Analysis of the Expression of Cell Division Cycle-Associated Genes and Its Prognostic Significance in Human Lung Carcinoma: A Review of the Literature Databases
- PMID: 32104702
- PMCID: PMC7037569
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/6412593
Analysis of the Expression of Cell Division Cycle-Associated Genes and Its Prognostic Significance in Human Lung Carcinoma: A Review of the Literature Databases
Abstract
Background: Lung cancer (LC) has become the top cause responsible for cancer-related deaths. Cell division cycle-associated (CDCA) genes exert an important role in the life process. Dysregulation in the process of cell division may lead to malignancy.
Methods: Transcriptional data on CDCA gene family and patient survival data were examined for lung cancer (LC) patients from the GEPIA, Oncomine, cBioPortal, and Kaplan-Meier Plotter databases.
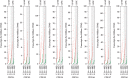
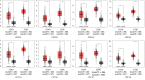
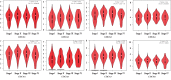
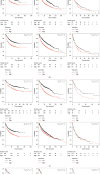
Results: CDCA1/2/3/4/5/7/8 expression levels were higher in lung adenocarcinoma tissues, and the CDCA1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8 expression levels were increased in squamous cell LC tissues compared with those in noncarcinoma lung tissues. The expression levels of CDCA1/2/3/4/5/8 showed correlation with tumor classification. The Kaplan-Meier Plotter database was employed to carry out survival analysis, indicating that increased CDCA1/2/3/4/5/6/7/8 expression levels were increased in squamous cell LC tissues compared with those in noncarcinoma lung tissues. The expression levels of P < 0.05). Only LC patients with increased CDCA3/4/5/8 expression were significantly related to lower post-progression survival (PPS) (P < 0.05). Only LC patients with increased CDCA gene family and patient survival data were examined for lung cancer (LC) patients from the GEPIA, Oncomine, cBioPortal, and Kaplan-Meier Plotter databases. CDCA8, INCENP, AURKB, and BIRC5); CORUM: 127: NDC80 kinetochore complex; M129: the PID PLK1 pathway; and GO: 0007080: mitotic metaphase plate congression, all of which were remarkably modulated since the alterations affected CDCA gene family and patient survival data were examined for lung cancer (LC) patients from the GEPIA, Oncomine, cBioPortal, and Kaplan-Meier Plotter databases.
Conclusions: Upregulated CDCA genes' expression levels in LC tissues probably play a crucial part in LC oncogenesis. The upregulated CDCA genes' expression levels are used as the potential prognostic markers to improve patient survival and the LC prognostic accuracy. CDCA genes probably exert their functions in tumorigenesis through the PLK1 pathway.CDCA gene family and patient survival data were examined for lung cancer (LC) patients from the GEPIA, Oncomine, cBioPortal, and Kaplan-Meier Plotter databases. CDCA gene family and patient survival data were examined for lung cancer (LC) patients from the GEPIA, Oncomine, cBioPortal, and Kaplan-Meier Plotter databases. CDCA gene family and patient survival data were examined for lung cancer (LC) patients from the GEPIA, Oncomine, cBioPortal, and Kaplan-Meier Plotter databases.
Copyright © 2020 Chongxiang Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The role of the CDCA gene family in ovarian cancer.Ann Transl Med. 2020 Mar;8(5):190. doi: 10.21037/atm.2020.01.99. Ann Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32309337 Free PMC article.
-
Bioinformatics analysis of the clinical relevance of CDCA gene family in prostate cancer.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Feb 4;101(5):e28788. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000028788. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 35119046 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional E2F1/2/5/8 as potential targets and transcriptional E2F3/6/7 as new biomarkers for the prognosis of human lung carcinoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2018 May 11;10(5):973-987. doi: 10.18632/aging.101441. Aging (Albany NY). 2018. PMID: 29754146 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of PLKs expression and prognosis in breast cancer.Cancer Genet. 2022 Nov;268-269:83-92. doi: 10.1016/j.cancergen.2022.09.007. Epub 2022 Sep 26. Cancer Genet. 2022. PMID: 36206661 Review.
-
Expression and prognosis analyses of the fibronectin type-III domain-containing (FNDC) protein family in human cancers: A Review.Medicine (Baltimore). 2022 Dec 9;101(49):e31854. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000031854. Medicine (Baltimore). 2022. PMID: 36626432 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Habitual consumption of alcohol with meals and lung cancer: a Mendelian randomization study.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Feb;9(3):263. doi: 10.21037/atm-20-3063. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 33708890 Free PMC article.
-
Keshan Disease: A Potentially Fatal Endemic Cardiomyopathy in Remote Mountains of China.Front Pediatr. 2021 Mar 9;9:576916. doi: 10.3389/fped.2021.576916. eCollection 2021. Front Pediatr. 2021. PMID: 33768083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell division cycle-associated 8 is a prognostic biomarker related to immune invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Med. 2023 Apr;12(8):10138-10155. doi: 10.1002/cam4.5718. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Cancer Med. 2023. PMID: 36855818 Free PMC article.
-
NUF2 promotes tumorigenesis by interacting with HNRNPA2B1 via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in ovarian cancer.J Ovarian Res. 2023 Jan 20;16(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13048-023-01101-9. J Ovarian Res. 2023. PMID: 36670423 Free PMC article.
-
Comprehensive analysis of the prognostic values and immune implication of ESYT3 in lung adenocarcinoma.Medicine (Baltimore). 2023 Sep 1;102(35):e34557. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000034557. Medicine (Baltimore). 2023. PMID: 37657044 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reck M., Rodriguez-Abreu D., Robinson A. G., et al. Updated analysis of KEYNOTE-024: pembrolizumab versus platinum-based chemotherapy for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer with PD-L1 tumor proportion score of 50% or greater. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2019;37(7):537–546. doi: 10.1200/jco.18.00149. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Preston-Martin S., Pike M. C., Ross R. K., Jones P. A., Henderson B. E. Increased cell division as a cause of human cancer. Cancer Research. 1990;50(23):7415–7421. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

