A mutation update for the FLNC gene in myopathies and cardiomyopathies
- PMID: 32112656
- PMCID: PMC7318287
- DOI: 10.1002/humu.24004
A mutation update for the FLNC gene in myopathies and cardiomyopathies
Abstract
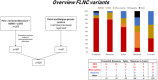
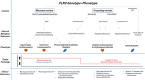
Filamin C (FLNC) variants are associated with cardiac and muscular phenotypes. Originally, FLNC variants were described in myofibrillar myopathy (MFM) patients. Later, high-throughput screening in cardiomyopathy cohorts determined a prominent role for FLNC in isolated hypertrophic and dilated cardiomyopathies (HCM and DCM). FLNC variants are now among the more prevalent causes of genetic DCM. FLNC-associated DCM is associated with a malignant clinical course and a high risk of sudden cardiac death. The clinical spectrum of FLNC suggests different pathomechanisms related to variant types and their location in the gene. The appropriate functioning of FLNC is crucial for structural integrity and cell signaling of the sarcomere. The secondary protein structure of FLNC is critical to ensure this function. Truncating variants with subsequent haploinsufficiency are associated with DCM and cardiac arrhythmias. Interference with the dimerization and folding of the protein leads to aggregate formation detrimental for muscle function, as found in HCM and MFM. Variants associated with HCM are predominantly missense variants, which cluster in the ROD2 domain. This domain is important for binding to the sarcomere and to ensure appropriate cell signaling. We here review FLNC genotype-phenotype correlations based on available evidence.
Keywords: FLNC; cardiomyopathy; filamin; genotype-phenotype correlation; myopathy.
© 2020 The Authors. Human Mutation published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Filamin C in cardiomyopathy: from physiological roles to DNA variants.Heart Fail Rev. 2022 Jul;27(4):1373-1385. doi: 10.1007/s10741-021-10172-z. Epub 2021 Sep 17. Heart Fail Rev. 2022. PMID: 34535832 Review.
-
Truncating FLNC Mutations Are Associated With High-Risk Dilated and Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathies.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016 Dec 6;68(22):2440-2451. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2016.09.927. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27908349
-
FLNC pathogenic variants in patients with cardiomyopathies: Prevalence and genotype-phenotype correlations.Clin Genet. 2019 Oct;96(4):317-329. doi: 10.1111/cge.13594. Epub 2019 Jul 18. Clin Genet. 2019. PMID: 31245841
-
ROD2 domain filamin C missense mutations exhibit a distinctive cardiac phenotype with restrictive/hypertrophic cardiomyopathy and saw-tooth myocardium.Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2023 May;76(5):301-311. doi: 10.1016/j.rec.2022.08.002. Epub 2022 Aug 8. Rev Esp Cardiol (Engl Ed). 2023. PMID: 35952944 English, Spanish.
-
Cardiac arrhythmia and late-onset muscle weakness caused by a myofibrillar myopathy with unusual histopathological features due to a novel missense mutation in FLNC.Rev Neurol (Paris). 2016 Oct;172(10):594-606. doi: 10.1016/j.neurol.2016.07.017. Epub 2016 Sep 12. Rev Neurol (Paris). 2016. PMID: 27633507 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy in Underrepresented Populations: Clinical and Genetic Landscape Based on a Russian Single-Center Cohort Study.Genes (Basel). 2023 Nov 4;14(11):2042. doi: 10.3390/genes14112042. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38002985 Free PMC article.
-
A child with dilated cardiomyopathy and homozygous splice site variant in FLNC gene.Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2023 Nov 23;38:101027. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2023.101027. eCollection 2024 Mar. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2023. PMID: 38077956 Free PMC article.
-
Exosome Liberation by Human Neutrophils under L-Amino Acid Oxidase of Calloselasma rhodostoma Venom Action.Toxins (Basel). 2023 Oct 25;15(11):625. doi: 10.3390/toxins15110625. Toxins (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37999488 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac Filaminopathies: Illuminating the Divergent Role of Filamin C Mutations in Human Cardiomyopathy.J Clin Med. 2021 Feb 4;10(4):577. doi: 10.3390/jcm10040577. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 33557094 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein phosphatase-1 regulates the binding of filamin C to FILIP1 in cultured skeletal muscle cells under mechanical stress.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 9;14(1):27348. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78953-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39521905 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alejandra Restrepo‐Cordoba, M. , Campuzano, O. , Ripoll‐Vera, T. , Cobo‐Marcos, M. , Mademont‐Soler, I. , Gamez, J. M. , … Garcia‐Pavia, P. (2017). Usefulness of genetic testing in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: An analysis using real‐world data. Journal of Cardiovascular Translational Research, 10(1), 35–46. 10.1007/s12265-017-9730-8 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Anastasi, G. , Cutroneo, G. , Trimarchi, F. , Santoro, G. , Bruschetta, D. , Bramanti, P. , … Favaloro, A. (2004). Evaluation of sarcoglycans, vinculin‐talin‐integrin system and filamin2 in alpha‐ and gamma‐sarcoglycanopathy: An immunohistochemical study. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 14(6), 989–999. - PubMed
-
- Augusto, J. B. , Eiros, R. , Nakou, E. , Moura‐Ferreira, S. , Treibel, T. A. , Captur, G. , … Lopes, L. R. (2019). Dilated cardiomyopathy and arrhythmogenic left ventricular cardiomyopathy: A comprehensive genotype‐imaging phenotype study. European Heart Journal Cardiovascular Imaging, 21(3), 326–336. 10.1093/ehjci/jez188 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Avila‐Smirnow, D. , Béhin, A. , Gueneau, L. , Claeys, K. , Beuvin, M. , Goudeau, B. , … Mathis, S. J. N. D. (2010). P2. 18 A novel missense FLNC mutation causes arrhythmia and late onset myofibrillar myopathy with particular histopathology features. Neuromuscular Disorders, 20(9), 623–624.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

