Elevated Serum TNF- α Is Related to Obesity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Is Associated with Glycemic Control and Insulin Resistance
- PMID: 32089876
- PMCID: PMC7013317
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/5076858
Elevated Serum TNF- α Is Related to Obesity in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Is Associated with Glycemic Control and Insulin Resistance
Abstract
Background: Diabetes and obesity are very common associated metabolic disorders that are linked to chronic inflammation. Leptin is one of the important adipokines released from adipocytes, and its level increases with increasing body mass index (BMI). Tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α) is a cytokine that is released by adipocytes and inflammatory cells in response to chronic inflammation. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is believed to be associated with low-grade chronic inflammation. The current study aims to investigate the involvement of leptin and TNF-α) is a cytokine that is released by adipocytes and inflammatory cells in response to chronic inflammation. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is believed to be associated with low-grade chronic inflammation. The current study aims to investigate the involvement of leptin and TNF-Methodology. This is a cross-sectional study involving 63 healthy volunteers and 65 patients with T2DM. Body composition was measured, and fasting venous blood samples were analyzed for blood glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), basal insulin, leptin, and TNF-α) is a cytokine that is released by adipocytes and inflammatory cells in response to chronic inflammation. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is believed to be associated with low-grade chronic inflammation. The current study aims to investigate the involvement of leptin and TNF-α) is a cytokine that is released by adipocytes and inflammatory cells in response to chronic inflammation. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is believed to be associated with low-grade chronic inflammation. The current study aims to investigate the involvement of leptin and TNF.
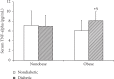
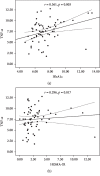
Results: Our study showed a significantly higher level of TNF-α) is a cytokine that is released by adipocytes and inflammatory cells in response to chronic inflammation. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is believed to be associated with low-grade chronic inflammation. The current study aims to investigate the involvement of leptin and TNF-p=0.008). In obese diabetic patients, the serum level of TNF-α) is a cytokine that is released by adipocytes and inflammatory cells in response to chronic inflammation. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is believed to be associated with low-grade chronic inflammation. The current study aims to investigate the involvement of leptin and TNF-p=0.008). In obese diabetic patients, the serum level of TNF-p=0.008). In obese diabetic patients, the serum level of TNF-α) is a cytokine that is released by adipocytes and inflammatory cells in response to chronic inflammation. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is believed to be associated with low-grade chronic inflammation. The current study aims to investigate the involvement of leptin and TNF-r = 0.361, p=0.008). In obese diabetic patients, the serum level of TNF-r = 0.361, p=0.008). In obese diabetic patients, the serum level of TNF.
Conclusion: TNF-α is associated with concurrent obesity and T2DM and correlates with HbA1c. This suggests that TNF-α needs further investigation to explore if it has a role in monitoring the effectiveness of management in individuals with obesity and T2DM.α) is a cytokine that is released by adipocytes and inflammatory cells in response to chronic inflammation. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is believed to be associated with low-grade chronic inflammation. The current study aims to investigate the involvement of leptin and TNF-α) is a cytokine that is released by adipocytes and inflammatory cells in response to chronic inflammation. Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is believed to be associated with low-grade chronic inflammation. The current study aims to investigate the involvement of leptin and TNF.
Copyright © 2020 Hana Alzamil.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute hyperinsulinemia raises plasma interleukin-6 in both nondiabetic and type 2 diabetes mellitus subjects, and this effect is inversely associated with body mass index.Metabolism. 2009 Jun;58(6):860-6. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2009.02.010. Metabolism. 2009. PMID: 19375766
-
Inflammatory Markers in Obese Adolescents with Type 2 Diabetes and Their Relationship to Hepatokines and Adipokines.J Pediatr. 2016 Jun;173:131-5. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.02.055. Epub 2016 Mar 17. J Pediatr. 2016. PMID: 26996723
-
The inflammatory status score including IL-6, TNF-α, osteopontin, fractalkine, MCP-1 and adiponectin underlies whole-body insulin resistance and hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus.Acta Diabetol. 2014 Feb;51(1):123-31. doi: 10.1007/s00592-013-0543-1. Epub 2013 Dec 27. Acta Diabetol. 2014. PMID: 24370923
-
Recent advances in the relationship between obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance.Eur Cytokine Netw. 2006 Mar;17(1):4-12. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2006. PMID: 16613757 Review.
-
Periodontal disease and diabetes mellitus: the role of tumor necrosis factor-alpha in a 2-way relationship.J Periodontol. 2003 Jan;74(1):97-102. doi: 10.1902/jop.2003.74.1.97. J Periodontol. 2003. PMID: 12593603 Review.
Cited by
-
Correlation of Diabetes Related Factors with Vitamin D and Immunological Parameters in T2DM Kashmiri Population.Indian J Clin Biochem. 2024 Oct;39(4):586-592. doi: 10.1007/s12291-023-01144-1. Epub 2023 Jul 28. Indian J Clin Biochem. 2024. PMID: 39346716
-
The Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Novel Antidiabetic Agents.Life (Basel). 2022 Nov 9;12(11):1829. doi: 10.3390/life12111829. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36362984 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Irisin: A Possible Marker of Adipose Tissue Dysfunction in Obesity.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 28;24(15):12082. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512082. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569456 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral inflammation is linked with emotion and mental health in people with obesity. A "head to toe" observational study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 Jul 14;14:1197648. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1197648. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37529617 Free PMC article.
-
Health-related factors and dysregulation of epigenetic related genes in metabolic syndrome trigger finger patients and smoker trigger finger patients: preliminary analysis of patient-derived sample.J Orthop Surg Res. 2023 Oct 18;18(1):785. doi: 10.1186/s13018-023-04271-w. J Orthop Surg Res. 2023. PMID: 37853419 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Owecki M., Nikisch E., Miczke A., Pupek-Musialik D., Sowiński J. Leptin, soluble leptin receptors, free leptin index, and their relationship with insulin resistance and BMI: high normal BMI is the threshold for serum leptin increase in humans. Hormone and Metabolic Research. 2010;42(8):585–589. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1253422. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

