Identification of Host Trafficking Genes Required for HIV-1 Virological Synapse Formation in Dendritic Cells
- PMID: 32075937
- PMCID: PMC7163131
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01597-19
Identification of Host Trafficking Genes Required for HIV-1 Virological Synapse Formation in Dendritic Cells
Abstract
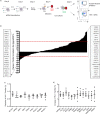
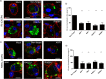
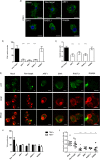
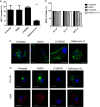
Dendritic cells (DCs) are one of the earliest targets of HIV-1 infection acting as a "Trojan horse," concealing the virus from the innate immune system and delivering it to T cells via virological synapses (VS). To explicate how the virus is trafficked through the cell to the VS and evades degradation, a high-throughput small interfering RNA screen targeting membrane trafficking proteins was performed in monocyte-derived DCs. We identified several proteins including BIN-1 and RAB7L1 that share common roles in transport from endosomal compartments. Depletion of target proteins resulted in an accumulation of virus in intracellular compartments and significantly reduced viral trans-infection via the VS. By targeting endocytic trafficking and retromer recycling to the plasma membrane, we were able to reduce the virus's ability to accumulate at budding microdomains and the VS. Thus, we identify key genes involved in a pathway within DCs that is exploited by HIV-1 to traffic to the VS.IMPORTANCE The lentivirus human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) targets and destroys CD4+ T cells, leaving the host vulnerable to life-threatening opportunistic infections associated with AIDS. Dendritic cells (DCs) form a virological synapse (VS) with CD4+ T cells, enabling the efficient transfer of virus between the two cells. We have identified cellular factors that are critical in the induction of the VS. We show that ADP-ribosylation factor 1 (ARF1), bridging integrator 1 (BIN1), and Rab GTPases RAB7L1 and RAB8A are important regulators of HIV-1 trafficking to the VS and therefore the infection of CD4+ T cells. We found these cellular factors were essential for endosomal protein trafficking and formation of the VS and that depletion of target proteins prevented virus trafficking to the plasma membrane by retaining virus in intracellular vesicles. Identification of key regulators in HIV-1 trans-infection between DC and CD4+ T cells has the potential for the development of targeted therapy to reduce trans-infection of HIV-1 in vivo.
Keywords: HIV-1; T-cell immunity; dendritic cell; host-cell interactions; virological synapse.
Copyright © 2020 Bayliss et al.
Figures

Similar articles
-
TLR-4 engagement of dendritic cells confers a BST-2/tetherin-mediated restriction of HIV-1 infection to CD4+ T cells across the virological synapse.Retrovirology. 2013 Jan 11;10:6. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-10-6. Retrovirology. 2013. PMID: 23311681 Free PMC article.
-
Virus particle release from glycosphingolipid-enriched microdomains is essential for dendritic cell-mediated capture and transfer of HIV-1 and henipavirus.J Virol. 2014 Aug;88(16):8813-25. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00992-14. Epub 2014 May 28. J Virol. 2014. PMID: 24872578 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 replication in dendritic cells occurs through a tetraspanin-containing compartment enriched in AP-3.Traffic. 2008 Feb;9(2):200-14. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0854.2007.00678.x. Epub 2007 Nov 22. Traffic. 2008. PMID: 18034776
-
Cell-to-Cell Spread of HIV and Viral Pathogenesis.Adv Virus Res. 2016;95:43-85. doi: 10.1016/bs.aivir.2016.03.001. Epub 2016 Apr 4. Adv Virus Res. 2016. PMID: 27112280 Review.
-
Dendritic Cells, the Double Agent in the War Against HIV-1.Front Immunol. 2019 Oct 23;10:2485. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02485. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31708924 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unconventional p97/VCP-Mediated Endoplasmic Reticulum-to-Endosome Trafficking of a Retroviral Protein.J Virol. 2021 Jun 24;95(14):e0053121. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00531-21. Epub 2021 Jun 24. J Virol. 2021. PMID: 33952644 Free PMC article.
-
The importance of virion-incorporated cellular RNA-Binding Proteins in viral particle assembly and infectivity.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Mar;111:108-118. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2020.08.002. Epub 2020 Sep 10. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 32921578 Free PMC article. Review.
-
De novo macrocyclic peptides for inhibiting, stabilizing, and probing the function of the retromer endosomal trafficking complex.Sci Adv. 2021 Dec 3;7(49):eabg4007. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abg4007. Epub 2021 Dec 1. Sci Adv. 2021. PMID: 34851660 Free PMC article.
-
G2-S16 Polyanionic Carbosilane Dendrimer Can Reduce HIV-1 Reservoir Formation by Inhibiting Macrophage Cell to Cell Transmission.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Aug 4;22(16):8366. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168366. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34445073 Free PMC article.
-
HIV-1 Hijacking of Host ATPases and GTPases That Control Protein Trafficking.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jul 8;9:622610. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.622610. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34307340 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Turville SG, Santos JJ, Frank I, Cameron PU, Wilkinson J, Miranda-Saksena M, Dable J, Stossel H, Romani N, Piatak M Jr, Lifson JD, Pope M, Cunningham AL. 2004. Immunodeficiency virus uptake, turnover, and two-phase transfer in human dendritic cells. Blood 103:2170–2179. doi:10.1182/blood-2003-09-3129. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Garcia E, Pion M, Pelchen-Matthews A, Collinson L, Arrighi JF, Blot G, Leuba F, Escola JM, Demaurex N, Marsh M, Piguet V. 2005. HIV-1 trafficking to the dendritic cell-T-cell infectious synapse uses a pathway of tetraspanin sorting to the immunological synapse. Traffic 6:488–501. doi:10.1111/j.1600-0854.2005.00293.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nobile C, Petit C, Moris A, Skrabal K, Abastado JP, Mammano F, Schwartz O. 2005. Covert human immunodeficiency virus replication in dendritic cells and in DC-SIGN-expressing cells promotes long-term transmission to lymphocytes. J Virol 79:5386–5399. doi:10.1128/JVI.79.9.5386-5399.2005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

