 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudorabies Virus Infection Results in a Broad Inhibition of Host Gene Transcription.J Virol. 2022 Jul 13;96(13):e0071422. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00714-22. Epub 2022 Jun 22. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35730976 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudorabies Virus Infection Activates the TLR-NF-κB Axis and AIM2 Inflammasome To Enhance Inflammatory Responses in Mice.J Virol. 2023 Mar 30;97(3):e0000323. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00003-23. Epub 2023 Mar 6. J Virol. 2023. PMID: 36877049 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation and function of IKK and IKK-related kinases.Sci STKE. 2006 Oct 17;2006(357):re13. doi: 10.1126/stke.3572006re13. Sci STKE. 2006. PMID: 17047224 Review.
-
Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-[kappa]B activity.Annu Rev Immunol. 2000;18:621-63. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.18.1.621. Annu Rev Immunol. 2000. PMID: 10837071 Review.
Cited by
-
Comparative transcriptomic analysis of PK15 cells infected with a PRV variant and the Bartha-K/61 vaccine strain.Front Microbiol. 2023 May 5;14:1164170. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1164170. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37213521 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudorabies Virus Infection Triggers NF-κB Activation via the DNA Damage Response but Actively Inhibits NF-κB-Dependent Gene Expression.J Virol. 2021 Nov 23;95(24):e0166621. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01666-21. Epub 2021 Oct 6. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 34613805 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudorabies virus-induced expression and antiviral activity of type I or type III interferon depend on the type of infected epithelial cell.Front Immunol. 2022 Nov 2;13:1016982. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1016982. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36405751 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic Analysis of Vero Cells Infected with Pseudorabies Virus.Viruses. 2022 Apr 4;14(4):755. doi: 10.3390/v14040755. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35458485 Free PMC article.
-
Progress on innate immune evasion and live attenuated vaccine of pseudorabies virus.Front Microbiol. 2023 Mar 3;14:1138016. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1138016. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 36937252 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

