Identification of Protein Expression Changes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma through iTRAQ
- PMID: 32076459
- PMCID: PMC7008262
- DOI: 10.1155/2020/2632716
Identification of Protein Expression Changes in Hepatocellular Carcinoma through iTRAQ
Abstract
Background: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a malignant tumor associated with a poor prognosis. Serum biomarkers of HCC have the potential to improve the diagnosis, provide a means to monitor the tumors, and predict their malignancy. Proteins that are expressed differentially between HCC patients and normal controls have the potential to be biomarkers.
Method: Serum samples from 10 confirmed HCC patients and 10 controls were collected. The differentially expressed proteins in the serum were identified using an isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation- (iTRAQ-) based method. Potential serum biomarkers were validated by ELISA in another 20 HCC patients and 20 controls. Their expression data in HCC were extracted from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) dataset.
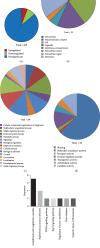
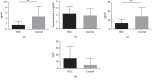
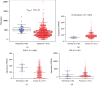
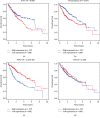
Results: A total of 260 proteins were measured in the serum of HCC patients and compared to those in sex- and age-matched normal controls. Forty-one proteins displayed significant changes, with 26 being downregulated and 15 being upregulated. Upregulated proteins included alpha-1-antitrypsin (A1AT) and peroxiredoxin 2 (PRDX2), and downregulated proteins included paraoxonase 1 (PON1) and C-reactive protein (CRP). We then used ELISA to measure serum levels of A1AT, PRDX2, PON1, and CRP in another 20 patients with HCC and found that only PON1 levels were consistent with the iTRAQ result. In TCGA dataset, PON1 expression was downregulated in HCC tissues (P < 0.001) and low expression of PON1 was associated with poor survival in HCC patients (P < 0.001) and low expression of PON1 was associated with poor survival in HCC patients (.
Conclusions: PON1 could act as a biomarker for HCC to assist in the diagnosis of HCC.
Copyright © 2020 Yuanyuan Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors who took part in this study declare that they do not have anything to disclose regarding funding or a conflict of interest with respect to this manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Quantitative proteomics reveals FLNC as a potential progression marker for the development of hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2016 Oct 18;7(42):68242-68252. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.11921. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27626164 Free PMC article.
-
Quantitative proteomic analysis identified paraoxonase 1 as a novel serum biomarker for microvascular invasion in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Proteome Res. 2013 Apr 5;12(4):1838-46. doi: 10.1021/pr3011815. Epub 2013 Mar 5. J Proteome Res. 2013. PMID: 23442176
-
Serum fucosylated paraoxonase 1 as a potential glycobiomarker for clinical diagnosis of early hepatocellular carcinoma using ELISA Index.Glycoconj J. 2015 May;32(3-4):119-25. doi: 10.1007/s10719-015-9576-8. Epub 2015 Feb 22. Glycoconj J. 2015. PMID: 25702281
-
[Research advances in application of isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation in proteomics of hepatocellular carcinoma].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2016 Dec 20;24(12):952-955. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2016.12.018. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2016. PMID: 28073423 Review. Chinese.
-
Upregulated and downregulated proteins in hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review of proteomic profiling studies.OMICS. 2011 Jan-Feb;15(1-2):61-71. doi: 10.1089/omi.2010.0061. Epub 2010 Aug 20. OMICS. 2011. PMID: 20726783 Review.
Cited by
-
Cross talk between genetics and biochemistry in the pathogenesis of hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepatol Forum. 2024 Jul 2;5(3):150-160. doi: 10.14744/hf.2023.2023.0028. eCollection 2024. Hepatol Forum. 2024. PMID: 39006147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: From Origin to Clinical Diagnosis.Biomedicines. 2023 Jun 28;11(7):1852. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11071852. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 37509493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential Plasma Proteins Identified via iTRAQ-Based Analysis Serve as Diagnostic Markers of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Dis Markers. 2023 Jan 20;2023:5145152. doi: 10.1155/2023/5145152. eCollection 2023. Dis Markers. 2023. PMID: 36712921 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptional and epigenetic landscape of Ca2+-signaling genes in hepatocellular carcinoma.J Cell Commun Signal. 2021 Sep;15(3):433-445. doi: 10.1007/s12079-020-00597-w. Epub 2021 Jan 4. J Cell Commun Signal. 2021. PMID: 33398721 Free PMC article.
-
Screening and identification of angiogenesis-related genes as potential novel prognostic biomarkers of hepatocellular carcinoma through bioinformatics analysis.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Jul 12;13(13):17707-17733. doi: 10.18632/aging.203260. Epub 2021 Jul 12. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 34252885 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

