The crowding dynamics of the motor protein kinesin-II
- PMID: 32053680
- PMCID: PMC7018031
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0228930
The crowding dynamics of the motor protein kinesin-II
Abstract
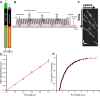
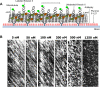
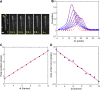
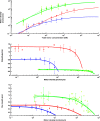
Intraflagellar transport (IFT) in C. elegans chemosensory cilia is an example of functional coordination and cooperation of two motor proteins with distinct motility properties operating together in large groups to transport cargoes: a fast and processive homodimeric kinesin-2, OSM-3, and a slow and less processive heterotrimeric kinesin-2, kinesin-II. To study the mechanism of the collective dynamics of kinesin-II of C. elegans cilia in an in vitro system, we used Total Internal Reflection Fluorescence microscopy to image the motility of truncated, heterodimeric kinesin-II constructs at high motor densities. Using an analysis technique based on correlation of the fluorescence intensities, we extracted quantitative motor parameters, such as motor density, velocity and average run length, from the image. Our experiments and analyses show that kinesin-II motility parameters are far less affected by (self) crowding than OSM-3. Our observations are supported by numerical calculations based on the TASEP-LK model (Totally Asymmetric Simple Exclusion Process-Langmuir Kinetics). From a comparison of data and modelling of OSM-3 and kinesin-II, a general picture emerges of the collective dynamics of the kinesin motors driving IFT in C. elegans chemosensory cilia and the way the motors deal with crowding.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Functional differentiation of cooperating kinesin-2 motors orchestrates cargo import and transport in C. elegans cilia.Nat Cell Biol. 2015 Dec;17(12):1536-45. doi: 10.1038/ncb3263. Epub 2015 Nov 2. Nat Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26523365
-
Mutation of the MAP kinase DYF-5 affects docking and undocking of kinesin-2 motors and reduces their speed in the cilia of Caenorhabditis elegans.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007 Apr 24;104(17):7157-62. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0606974104. Epub 2007 Apr 9. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007. PMID: 17420466 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of transport of IFT particles in C. elegans cilia by the concerted action of kinesin-II and OSM-3 motors.J Cell Biol. 2006 Sep 25;174(7):1035-45. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200606003. J Cell Biol. 2006. PMID: 17000880 Free PMC article.
-
Intraflagellar transport: mechanisms of motor action, cooperation, and cargo delivery.FEBS J. 2017 Sep;284(18):2905-2931. doi: 10.1111/febs.14068. Epub 2017 Apr 18. FEBS J. 2017. PMID: 28342295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Intraflagellar transport: keeping the motors coordinated.Curr Biol. 2005 Oct 11;15(19):R798-801. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2005.09.020. Curr Biol. 2005. PMID: 16213810 Review.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of Regulation in Intraflagellar Transport.Cells. 2022 Sep 2;11(17):2737. doi: 10.3390/cells11172737. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36078145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The interplay of active and passive mechanisms in slow axonal transport.Biophys J. 2023 Jan 17;122(2):333-345. doi: 10.1016/j.bpj.2022.12.011. Epub 2022 Dec 10. Biophys J. 2023. PMID: 36502274 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

