Effectively suppressed angiogenesis-mediated retinoblastoma growth using celastrol nanomicelles
- PMID: 32091275
- PMCID: PMC7054910
- DOI: 10.1080/10717544.2020.1730522
Effectively suppressed angiogenesis-mediated retinoblastoma growth using celastrol nanomicelles
Abstract
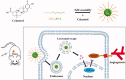
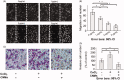
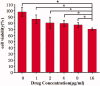
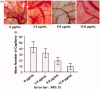
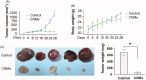
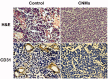
Celastrol, a Chinese herbal medicine, has already shown an inhibition effect on retinoblastoma growth activity in our previous research, but its mechanism is not well understood. Angiogenesis is a main driving force in many tumors. Here, we studied whether celastrol could inhibit angiogenesis-mediated retinoblastoma growth, if so, through what mechanism. In this work, we developed celastrol-loaded polymeric nanomicelles to improve the poor water solubility of celastrol. When given an intraperitoneal injection to mice bearing human retinoblastoma xenografts, celastrol nanomicelles (CNMs, 27.2 mg/kg/2 days) significantly reduced the weight and the volume of tumors and decreased tumor angiogenesis. We found that CNMs suppressed hypoxia-induced proliferation, migration, and invasion by human umbilical vascular endothelial cells (EA.hy 926) in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, CNMs inhibited SO-Rb 50 cells-induced sprouting of the vessels and vascular formation in chick embryo chorioallantoic membrane assay in vitro. To understand the molecular mechanism of these activities, we assessed the signaling pathways in CoCl2 treated EA.hy 926. CNMs inhibited the hypoxia-induced HIF-1α and VEGF. In conclusion, our results reveal that CNMs target the HIF-1α/VEGF pathway, which may be an important reason for the suppression of retinoblastoma growth and angiogenesis.
Keywords: Celastrol; SO-Rb 50 cells; angiogenesis; nanomicelles; retinoblastoma.
Figures
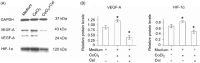
Similar articles
-
Celastrol nanomicelles attenuate cytokine secretion in macrophages and inhibit macrophage-induced corneal neovascularization in rats.Int J Nanomedicine. 2016 Nov 18;11:6135-6148. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S117425. eCollection 2016. Int J Nanomedicine. 2016. PMID: 27920521 Free PMC article.
-
Antitumor activity of celastrol nanoparticles in a xenograft retinoblastoma tumor model.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:2389-98. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S29945. Epub 2012 May 9. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22661892 Free PMC article.
-
Celastrol suppresses angiogenesis-mediated tumor growth through inhibition of AKT/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway.Cancer Res. 2010 Mar 1;70(5):1951-9. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3201. Epub 2010 Feb 16. Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20160026 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced Technologies of Drug Delivery to the Posterior Eye Segment Targeting Angiogenesis and Ocular Cancer.Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2024;41(1):85-124. doi: 10.1615/CritRevTherDrugCarrierSyst.2023045298. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst. 2024. PMID: 37824419 Review.
-
Celastrol: The new dawn in the treatment of vascular remodeling diseases.Biomed Pharmacother. 2023 Feb;158:114177. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2022.114177. Epub 2023 Jan 3. Biomed Pharmacother. 2023. PMID: 36809293 Review.
Cited by
-
Successful growth of fresh retinoblastoma cells in chorioallantoic membrane.Int J Retina Vitreous. 2020 Jul 29;6:33. doi: 10.1186/s40942-020-00236-x. eCollection 2020. Int J Retina Vitreous. 2020. PMID: 32760596 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted liposomes for macrophages-mediated pulmonary fibrosis therapy.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024 Sep;14(9):2356-2369. doi: 10.1007/s13346-023-01508-3. Epub 2024 Jan 2. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38167826
-
Targeting OPA1-Mediated Mitochondrial Fusion Contributed to Celastrol's Anti-Tumor Angiogenesis Effect.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Dec 23;15(1):48. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15010048. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36678677 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-Responsive Polymeric Micelles for Enhancing Cancer Treatment.Front Chem. 2020 Sep 4;8:742. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2020.00742. eCollection 2020. Front Chem. 2020. PMID: 33033713 Free PMC article.
-
Nanotechnology-Based Celastrol Formulations and Their Therapeutic Applications.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Jun 11;12:673209. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.673209. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34177584 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abramson DH, Dunkel IJ, Brodie SE, et al. (2010). Superselective ophthalmic artery chemotherapy as primary treatment for retinoblastoma (chemosurgery). Ophthalmology 117:1623–9. - PubMed
-
- Abramson DH, Shields CL, Munier FL, et al. (2015). Treatment of retinoblastoma in 2015: agreement and disagreement. JAMA Ophthalmol 133:1341–7. - PubMed
-
- Bi S, Liu JR, Li Y, et al. (2010). γ-Tocotrienol modulates the paracrine secretion of VEGF induced by cobalt (II) chloride via ERK signaling pathway in gastric adenocarcinoma SGC-7901 cell line. Toxicology 274:27–33. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
